Here are the answers to the review questions from the document:
1. List at least three significant events in the evolution of CDMA networks:
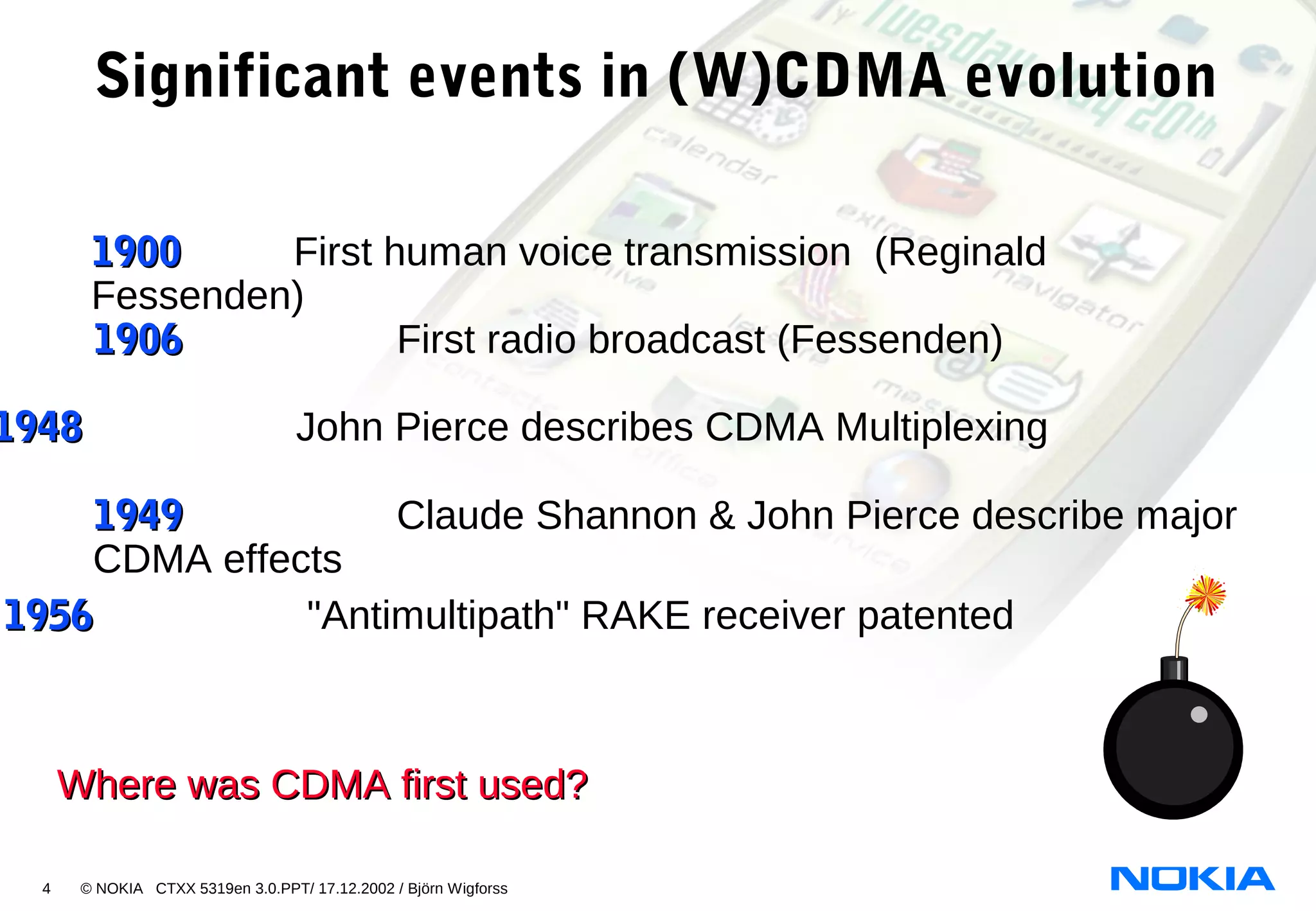
- 1948 John Pierce describes CDMA Multiplexing
- 1956 "Antimultipath" RAKE receiver patented
- 1970s CDMA used in several military communication and navigation systems
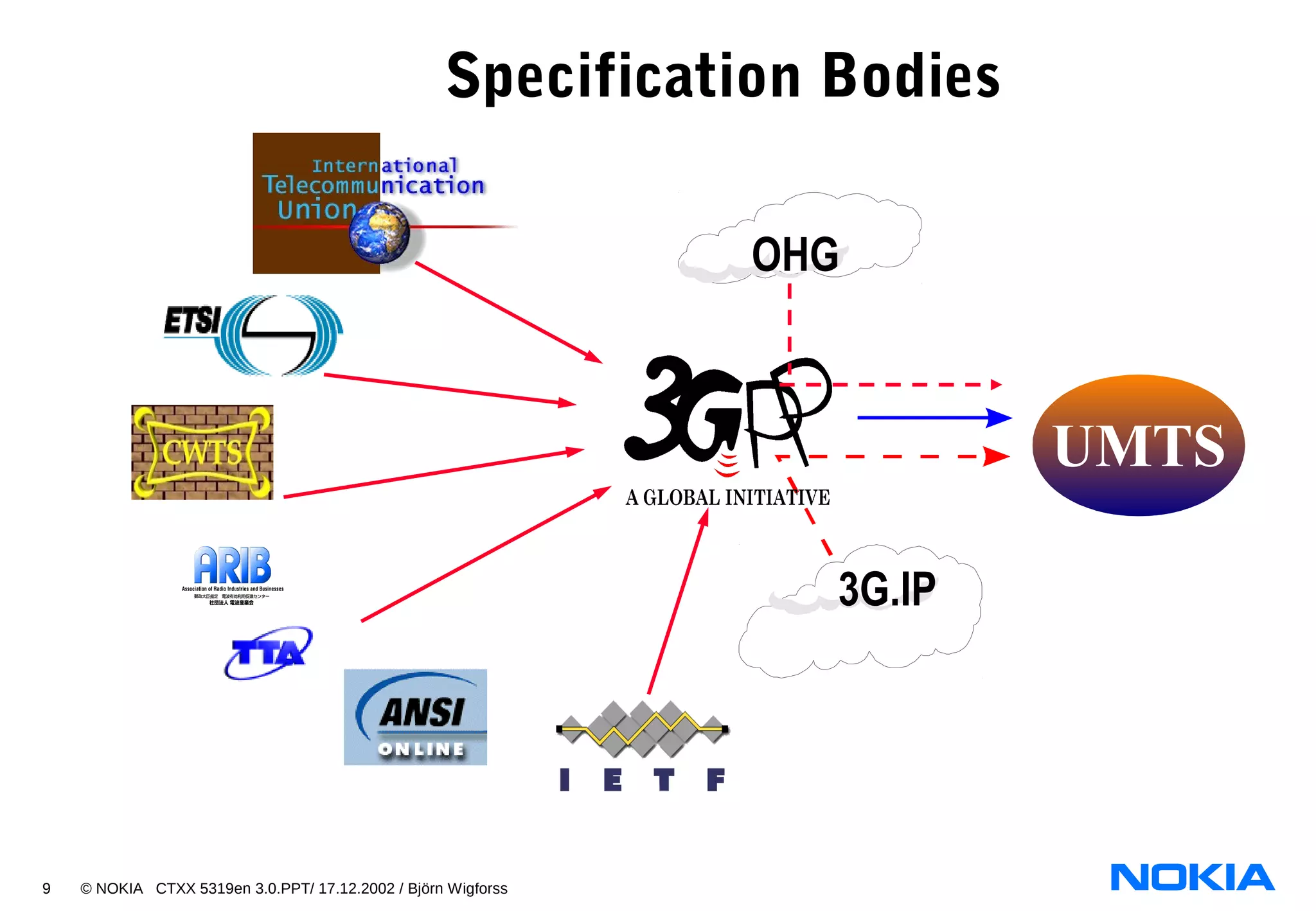
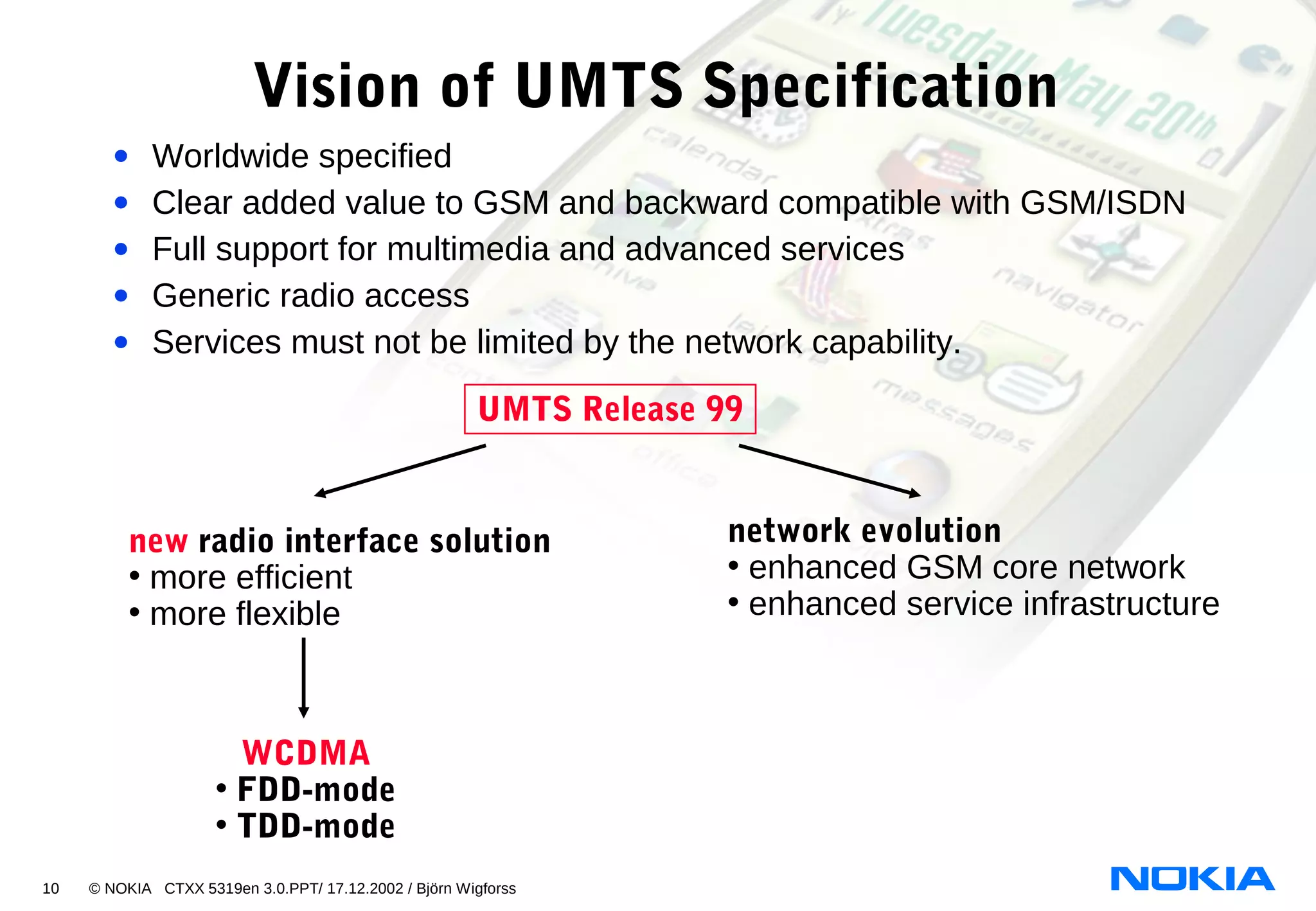
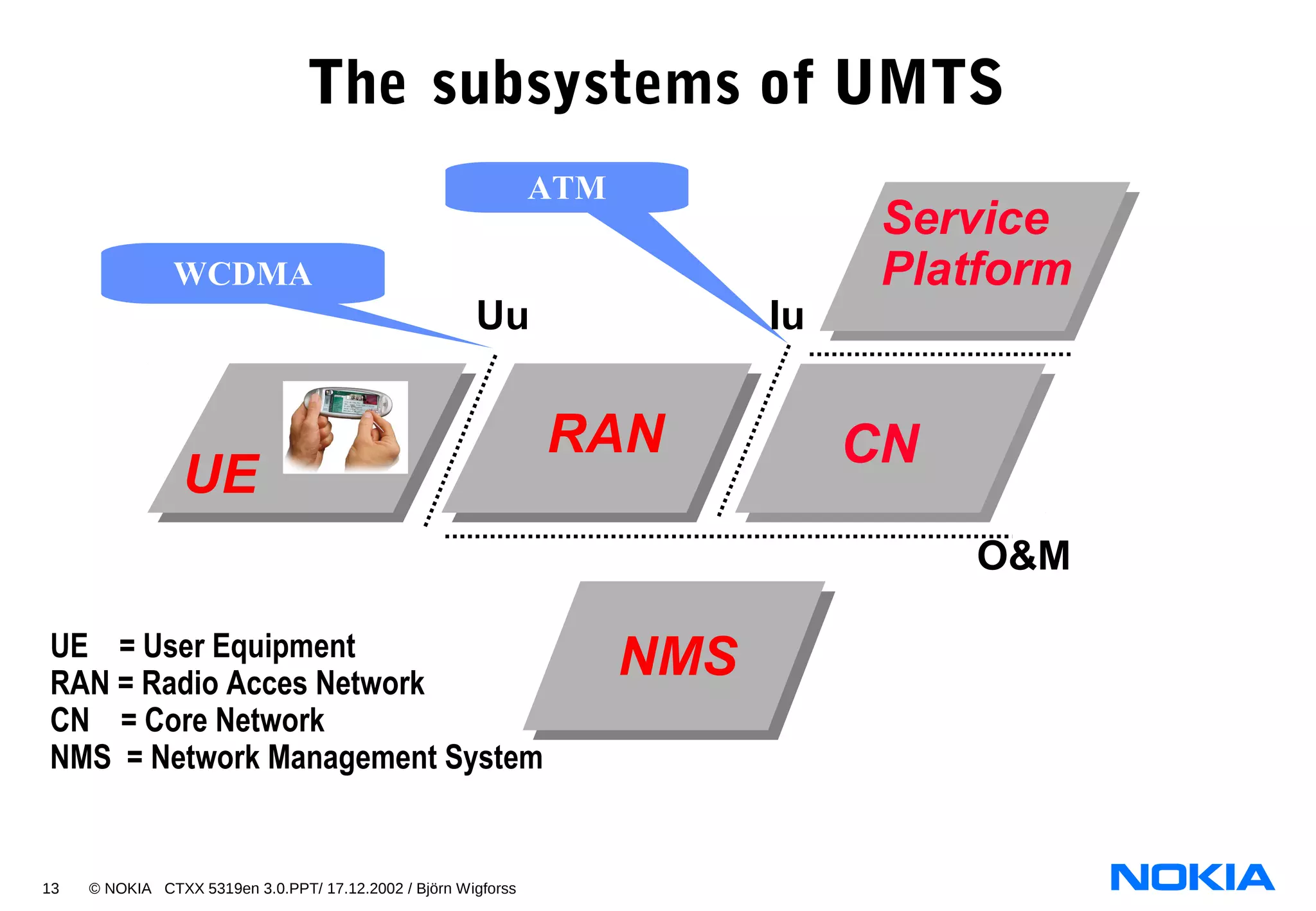
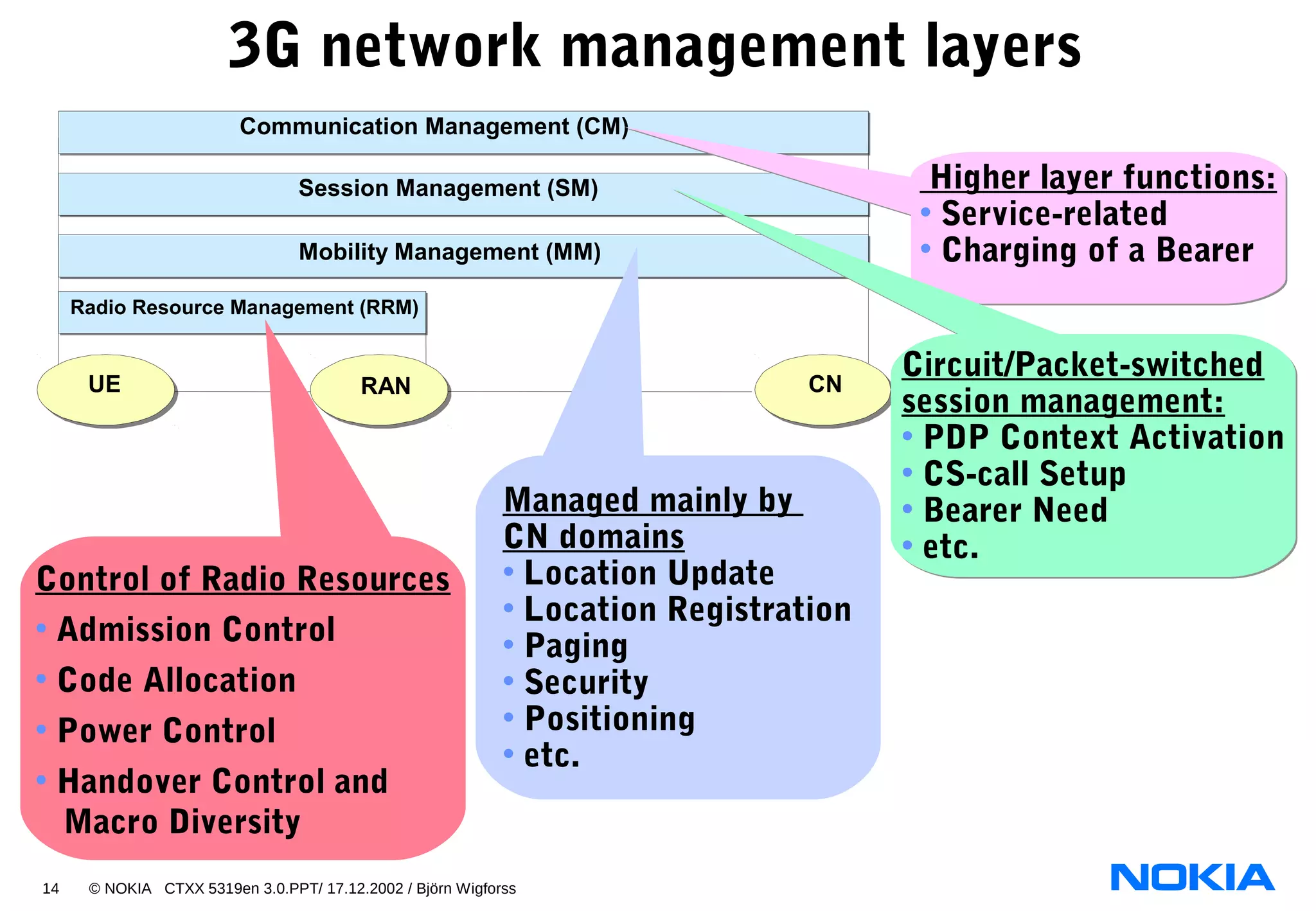
2. List the four main network subsystems of UMTS Release 99:
- UTRAN
- CN
- NMS
- Service Platform
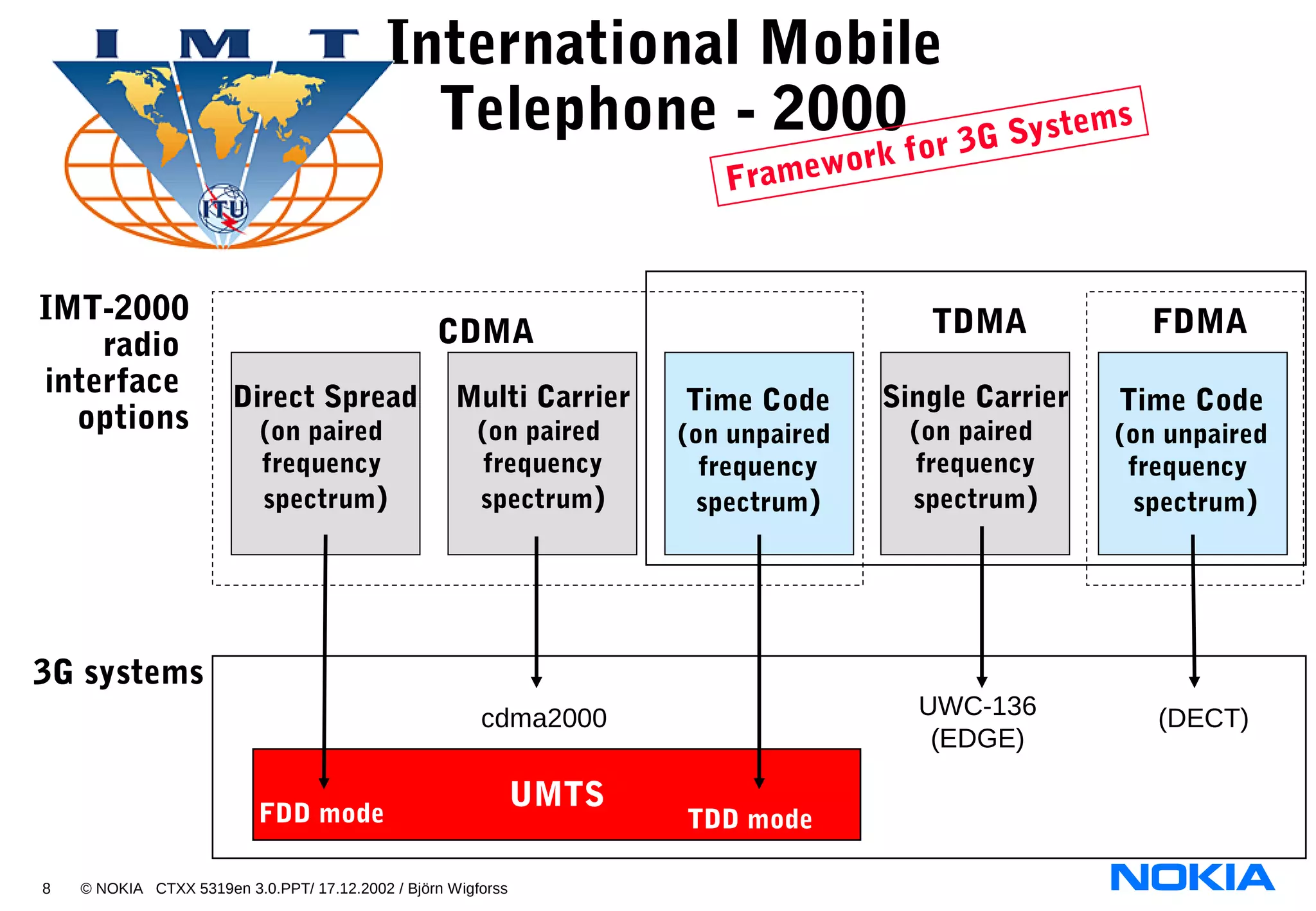
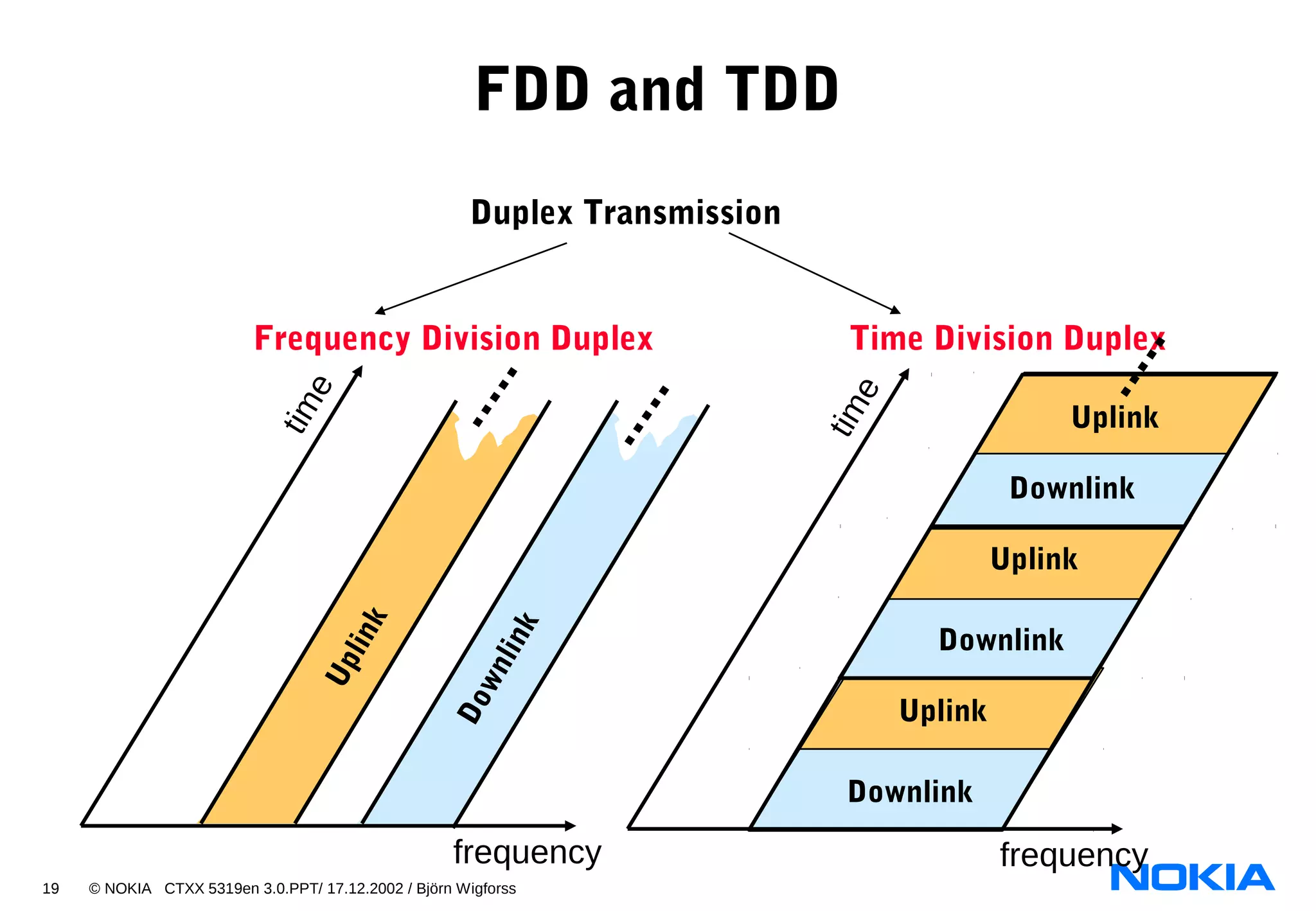
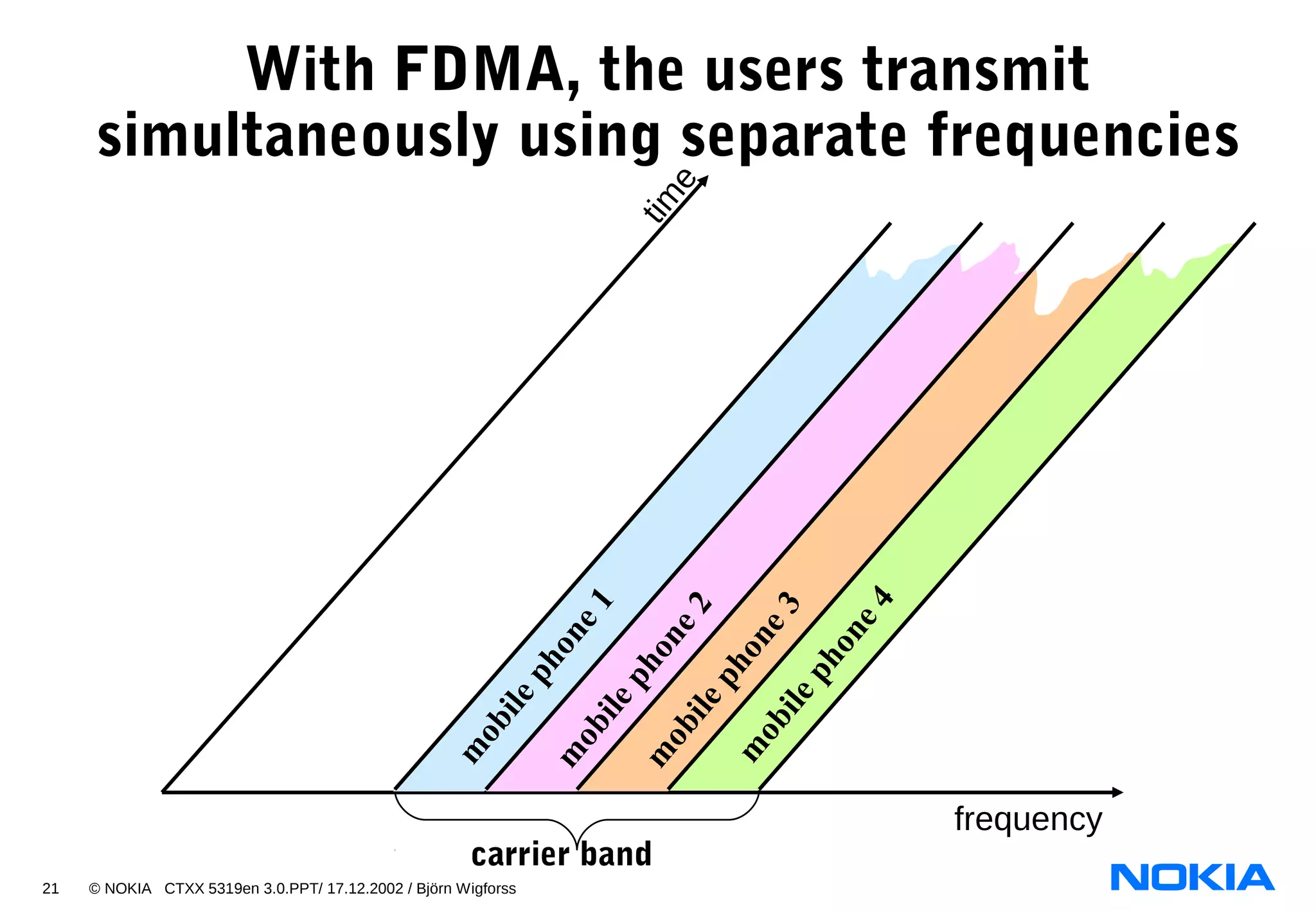
3. Name the four basic air interface access technologies:
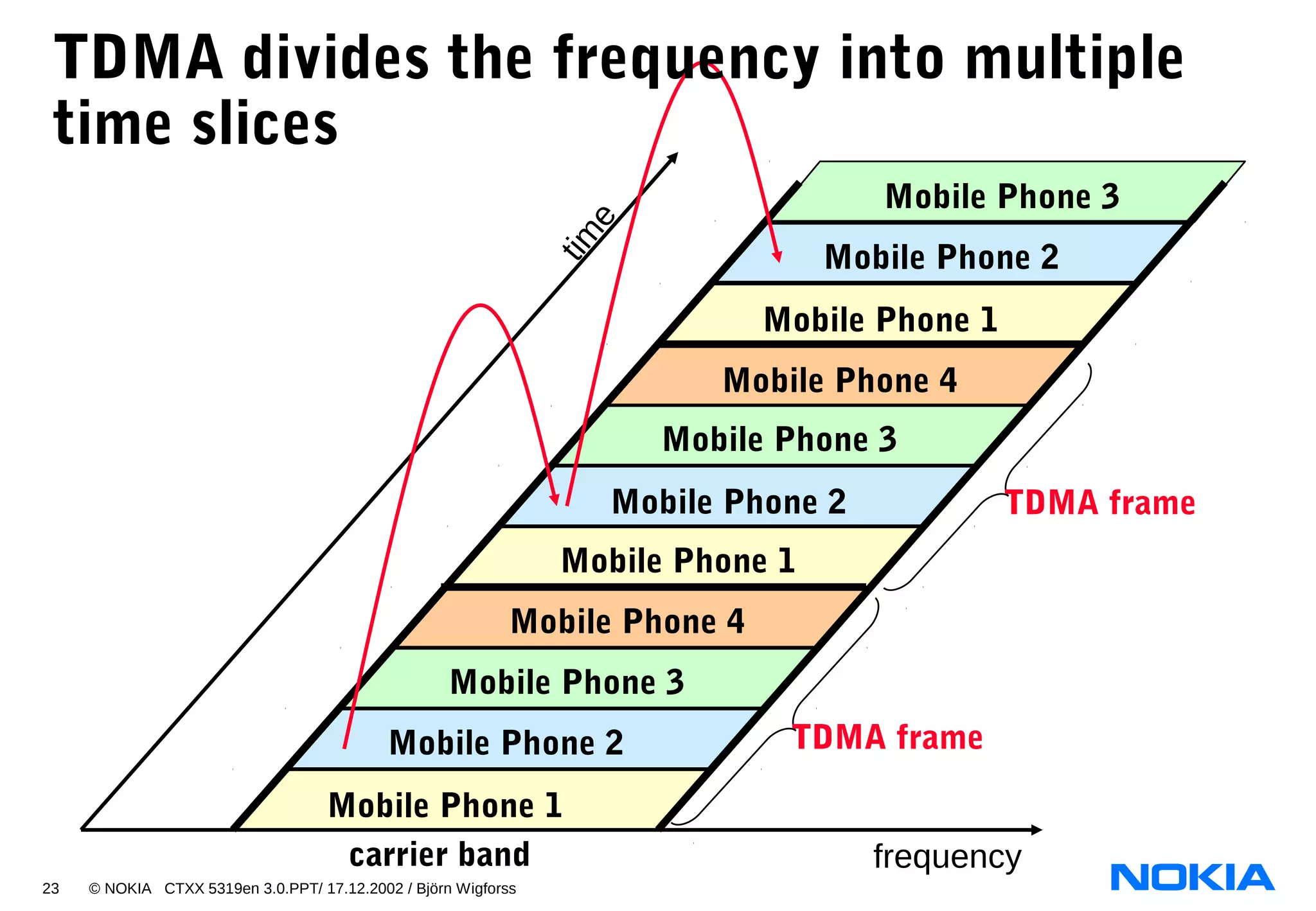
- TDMA
- FDMA
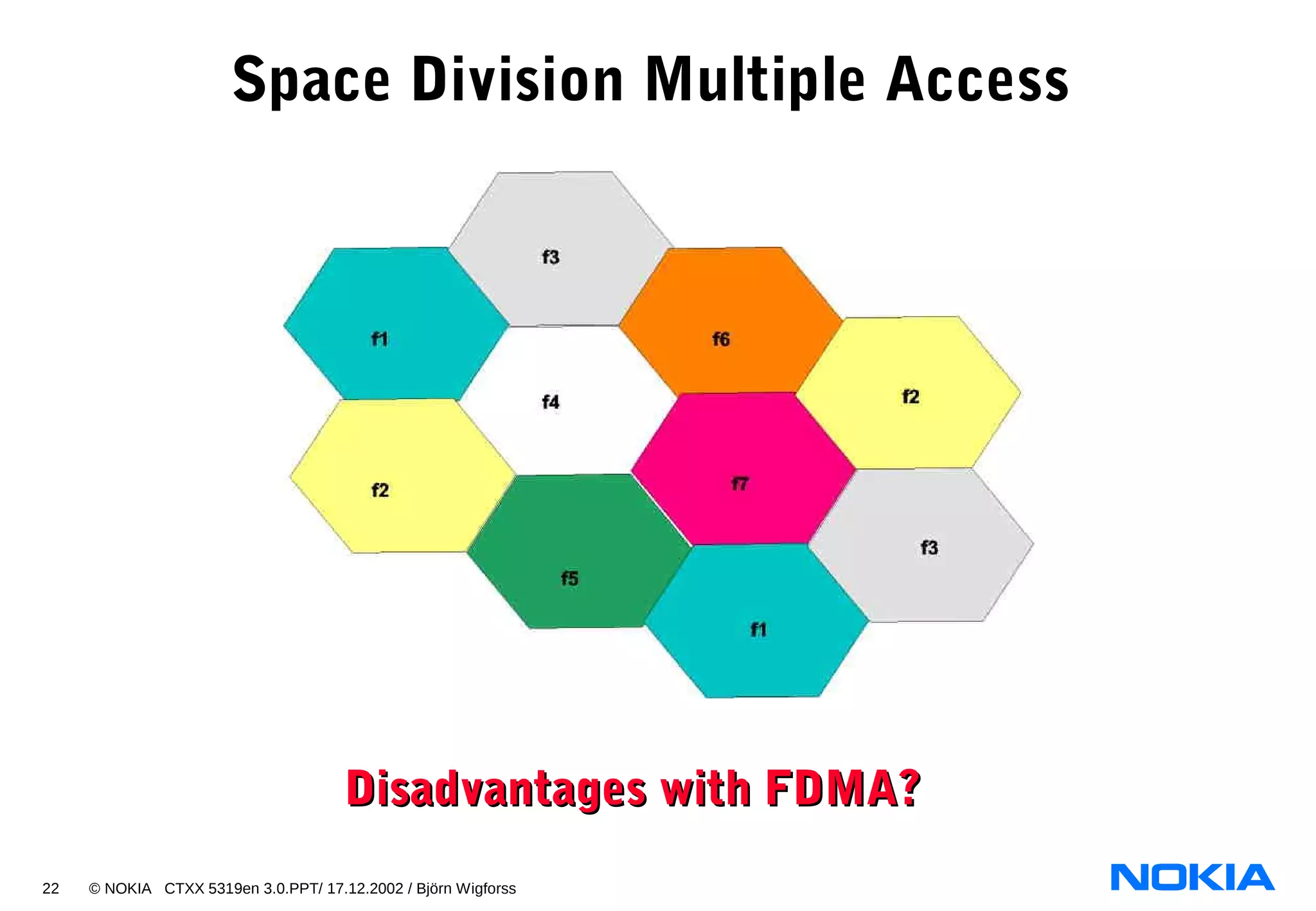
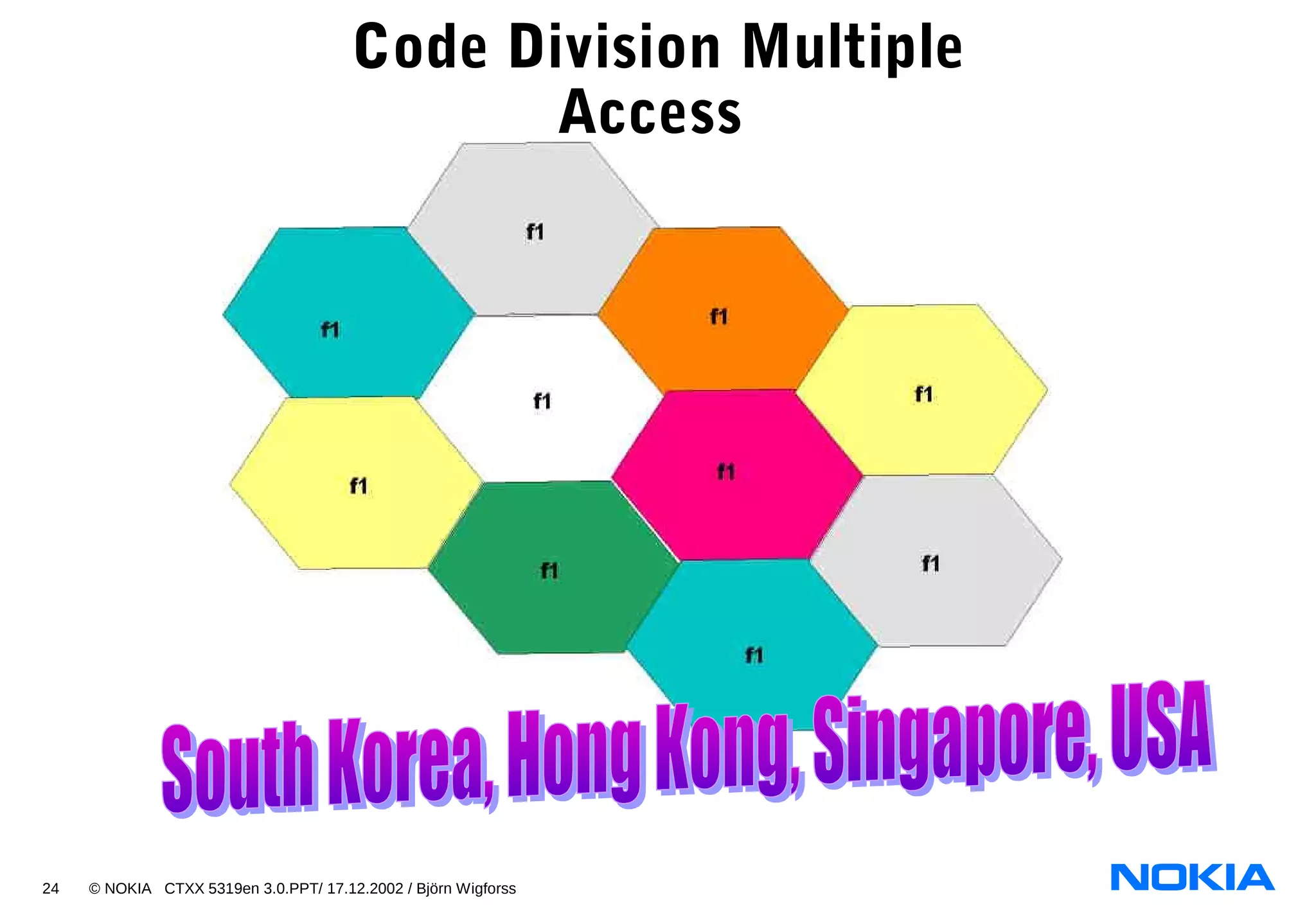
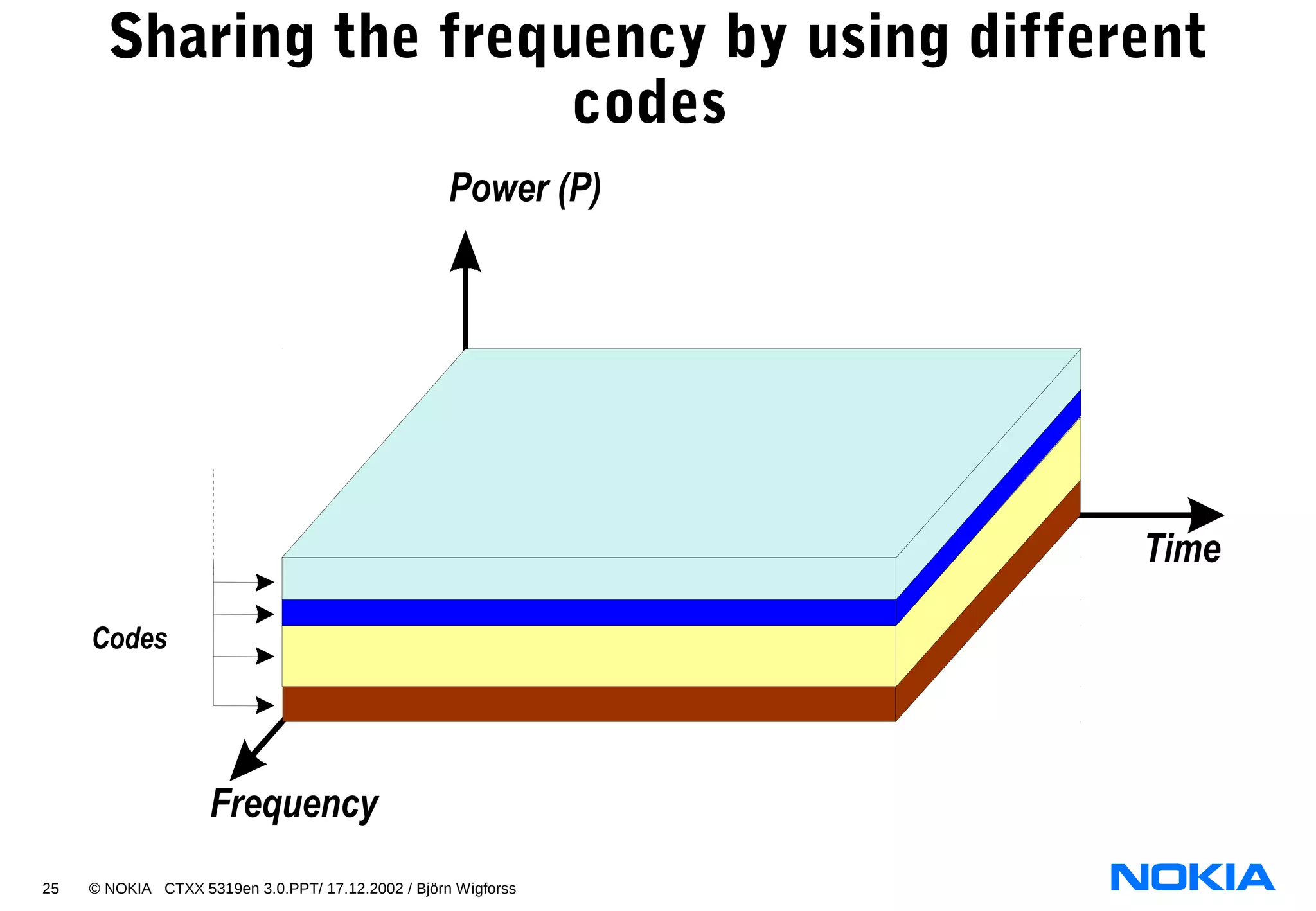
- CDMA
- OFDMA