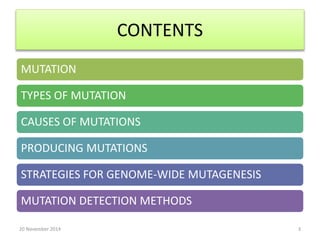
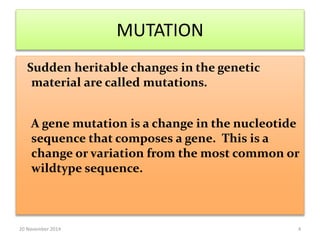
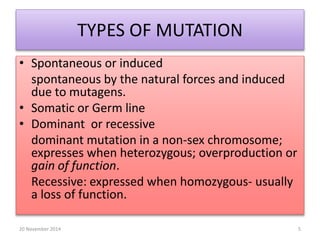
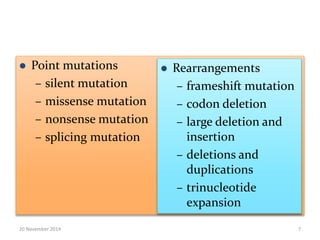
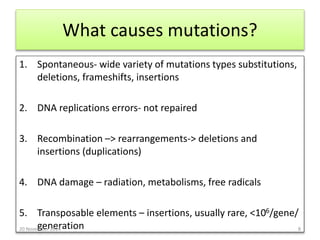
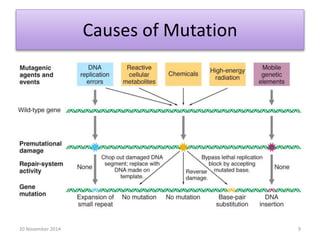
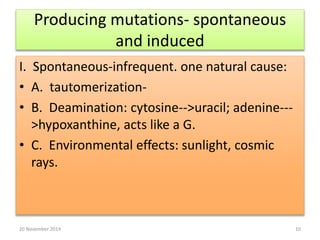
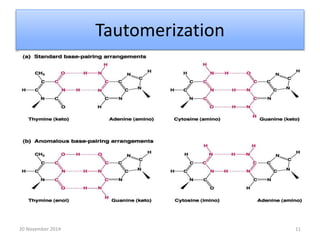
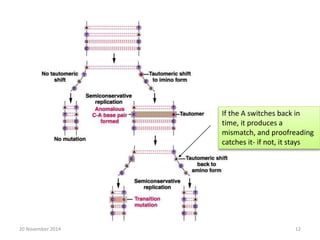
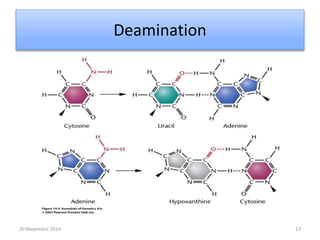
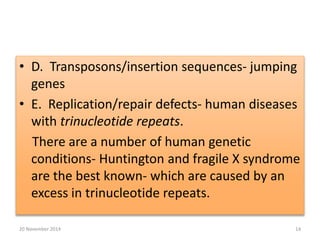
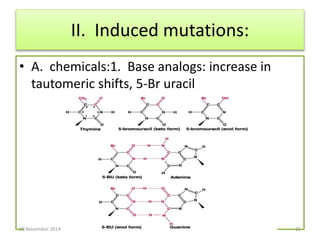
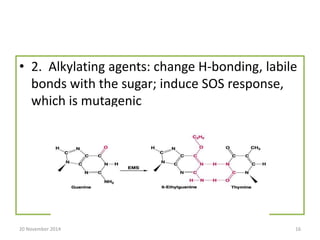
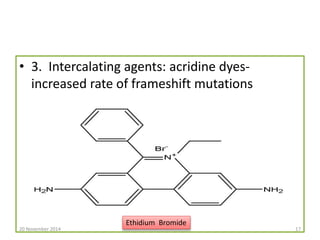
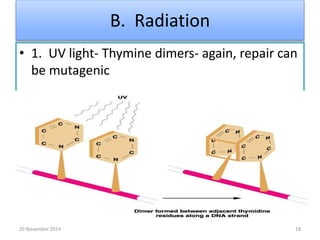
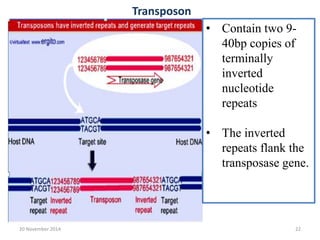
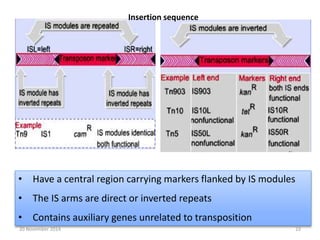
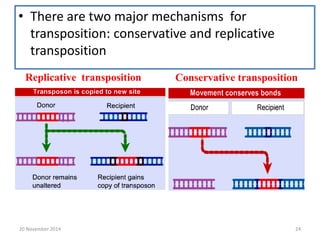
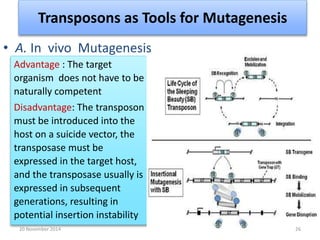
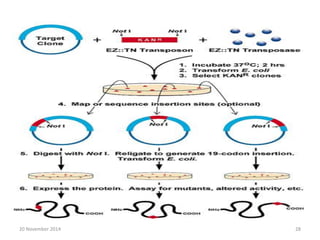
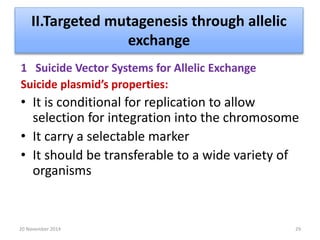
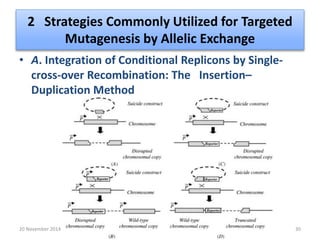
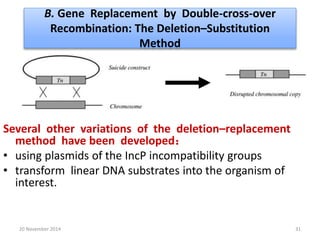
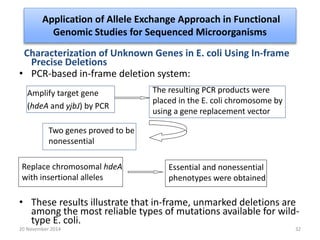
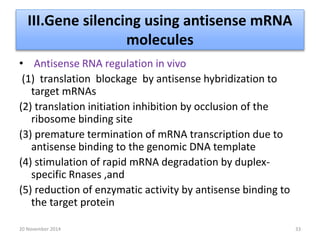
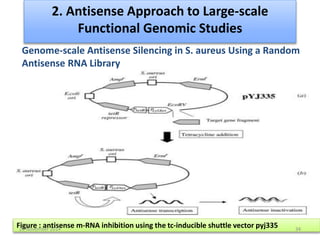
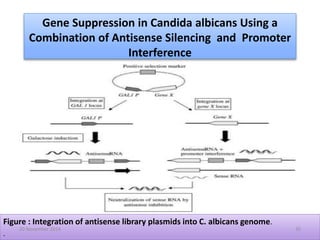
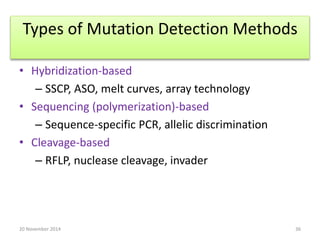
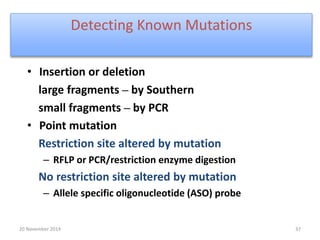
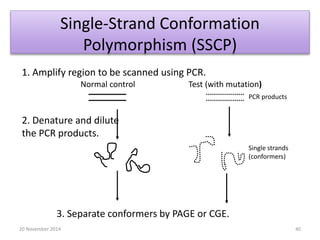
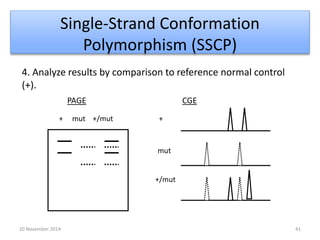
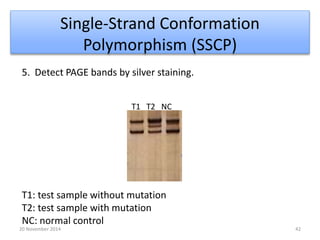
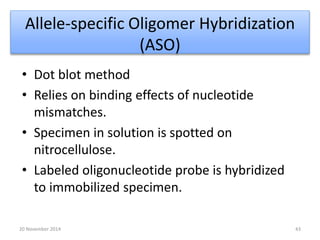
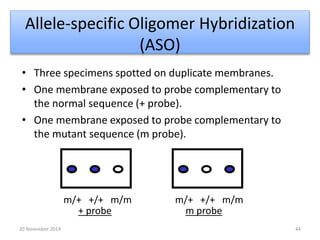
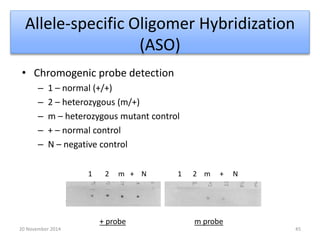
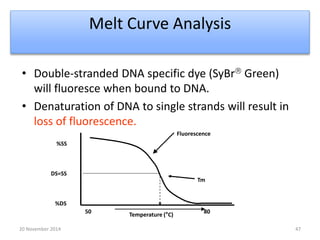
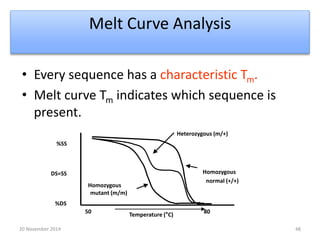
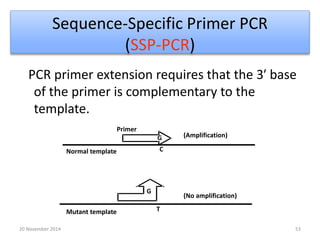
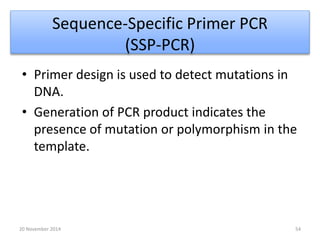
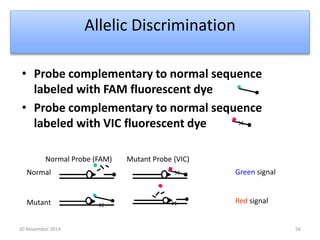
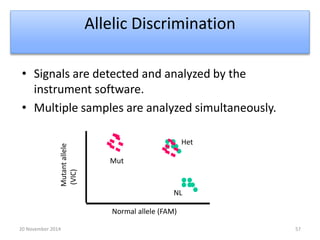
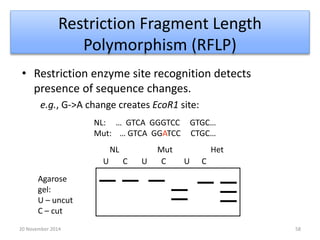
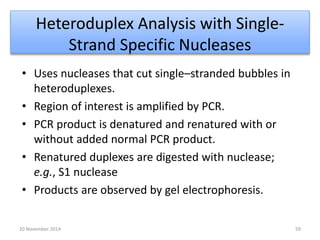
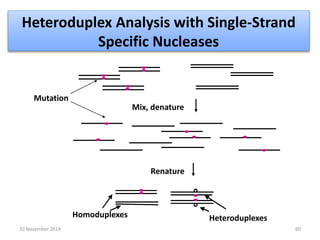
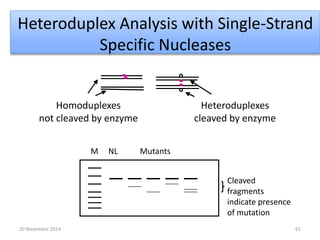
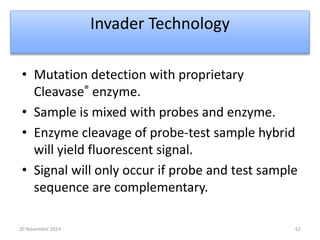
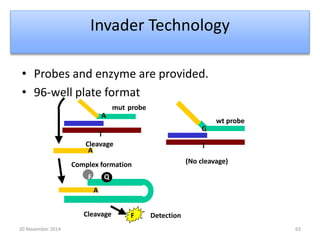
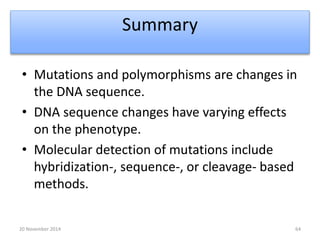
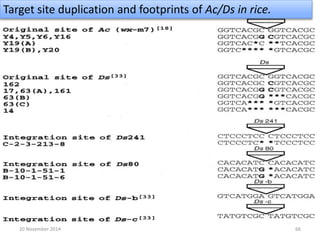
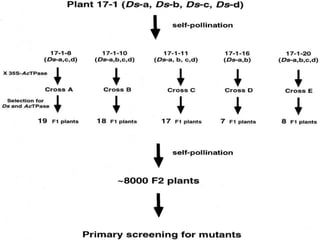
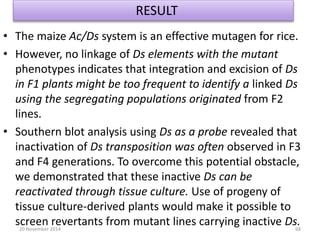
This document discusses strategies for genome-wide mutagenesis. It describes three main strategies: transposon insertion, gene disruption through allelic exchange, and expression inhibition using antisense RNA. Transposon insertion involves using transposable elements to randomly insert into genomes. Gene disruption uses targeted homologous recombination to replace genes. Antisense RNA inhibits gene expression by binding to target mRNA. The document also discusses various methods for detecting mutations, such as single-strand conformation polymorphism and allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization.