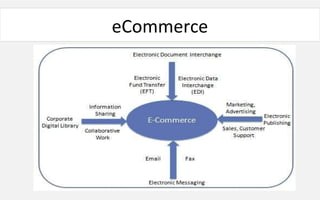
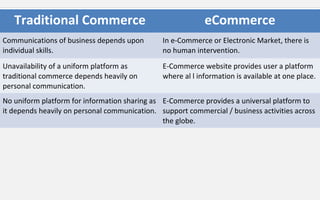
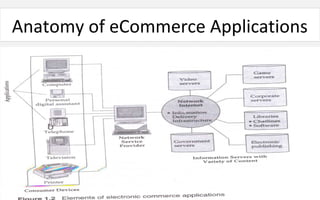
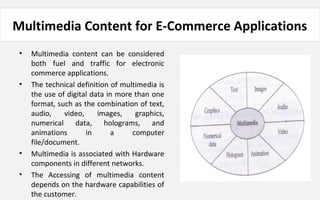
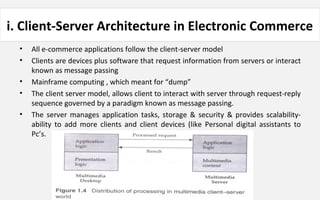
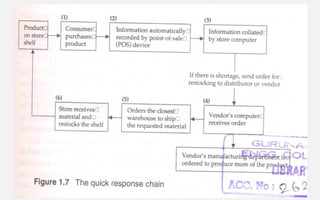
The document provides an overview of eCommerce, including definitions, key features, comparisons to traditional commerce, advantages for organizations, customers, and society. It discusses the eCommerce framework and anatomy of eCommerce applications. Specifically, it outlines how multimedia content serves as both "fuel and traffic" for eCommerce, and how robust storage servers are needed to handle large amounts of digital content for customers. The document provides a comprehensive introduction to the fundamental concepts of eCommerce.