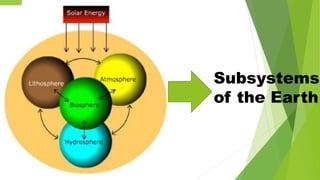
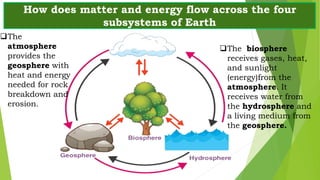
The document discusses the four main subsystems that make up the Earth: the atmosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. It provides details on each subsystem, including the composition and layers of the atmosphere. The subsystems interact with each other through flows of matter and energy. For example, the atmosphere provides heat and energy to the geosphere while the biosphere receives gases, heat, sunlight and water from the other subsystems. This dynamic interaction between the subsystems creates a habitable environment for life on Earth.