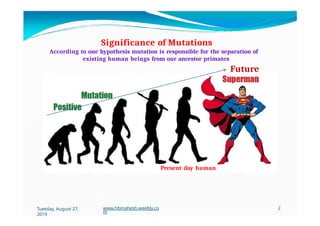
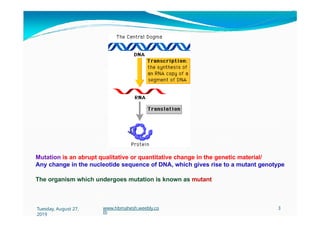
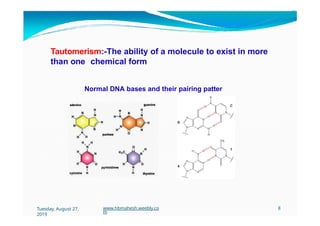
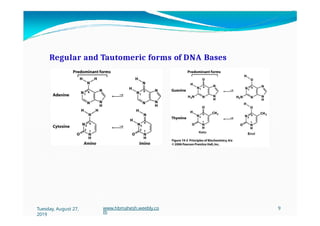
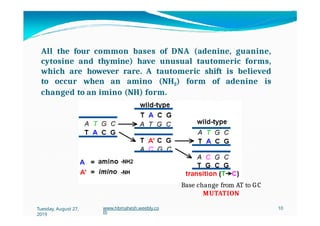
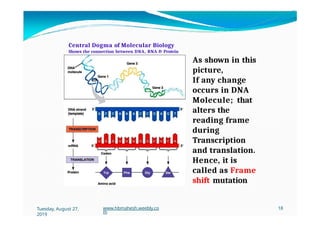
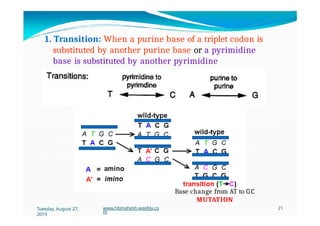
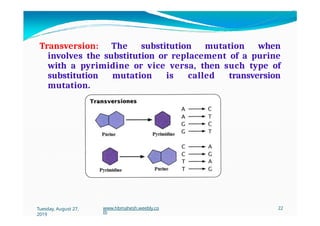
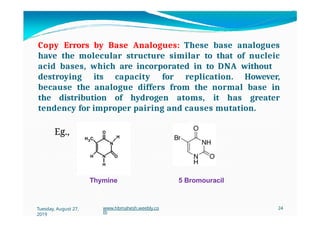
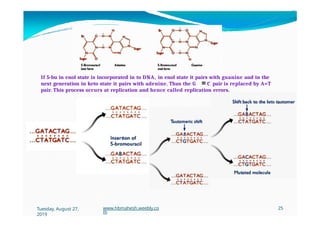
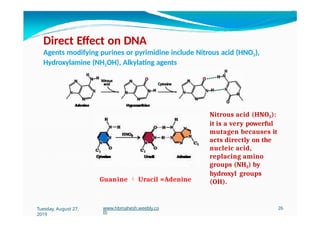
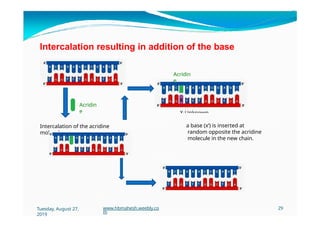
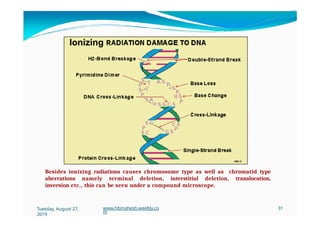
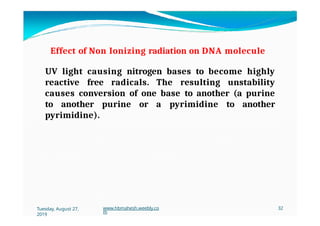
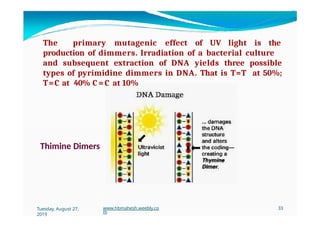
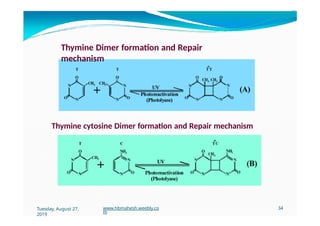
The document discusses the significance and classification of mutations, defining them as changes in genetic material that can lead to mutant genotypes. It explores the history and types of mutations, including natural and induced mutations via physical, chemical, and biological agents. Additionally, the document details mechanisms of mutation such as point mutations, frame shift mutations, and the effects of radiations on DNA.