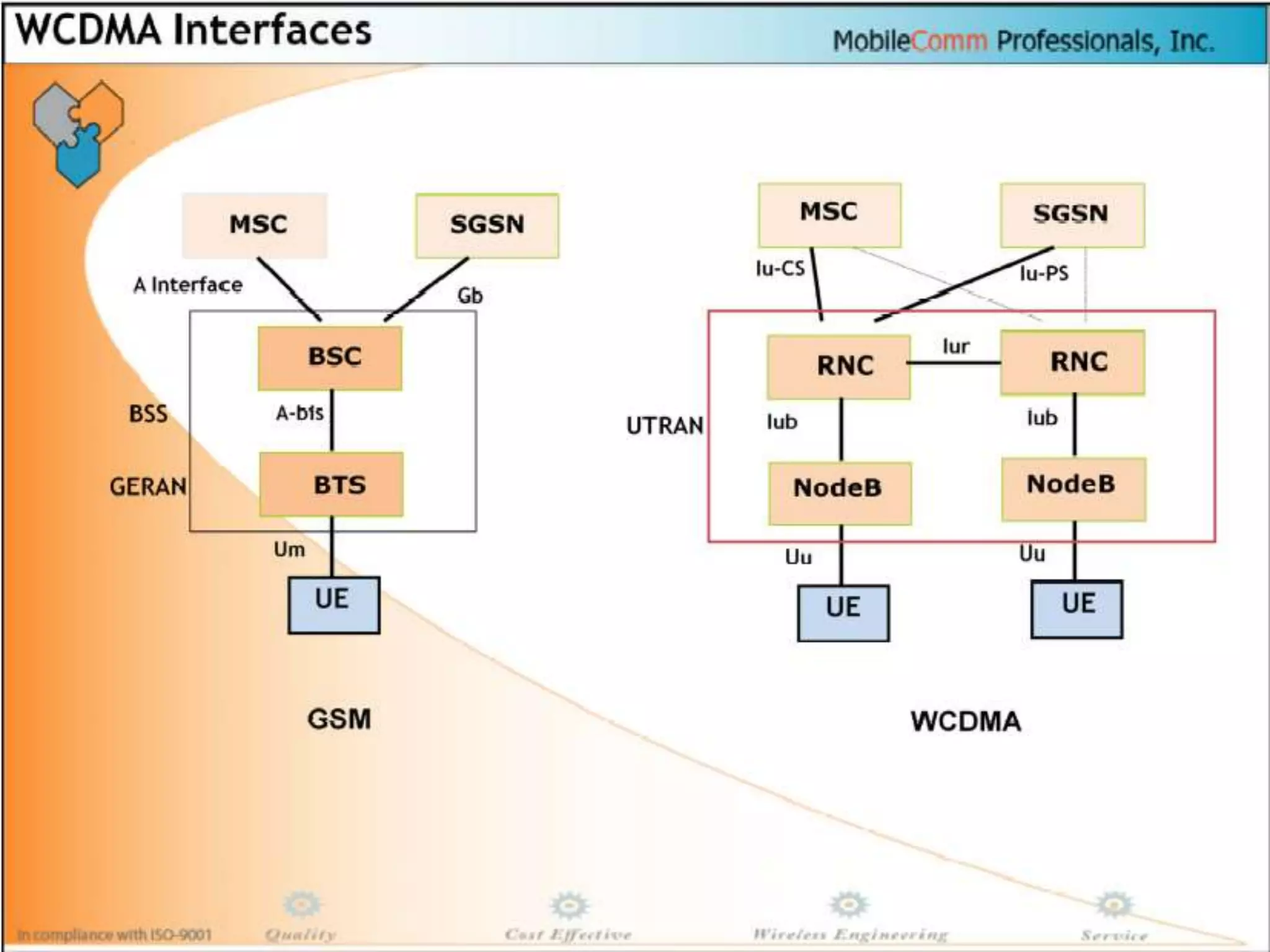
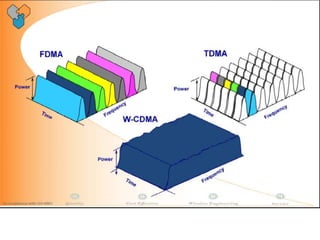
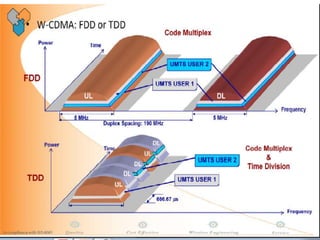
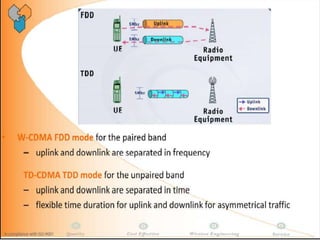
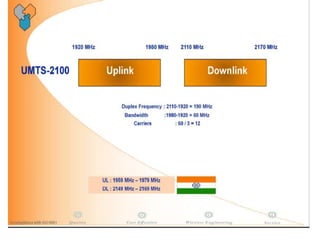
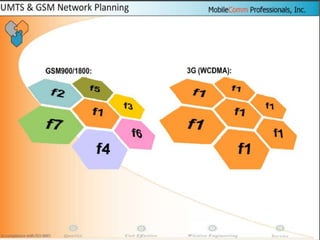
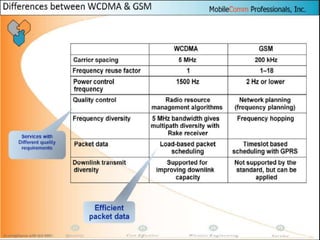
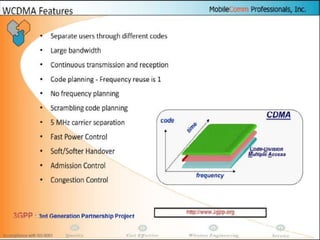
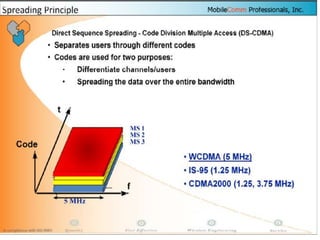
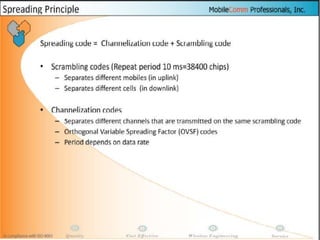
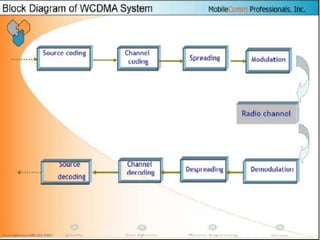
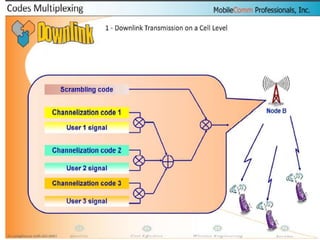
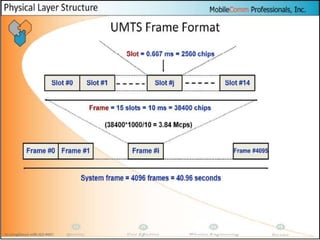
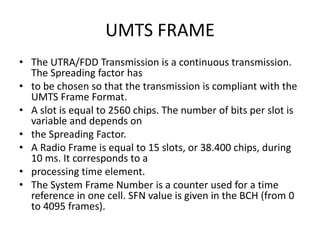
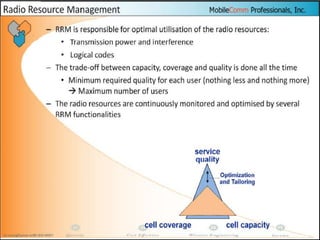
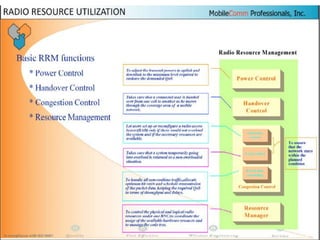
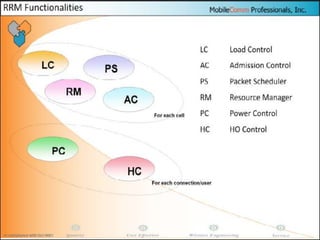
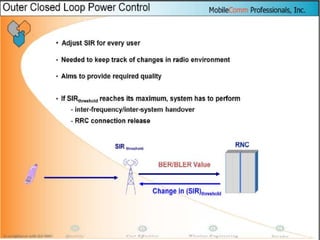
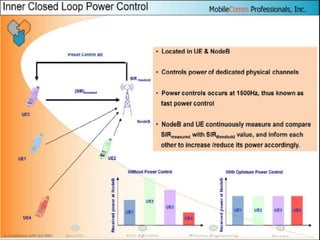
The document discusses different methods for establishing channels in radio technologies: FDMA uses different frequencies for each user; TDMA uses different time slots on the same frequency; W-CDMA uses unique code patterns to distinguish each user on the same frequency. It also describes the UMTS frame format and power control mechanisms in UMTS, including inner loop power control which adjusts transmission power based on comparisons to Eb/Nt objectives, and outer loop power control which estimates Eb/Nt objectives based on measured frame error rates.