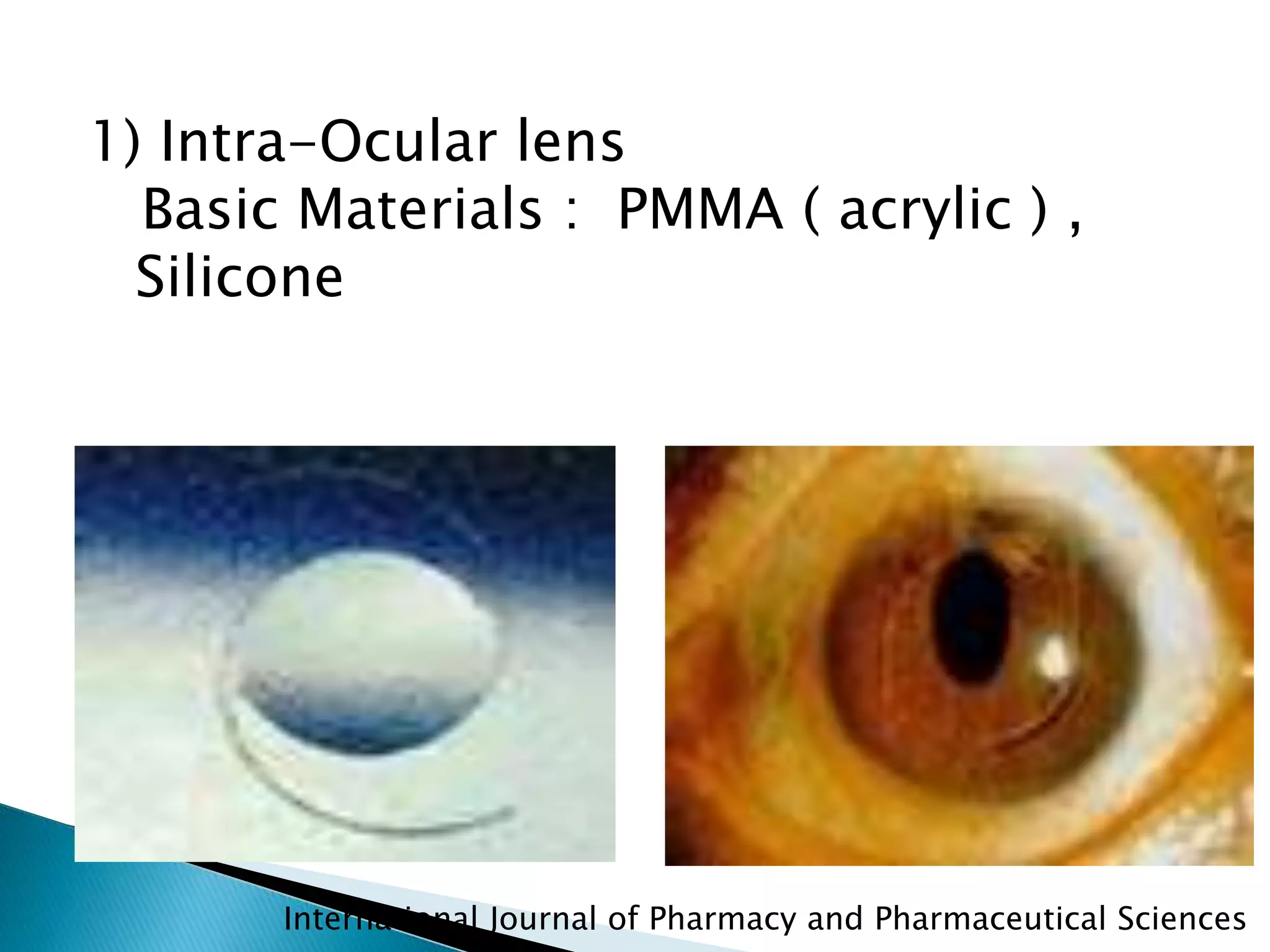
The document discusses biomaterials and their applications in dentistry and medicine. It provides examples of common biomaterials such as metals, ceramics, and polymers used in applications like dental implants, joint replacements, and vascular grafts. Dental materials are categorized as preventive, restorative, or auxiliary. Impression materials are discussed, including their properties and types like elastic and non-elastic materials.