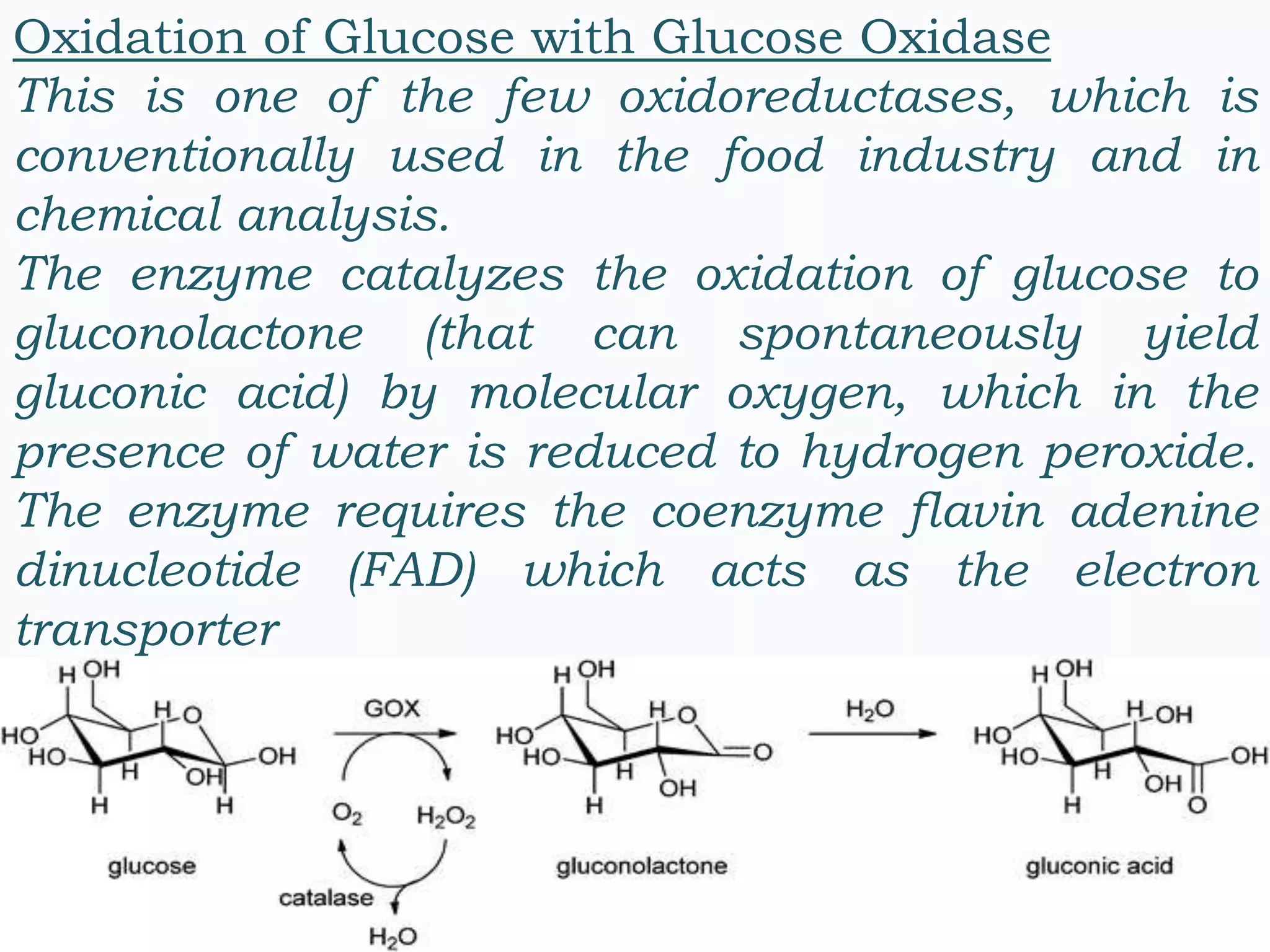
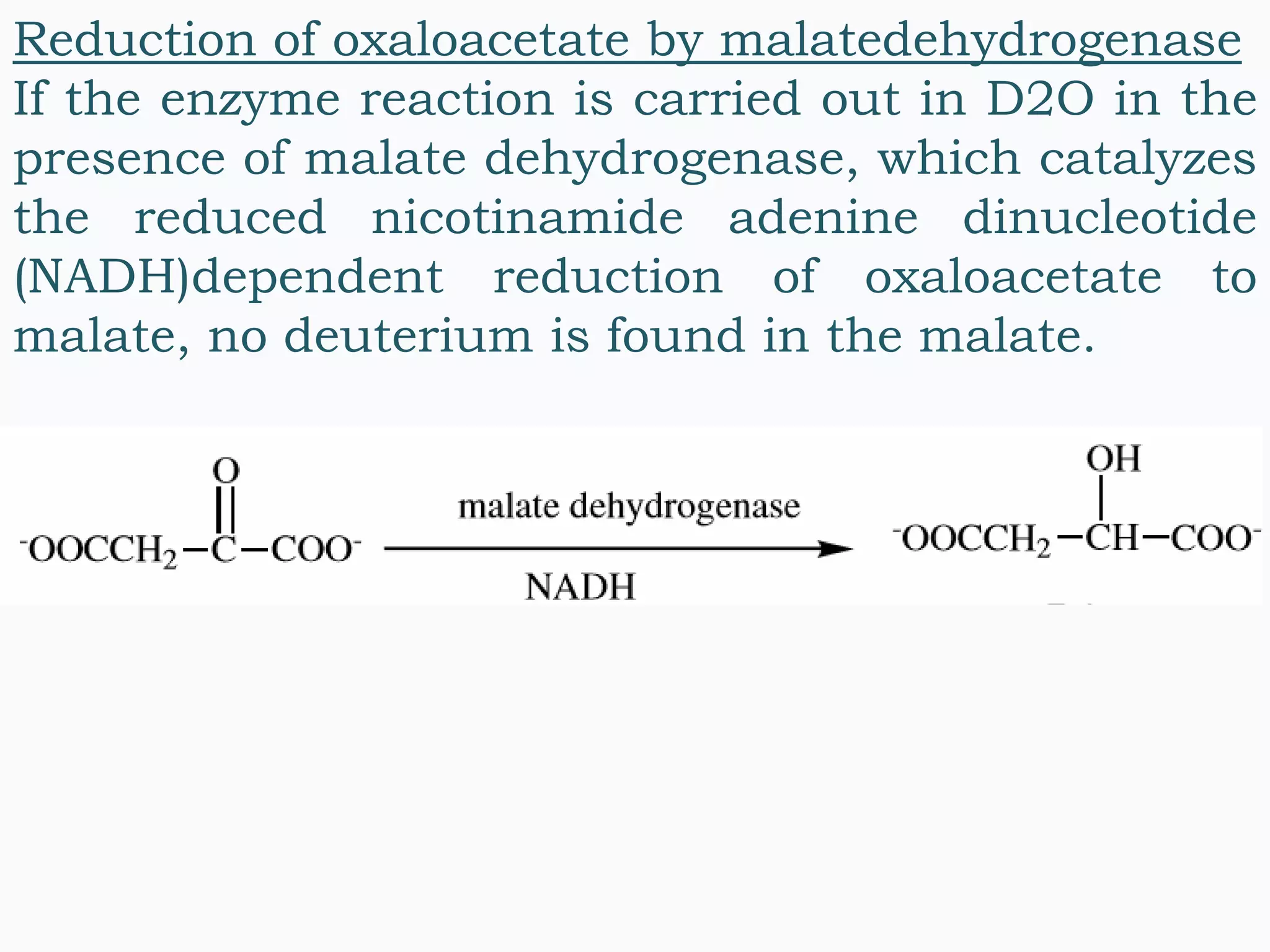
This document discusses enzyme-catalyzed organic redox reactions, specifically examples of enzymes that catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions. It provides details on several enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of molecules like glucose, carbohydrates, and alcohols. It also gives examples of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of molecules like oxaloacetate and haloacetophenones. Enzymes are able to speed up redox reactions and allow these reactions to proceed more efficiently in living systems.