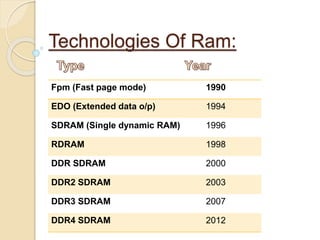
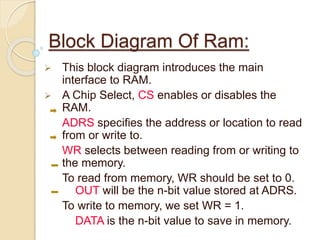
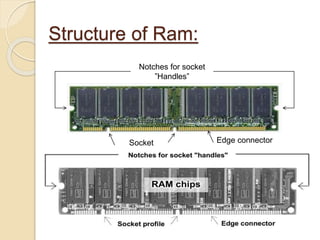
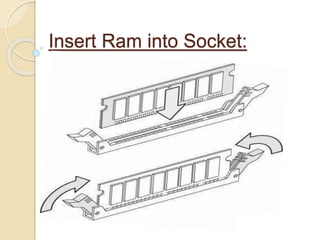
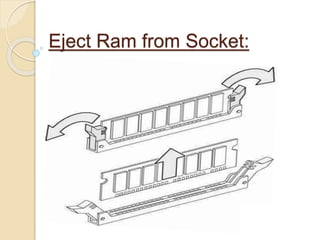
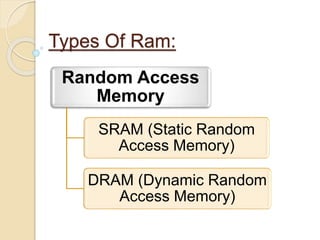
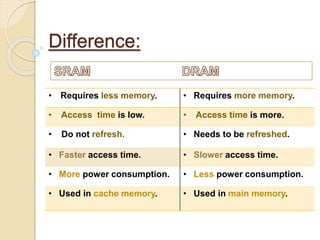
This document provides an overview of random access memory (RAM). It discusses that RAM is a type of volatile memory used to store running programs and data. The document outlines the history, technologies, components, types (SRAM and DRAM), capacities, manufacturers, and advantages/disadvantages of RAM. It also includes diagrams of a RAM block and the positioning and structure of RAM modules.