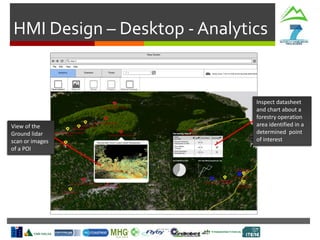
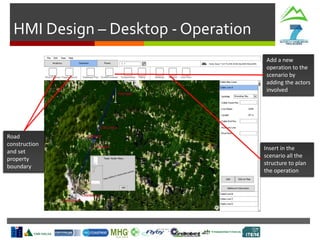
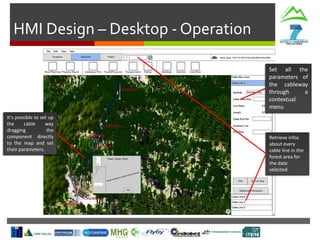
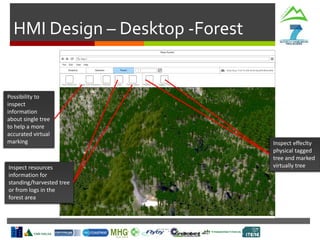
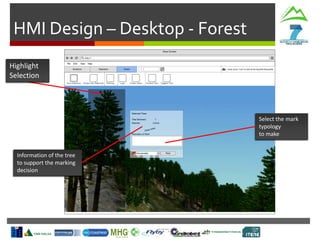
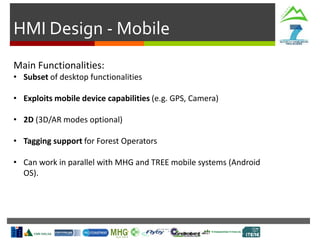
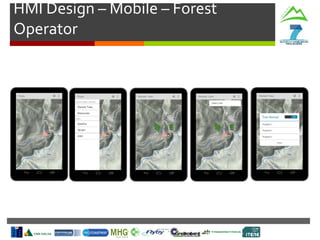
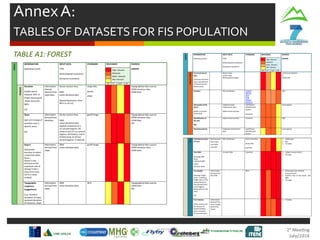
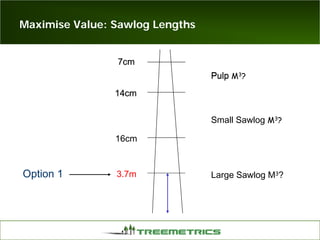
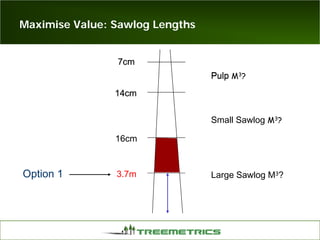
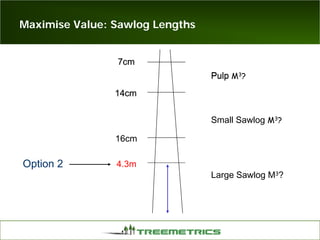
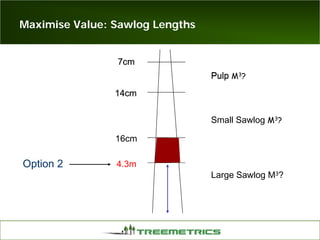
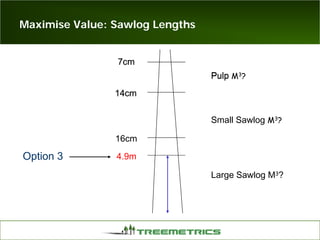
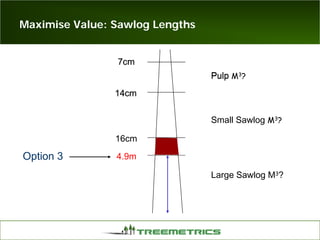
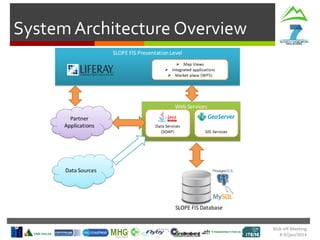
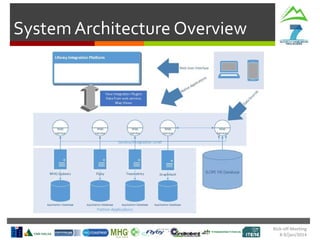
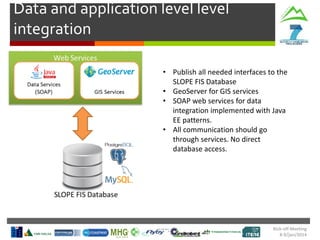
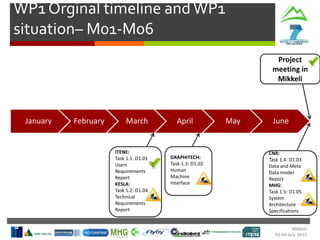
- Weather
- Production Targets
- Contingency Plans
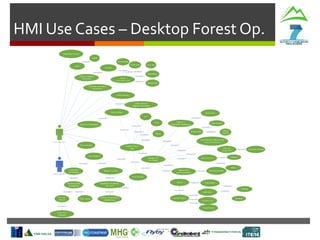
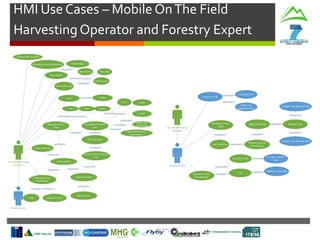
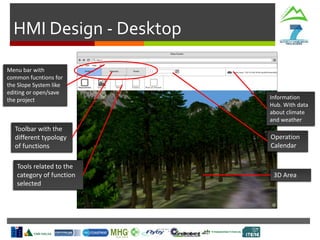
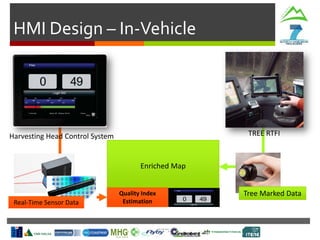
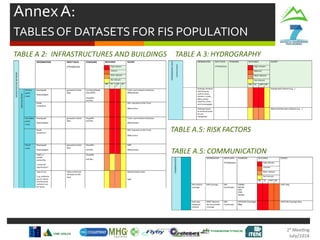
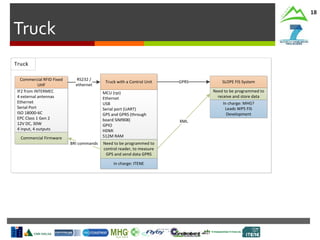
Harvesting Head
Control Interface
Production
Statistics
Machine
Parameters
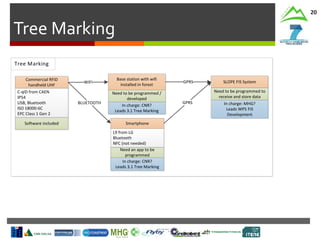
Tree Detection
& Recognition
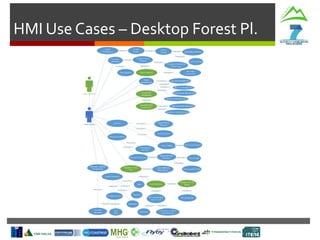
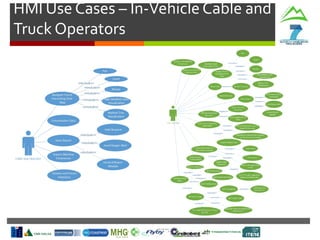
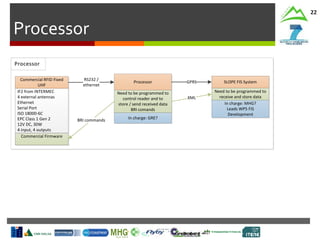
SLOPE
In-Vehicle
Interface
Machine
Monitoring
Route
Planning
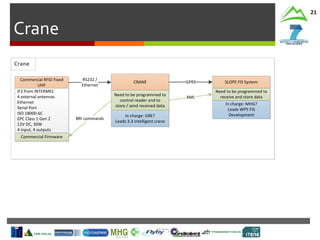
Cable Crane
Control
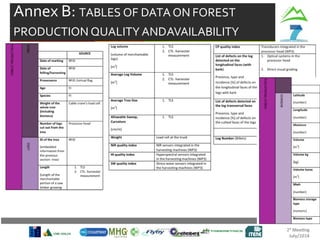
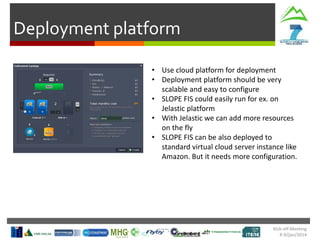
Risks and Mitigation Actions
Technical Meeting
2-4/Jul/2014
Risks:
- Integration with existing systems (MHG, TREE) not seamless
- Mobile/In-Vehicle interfaces not robust enough for field conditions
- User acceptance of new interfaces
Mitigation Actions:
- Early prototyping and testing with end users
- Modular design allowing independent development















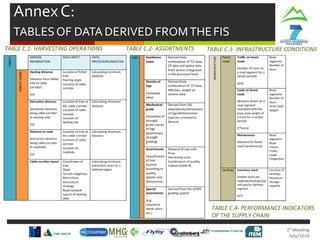
![User Interface Analysis
Technical Meeting
2-4/Jul/2014
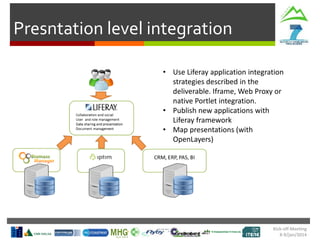
“Human-Machine Interfaces can be seen as the parts, software or
hardware handling the interaction between humans and machines
[…] Computer can have several different purposes ending in an
open-ended dialog between users and computer.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02technicalmeetingmay2014-wp1-161024095320/85/1st-Technical-Meeting-WP1-26-320.jpg)