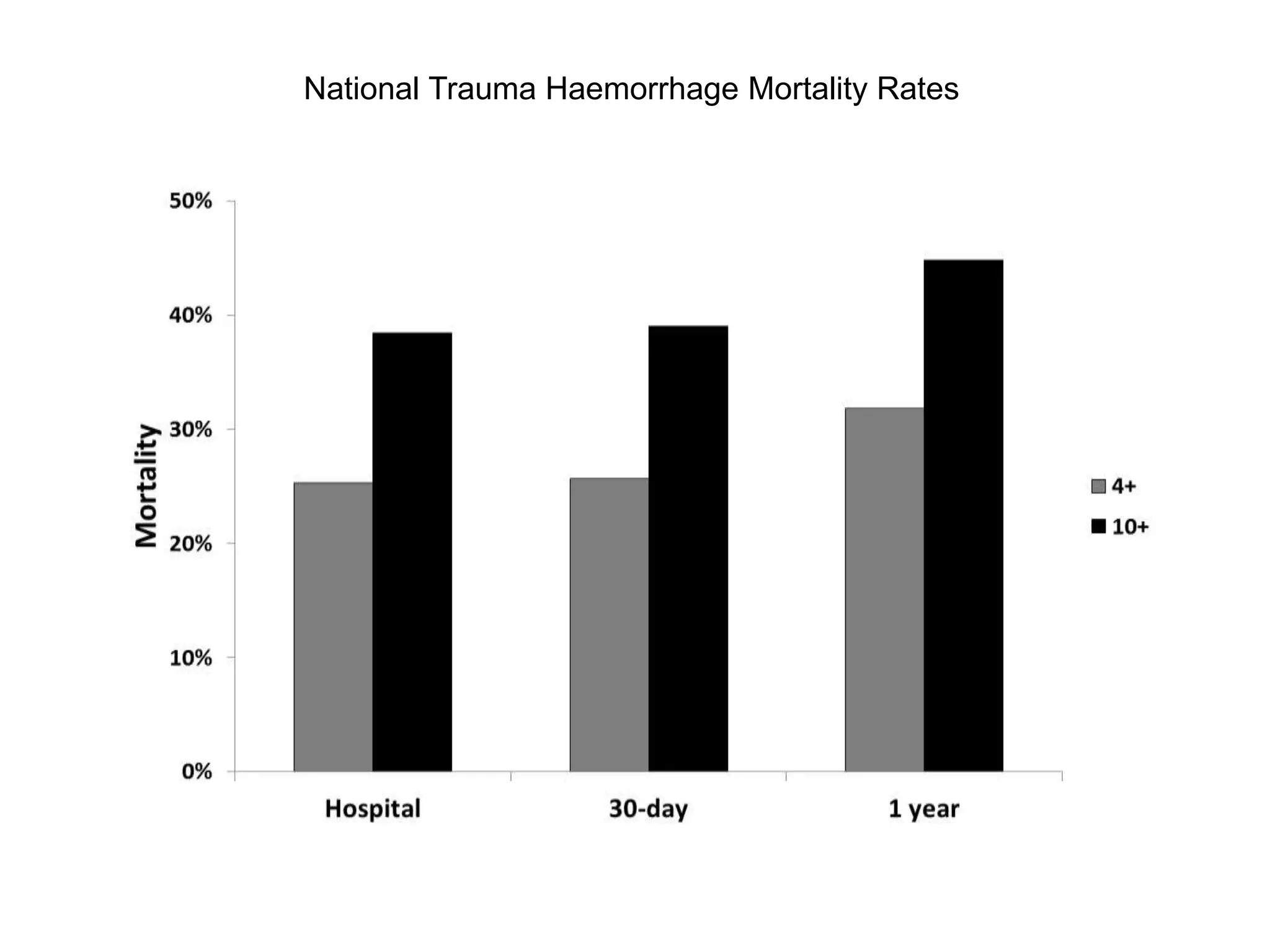
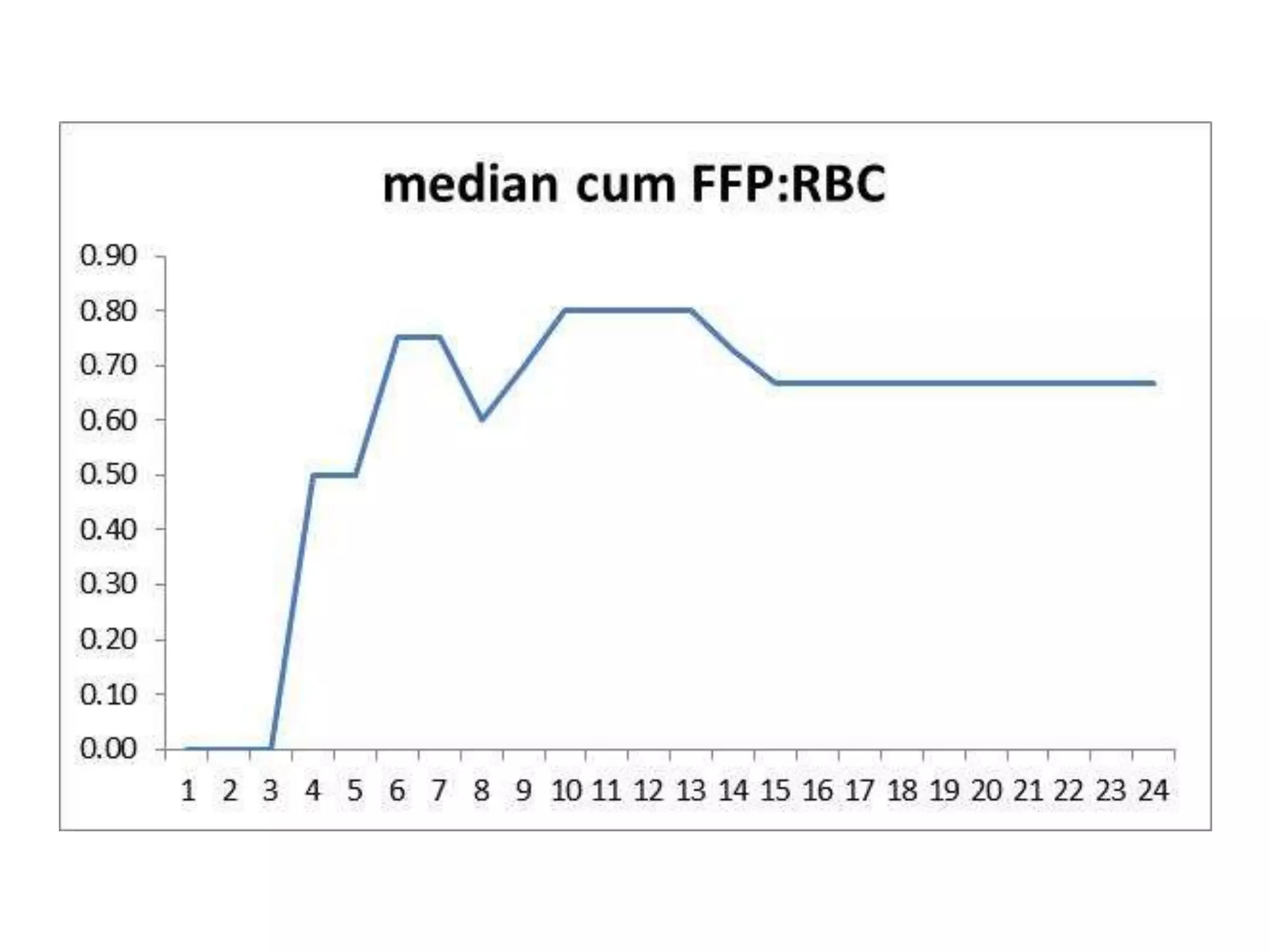
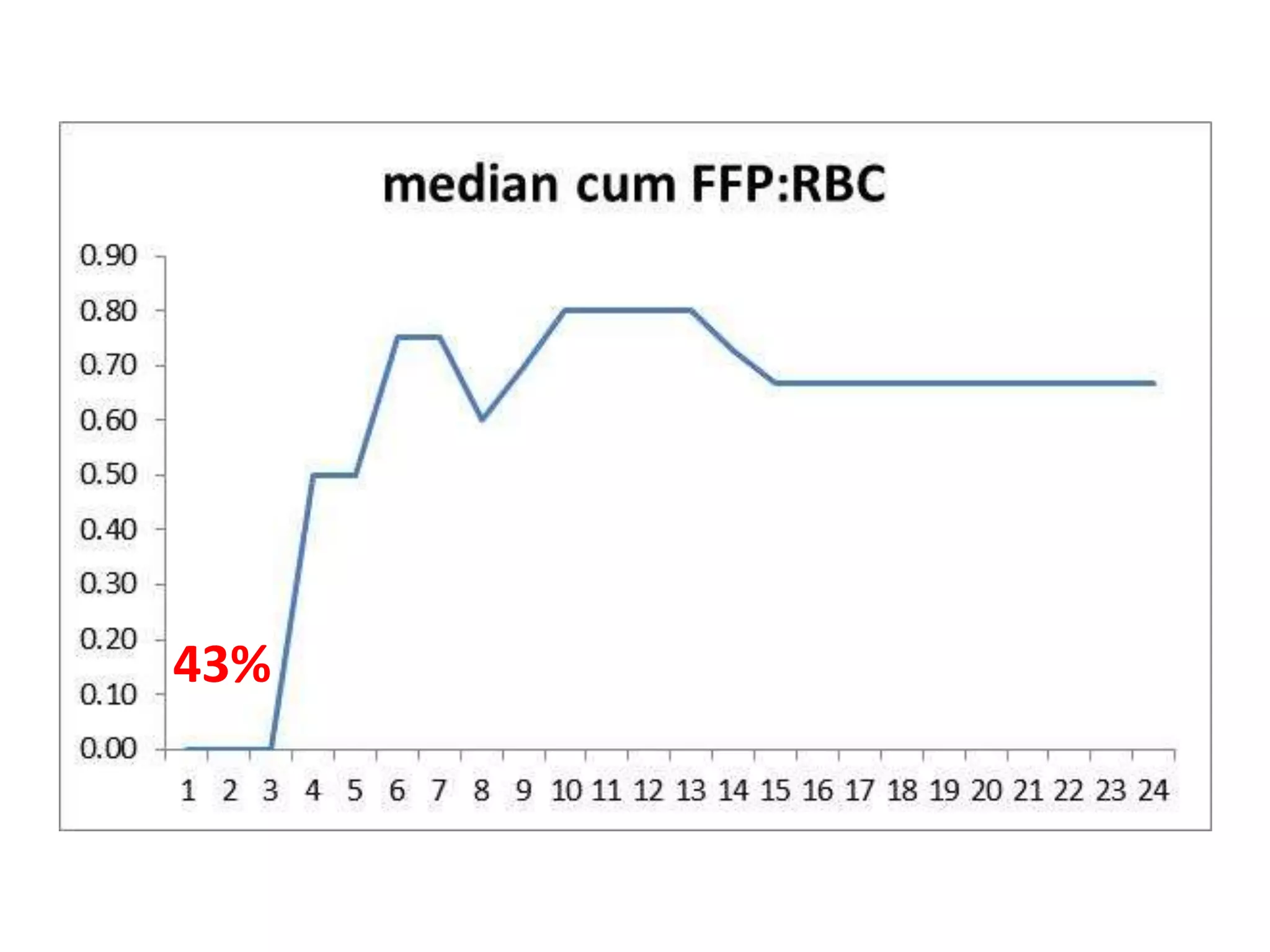
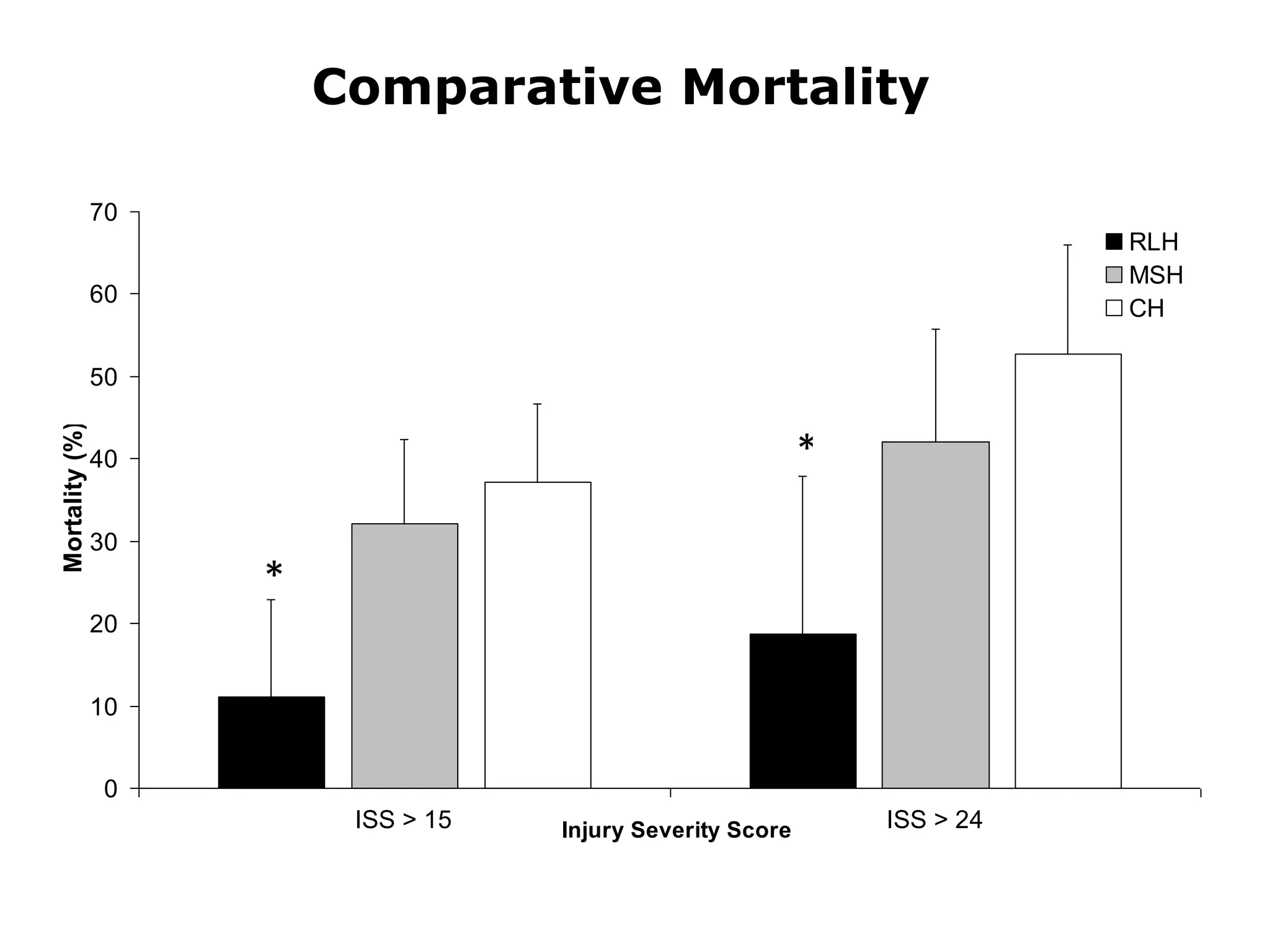
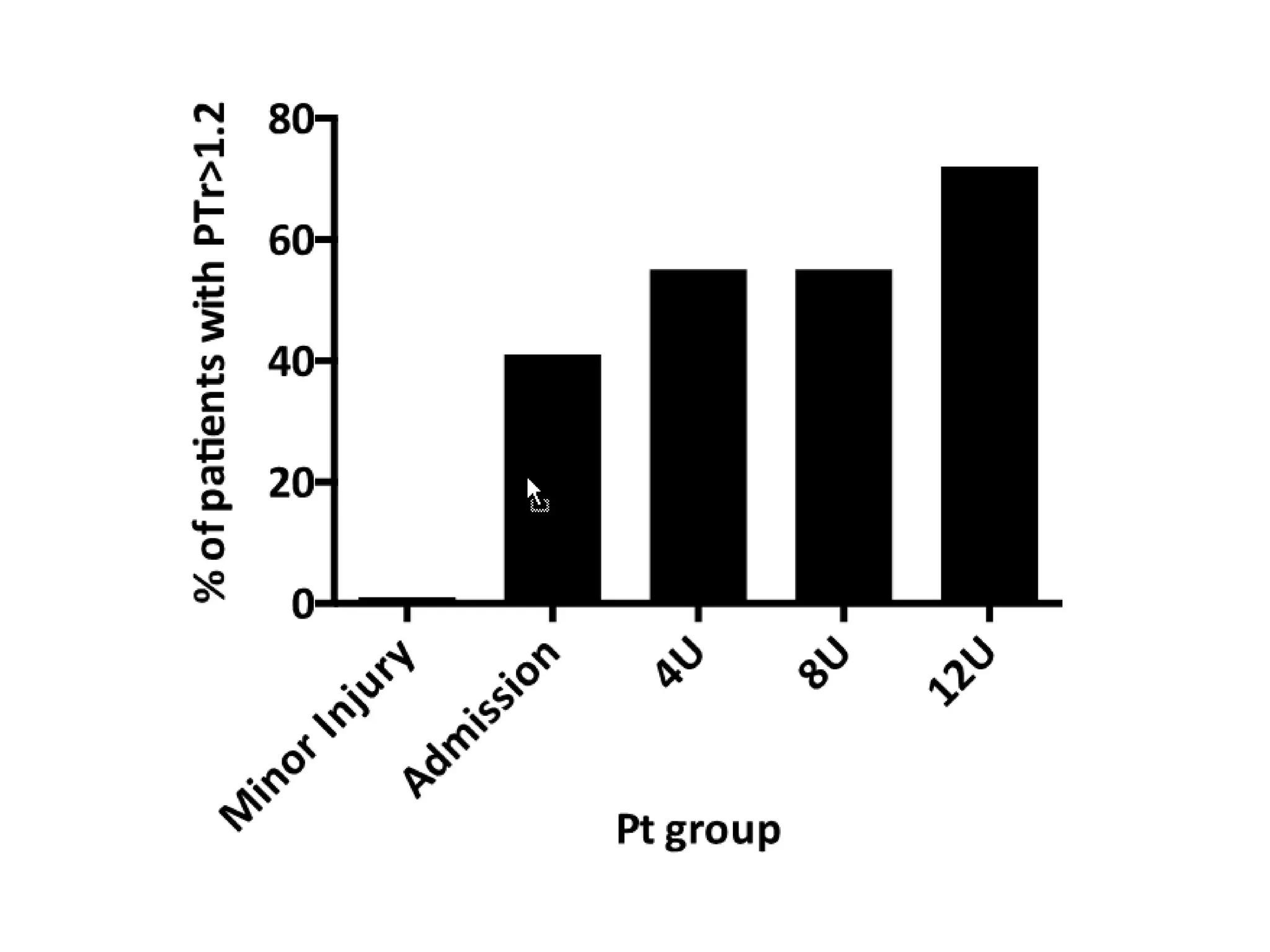
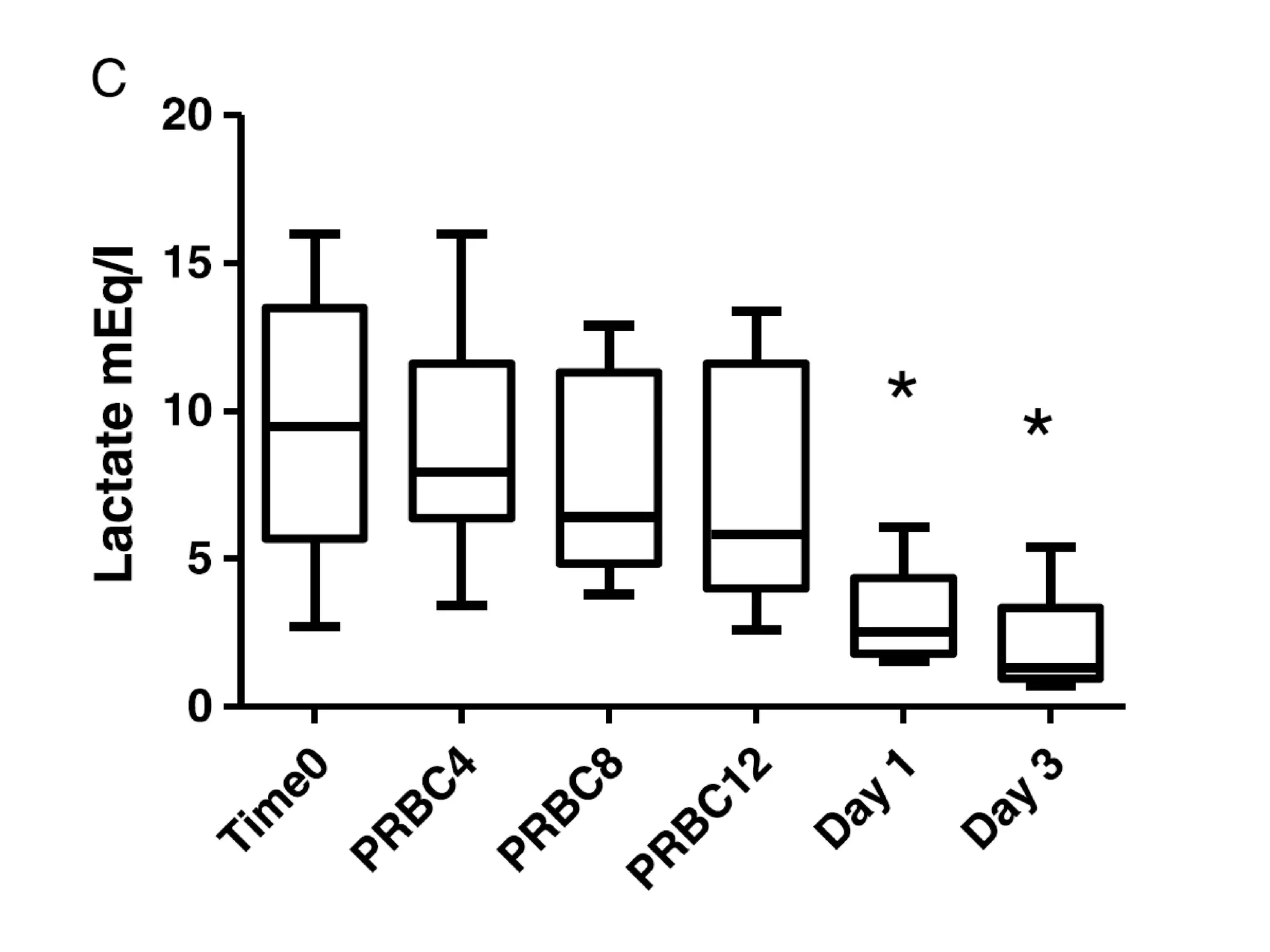
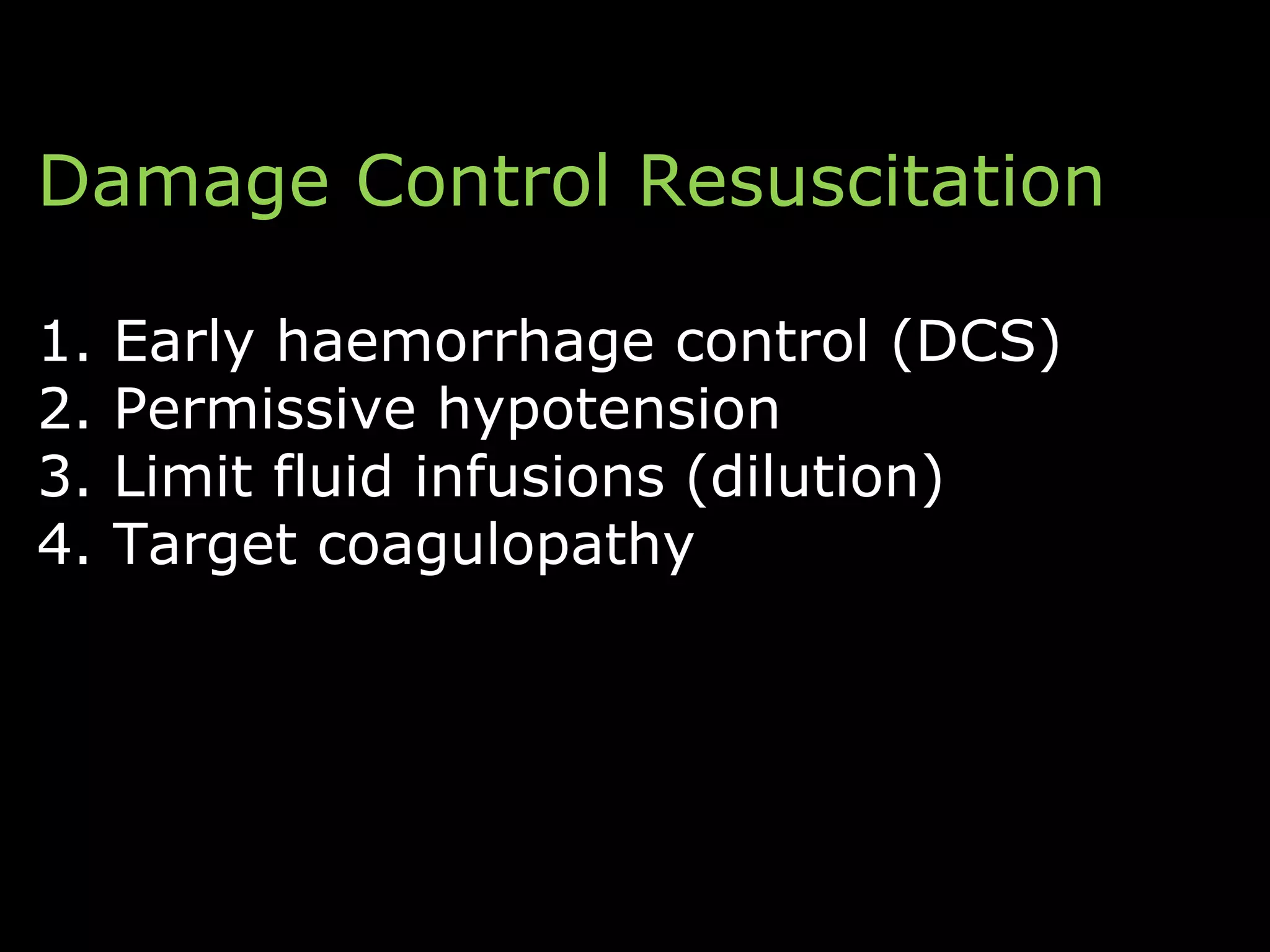
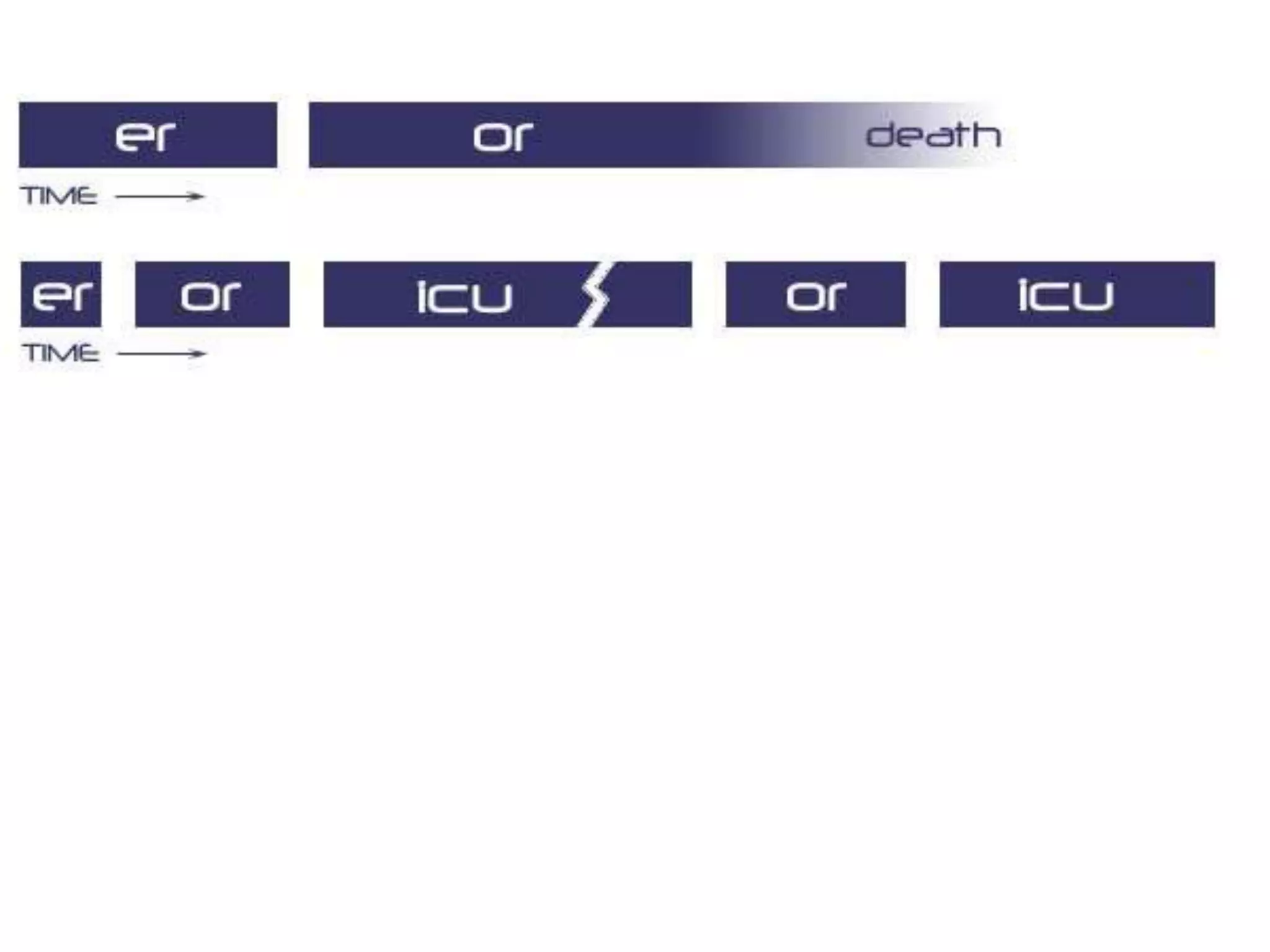
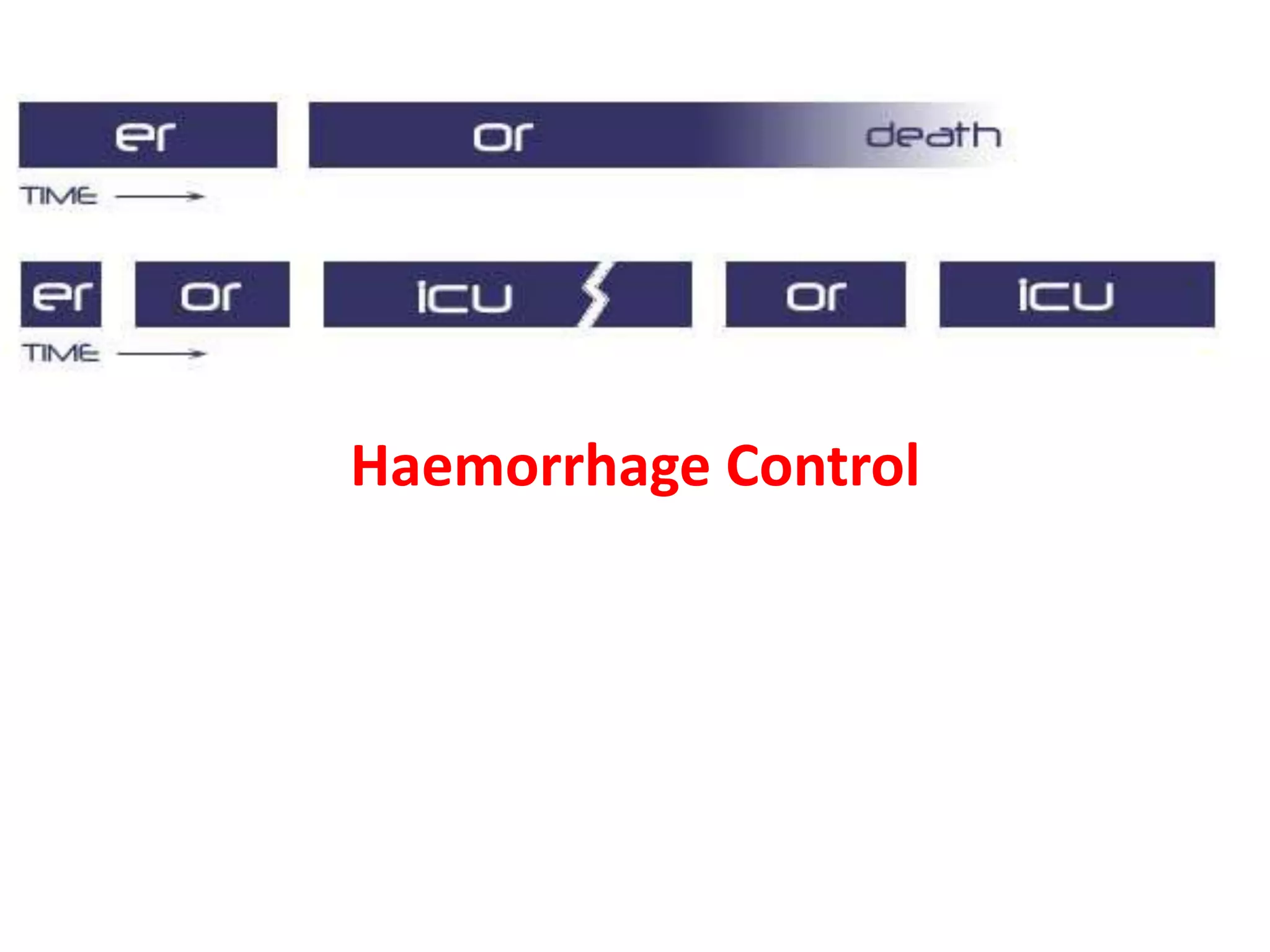
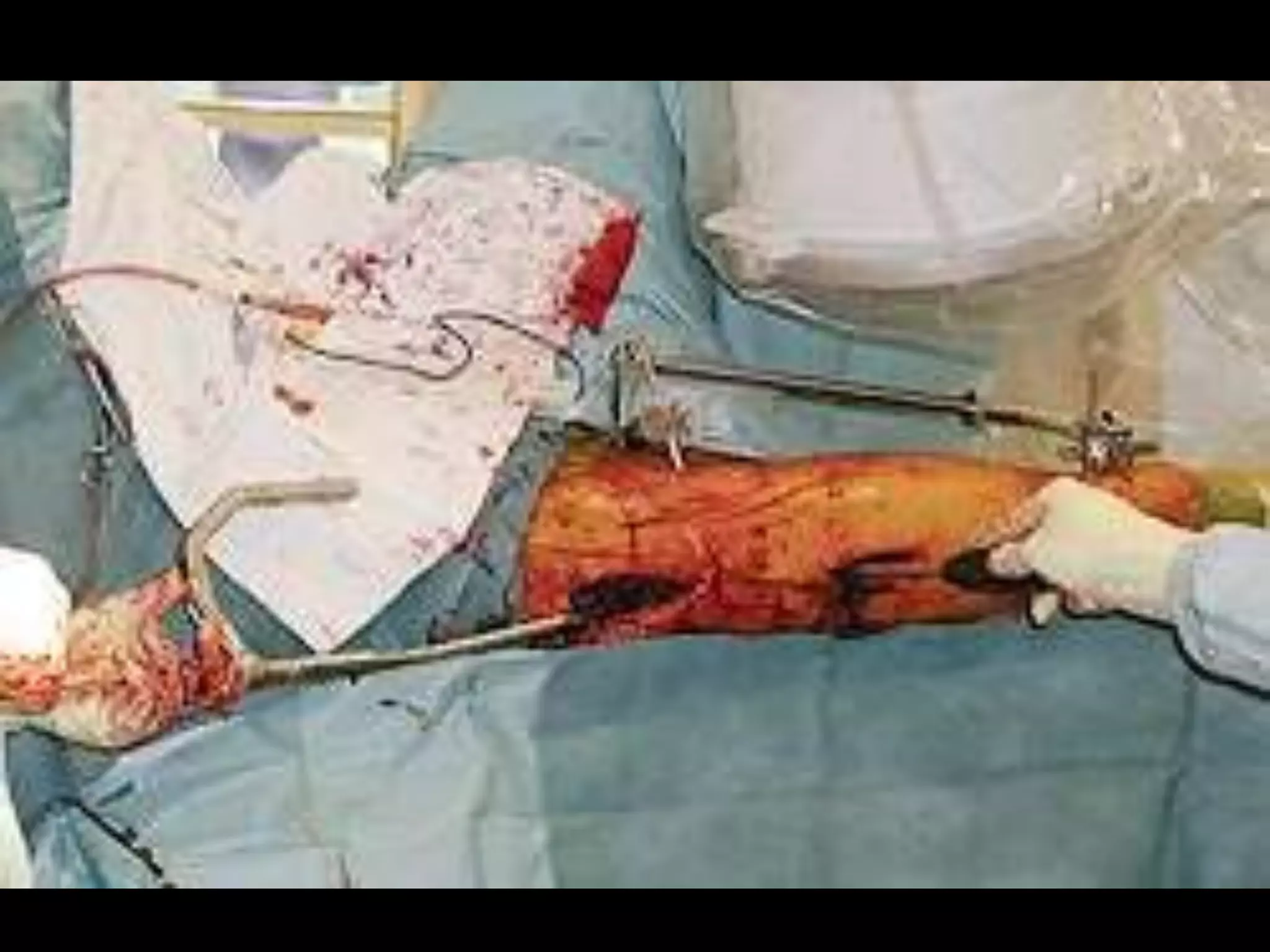
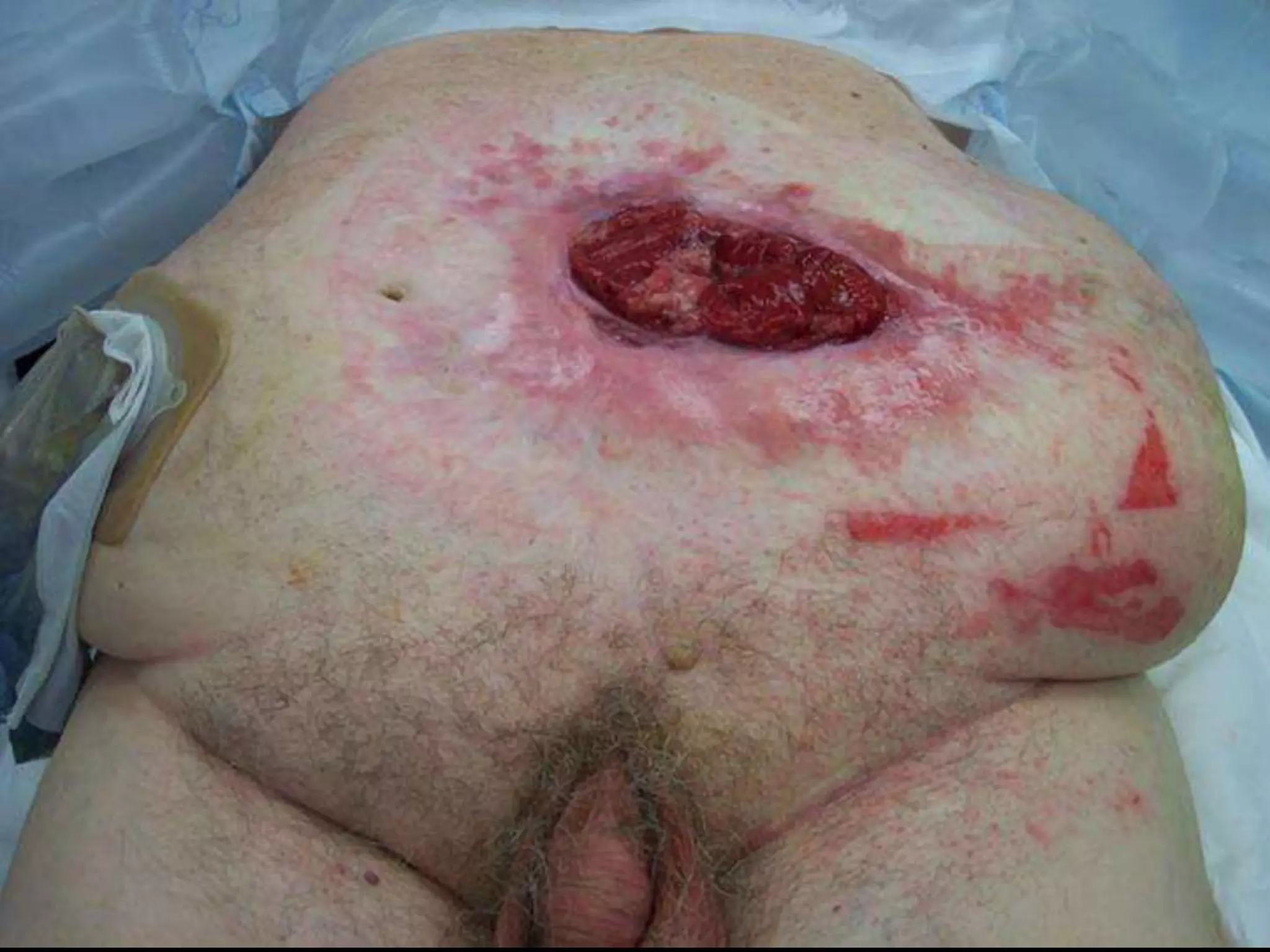
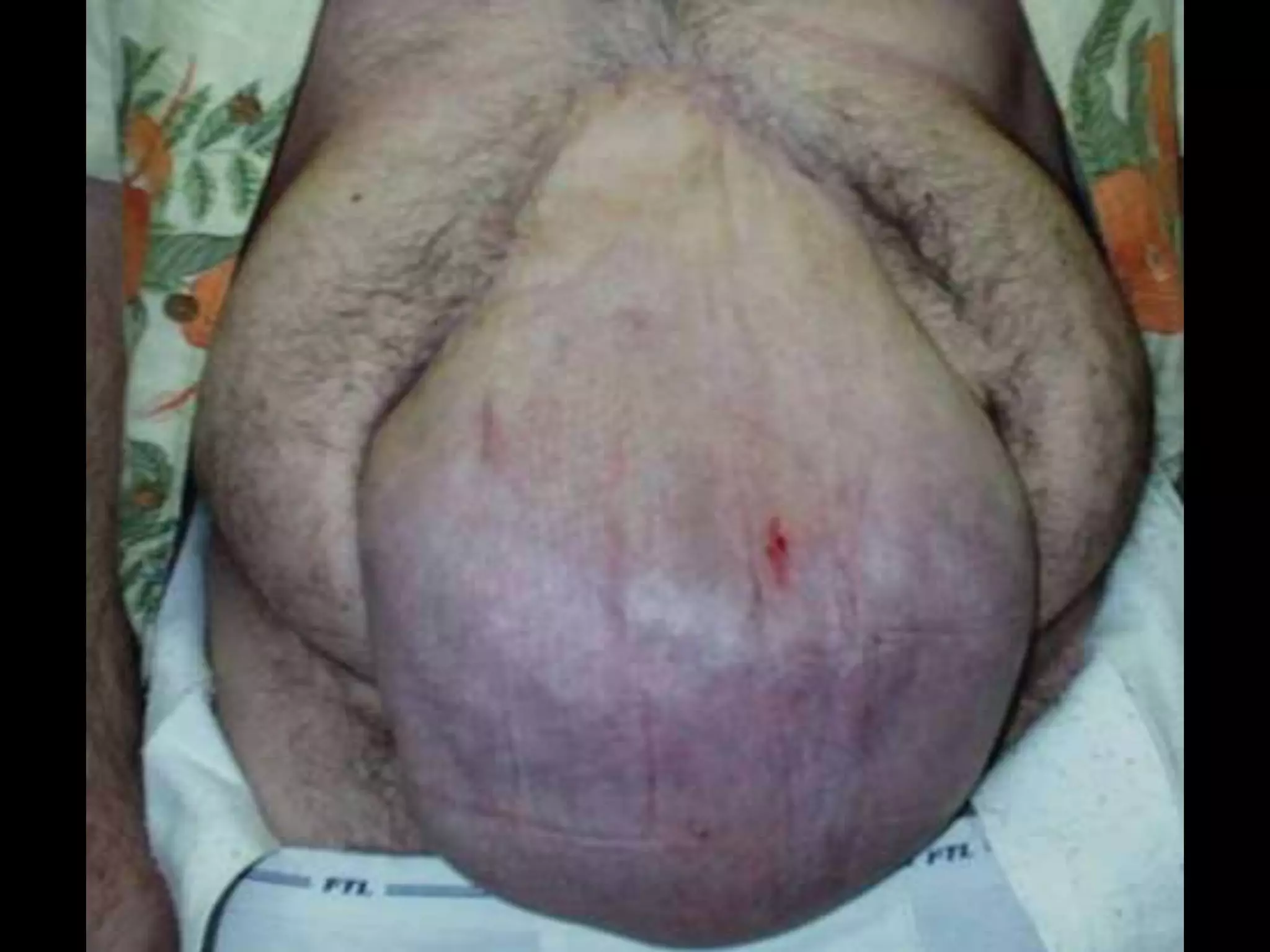
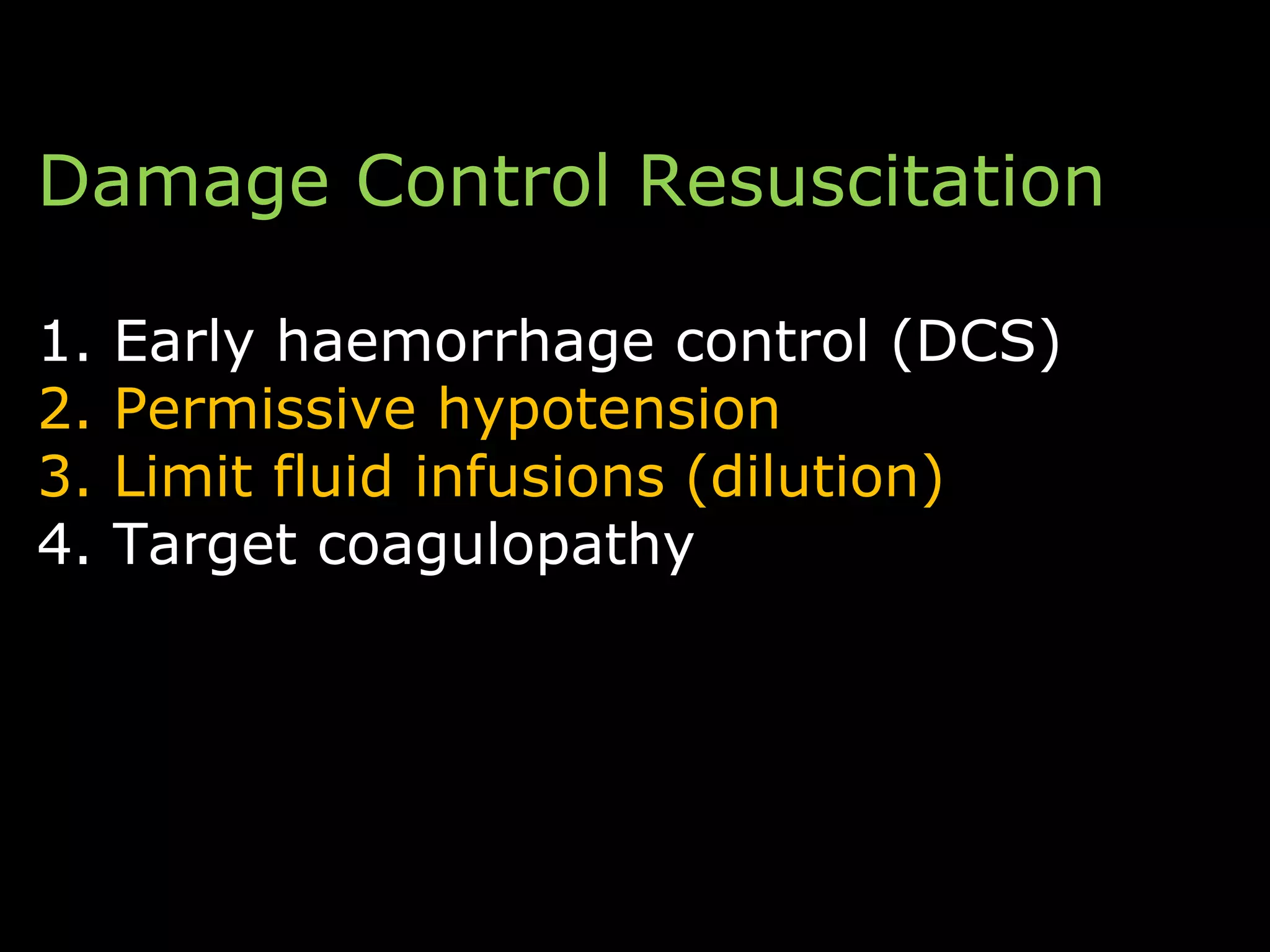
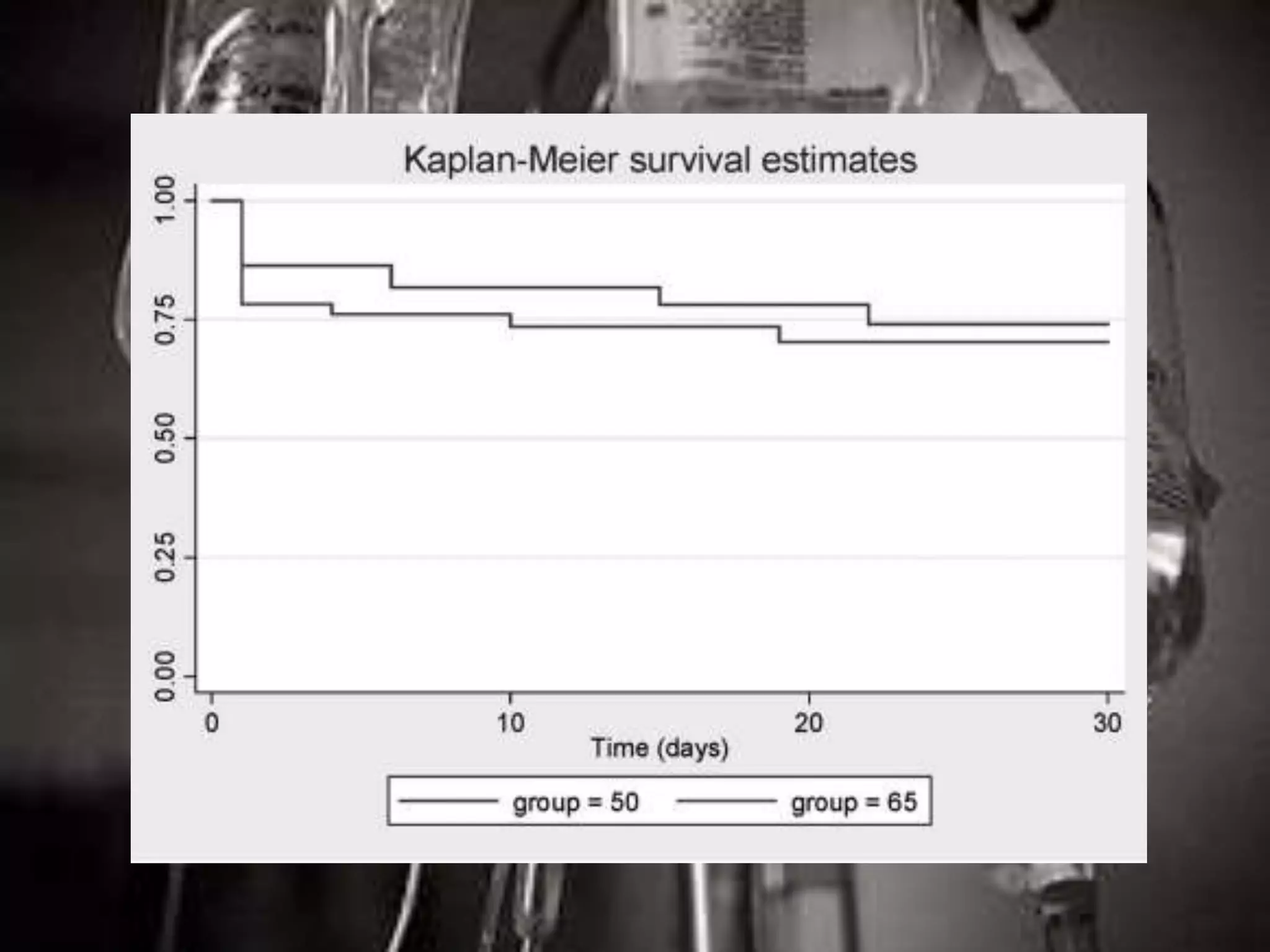
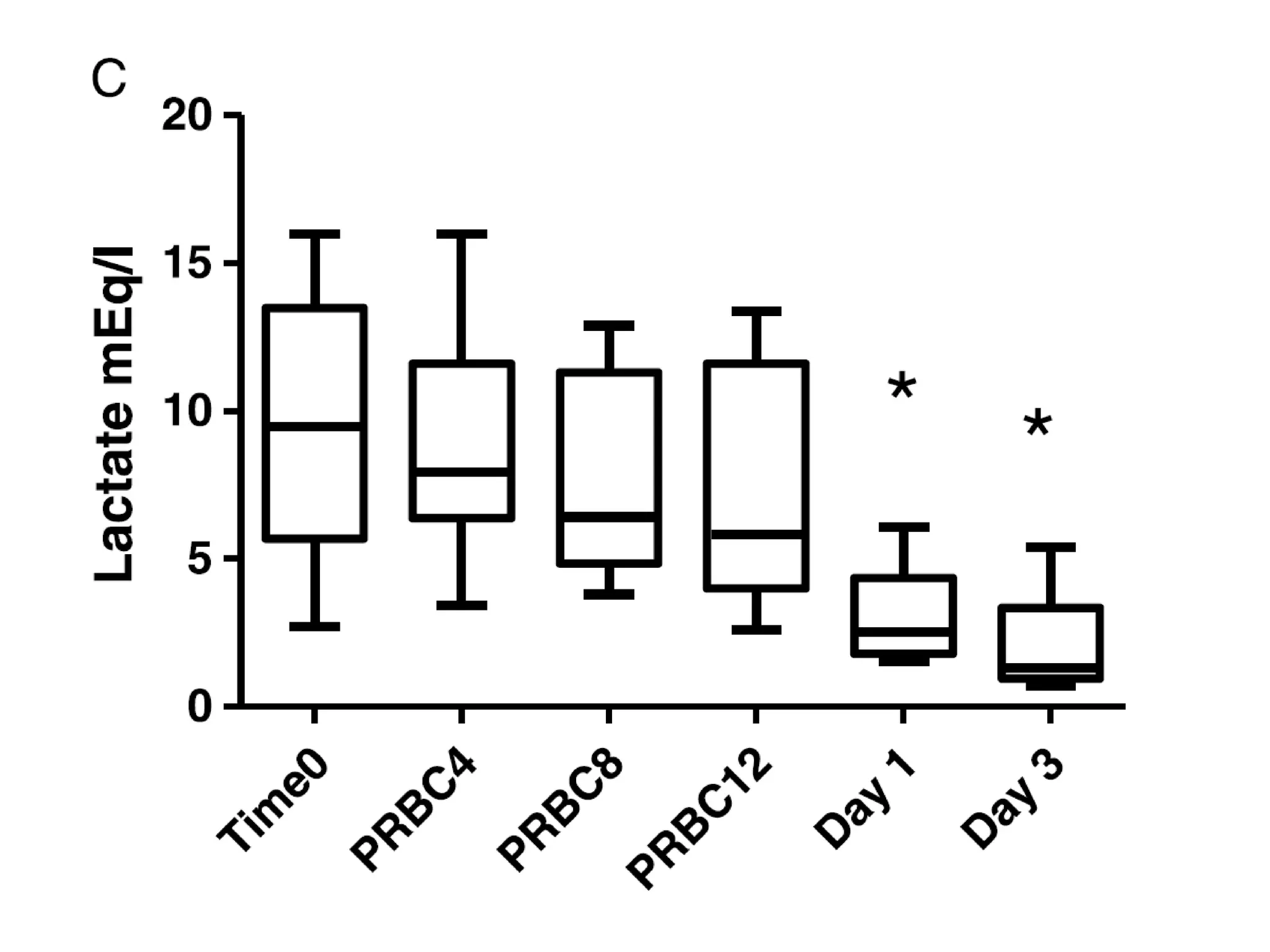
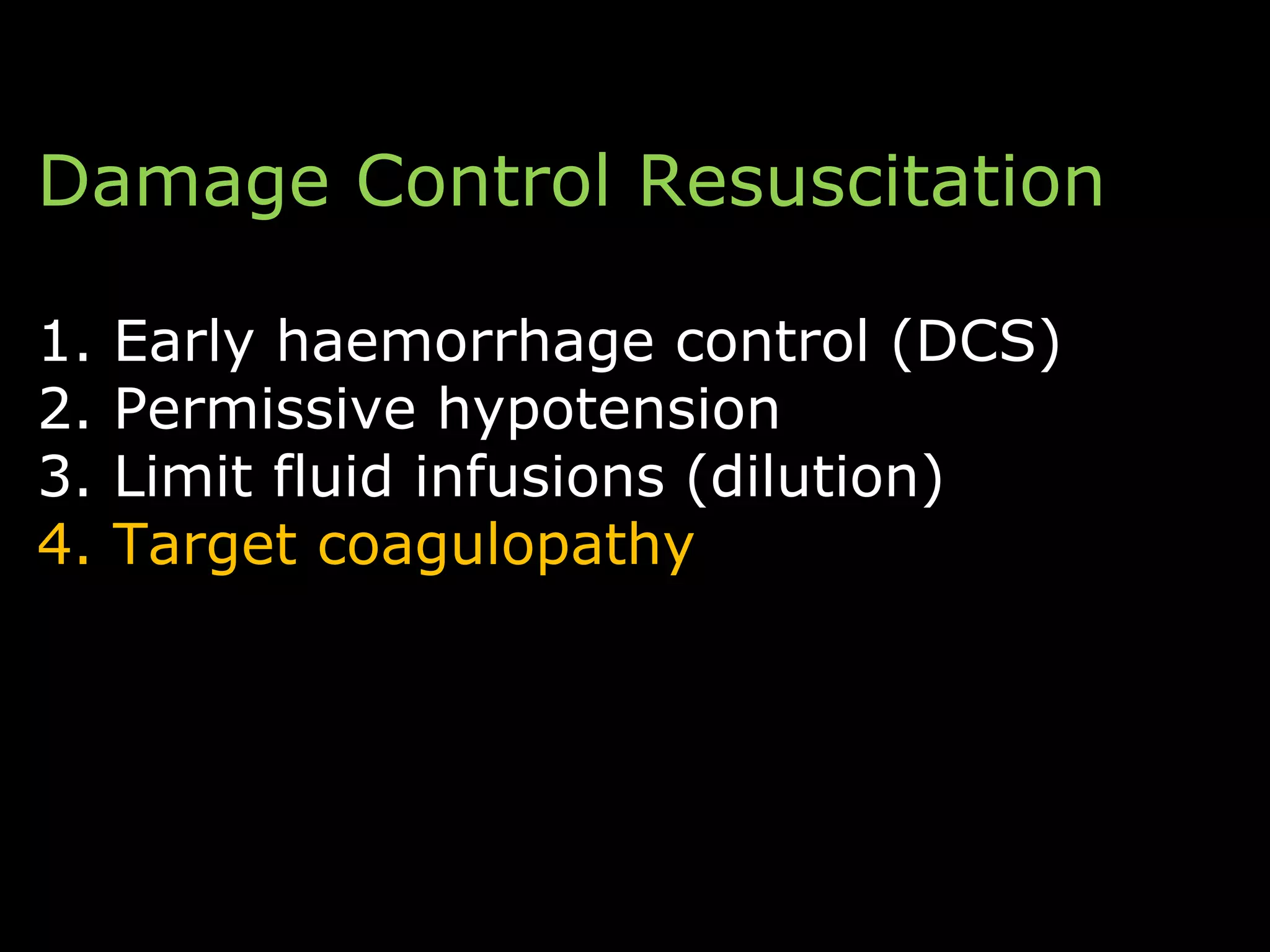
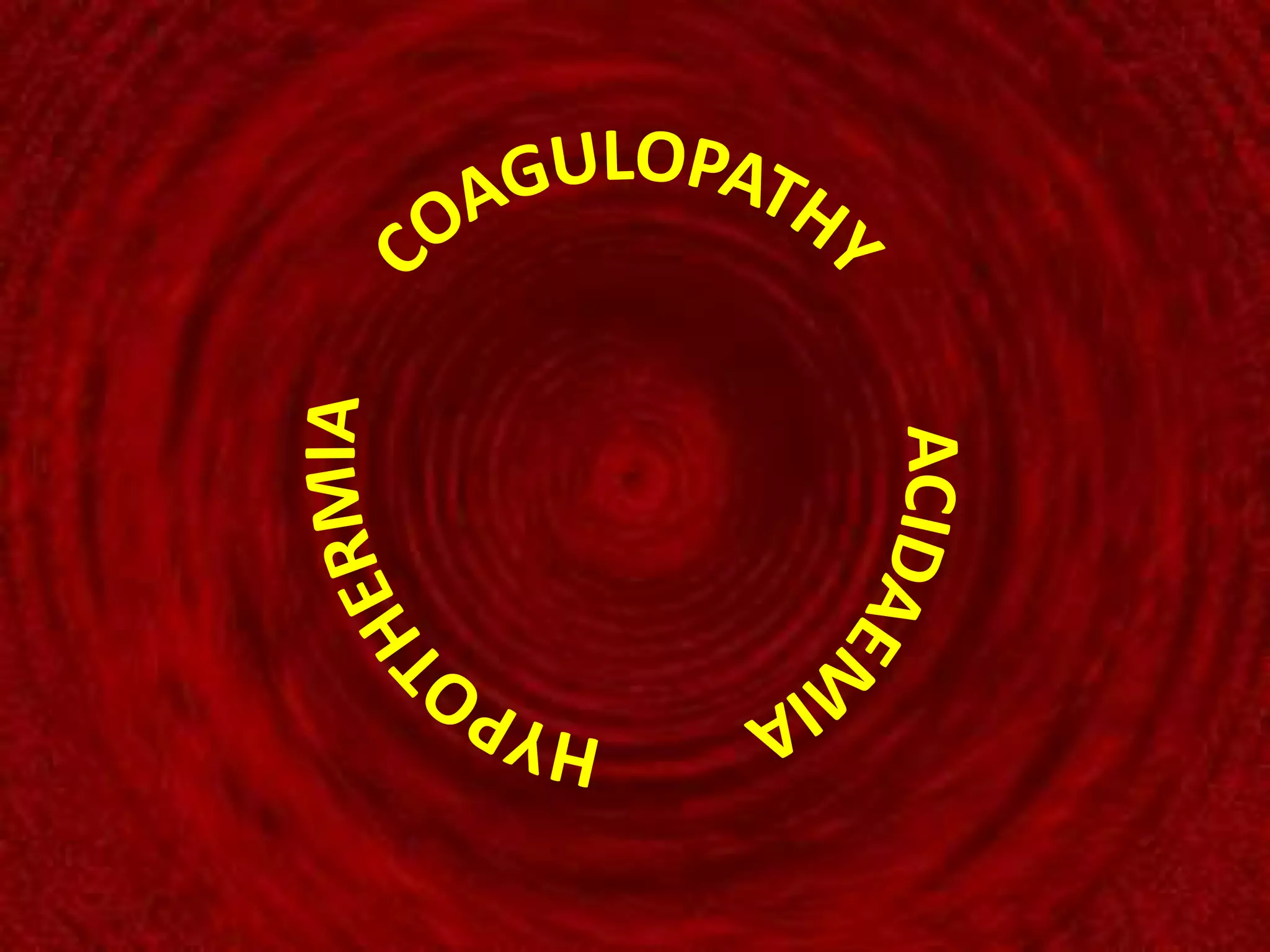
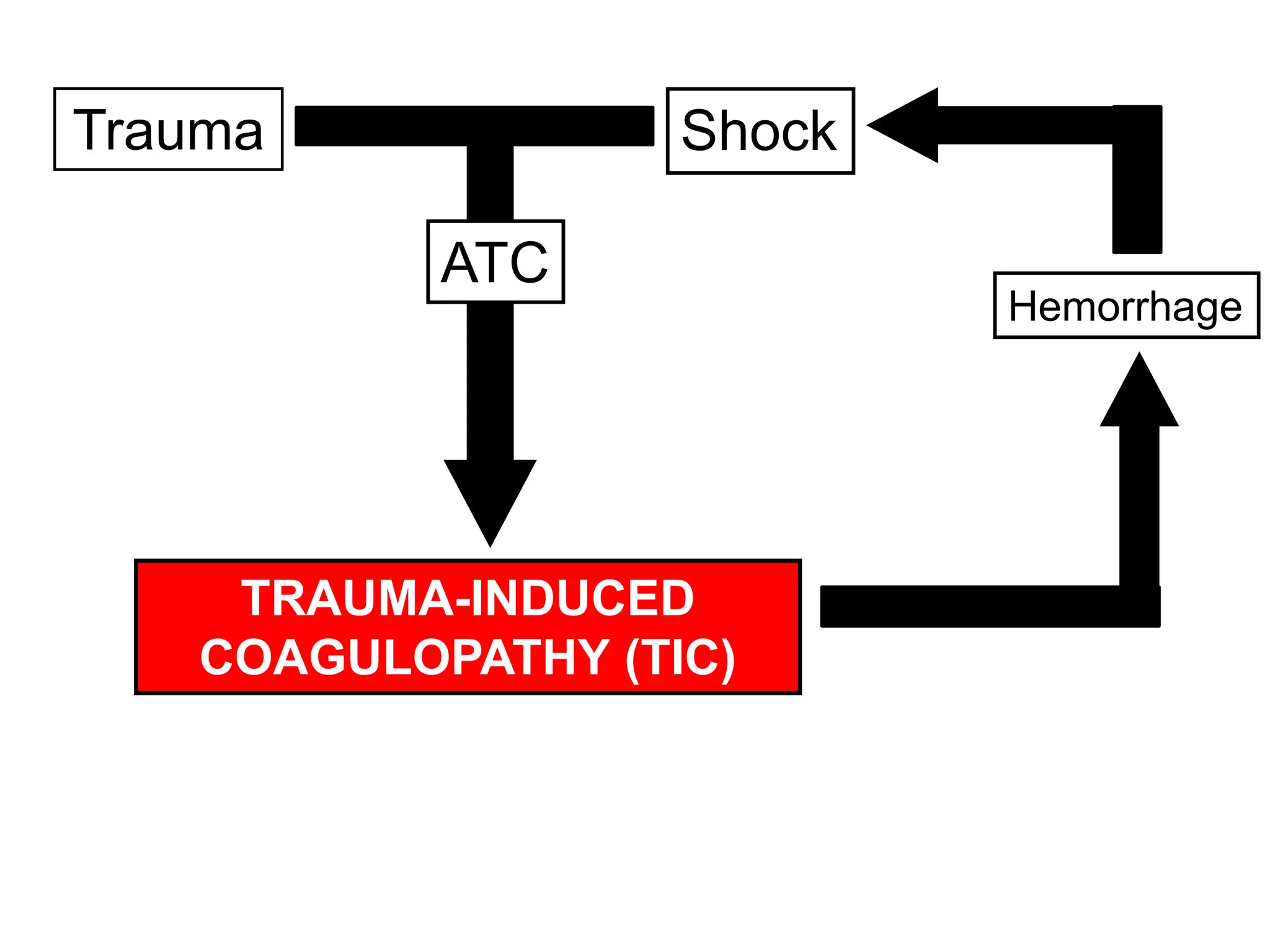
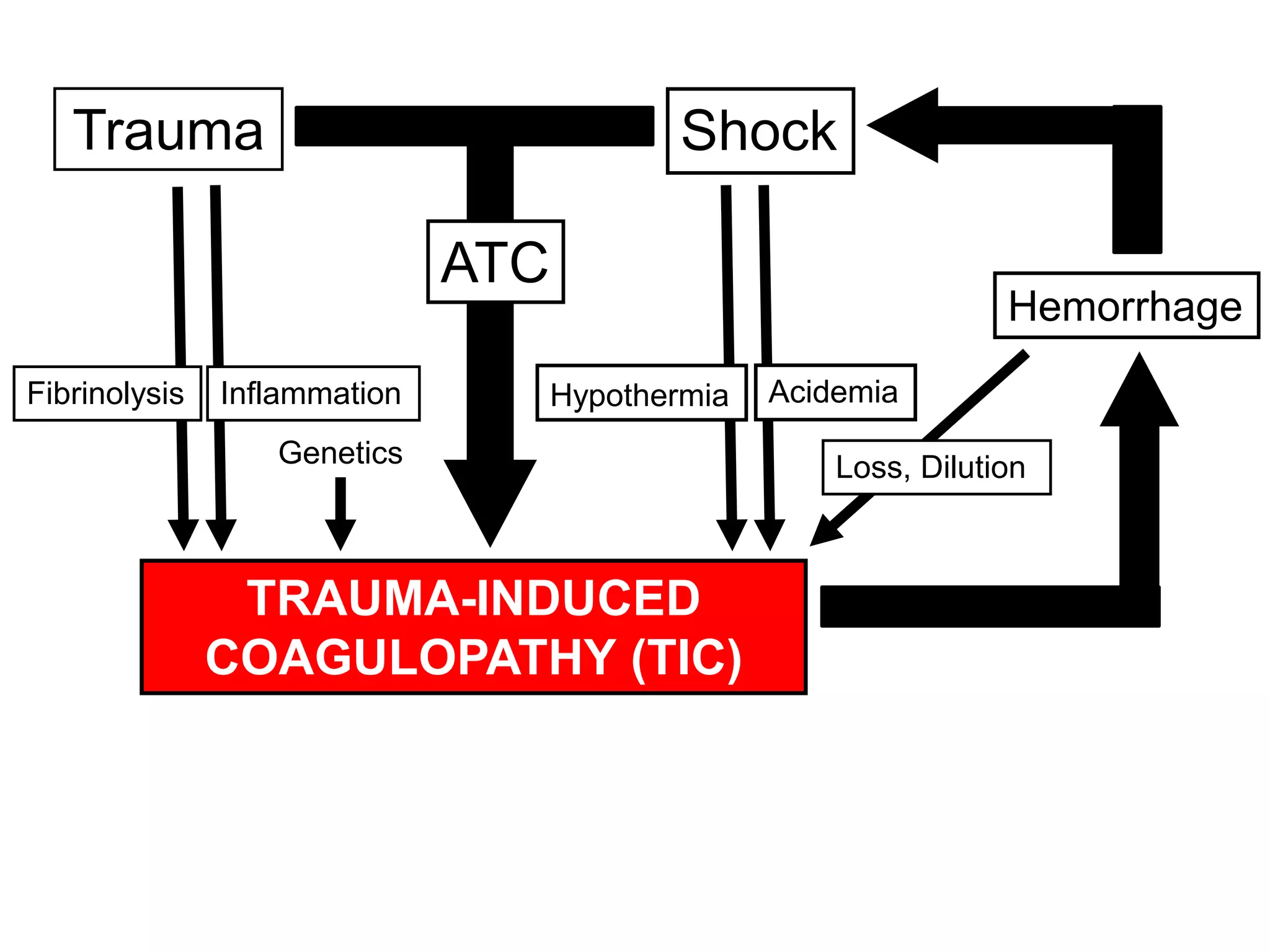
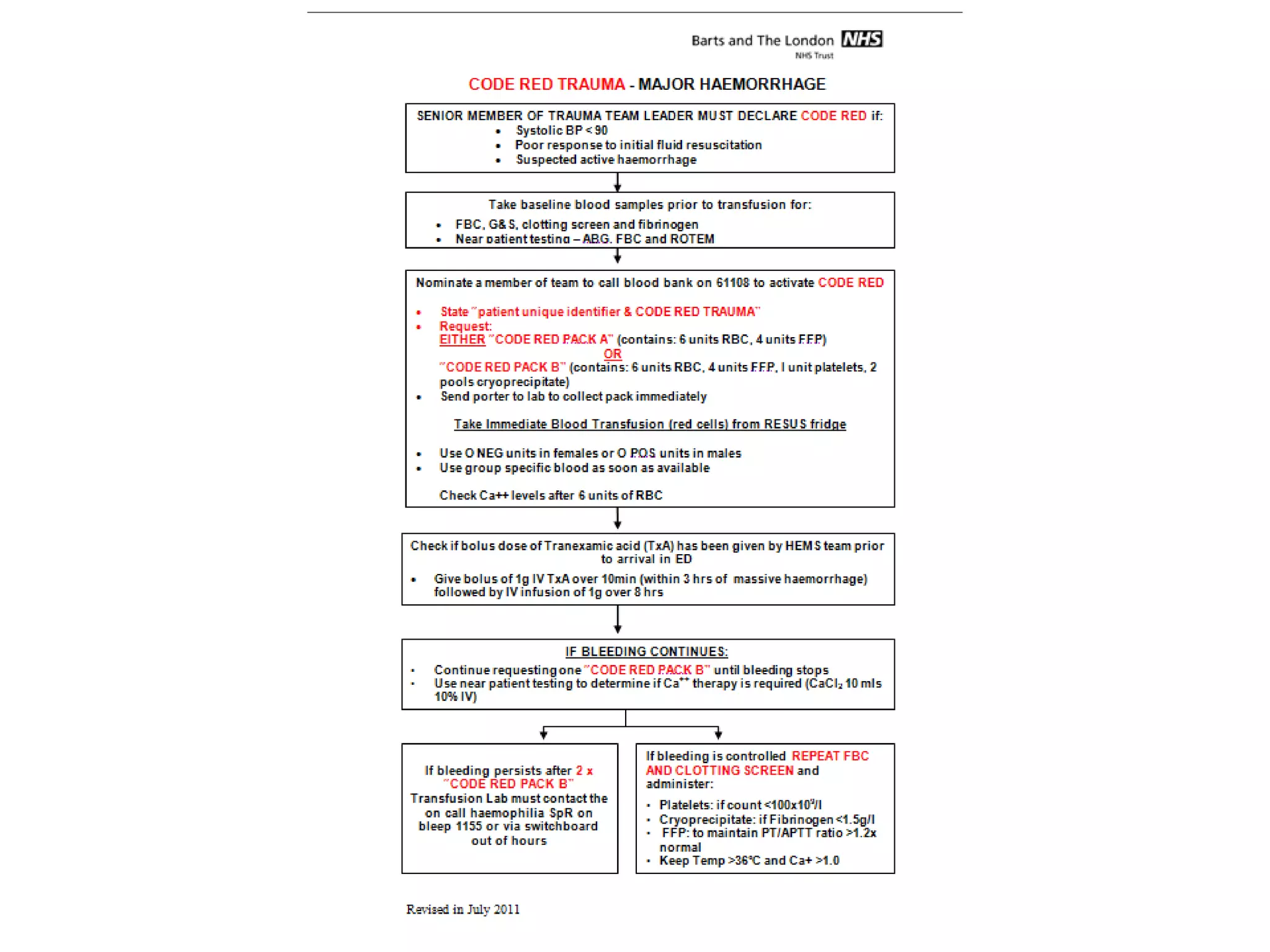
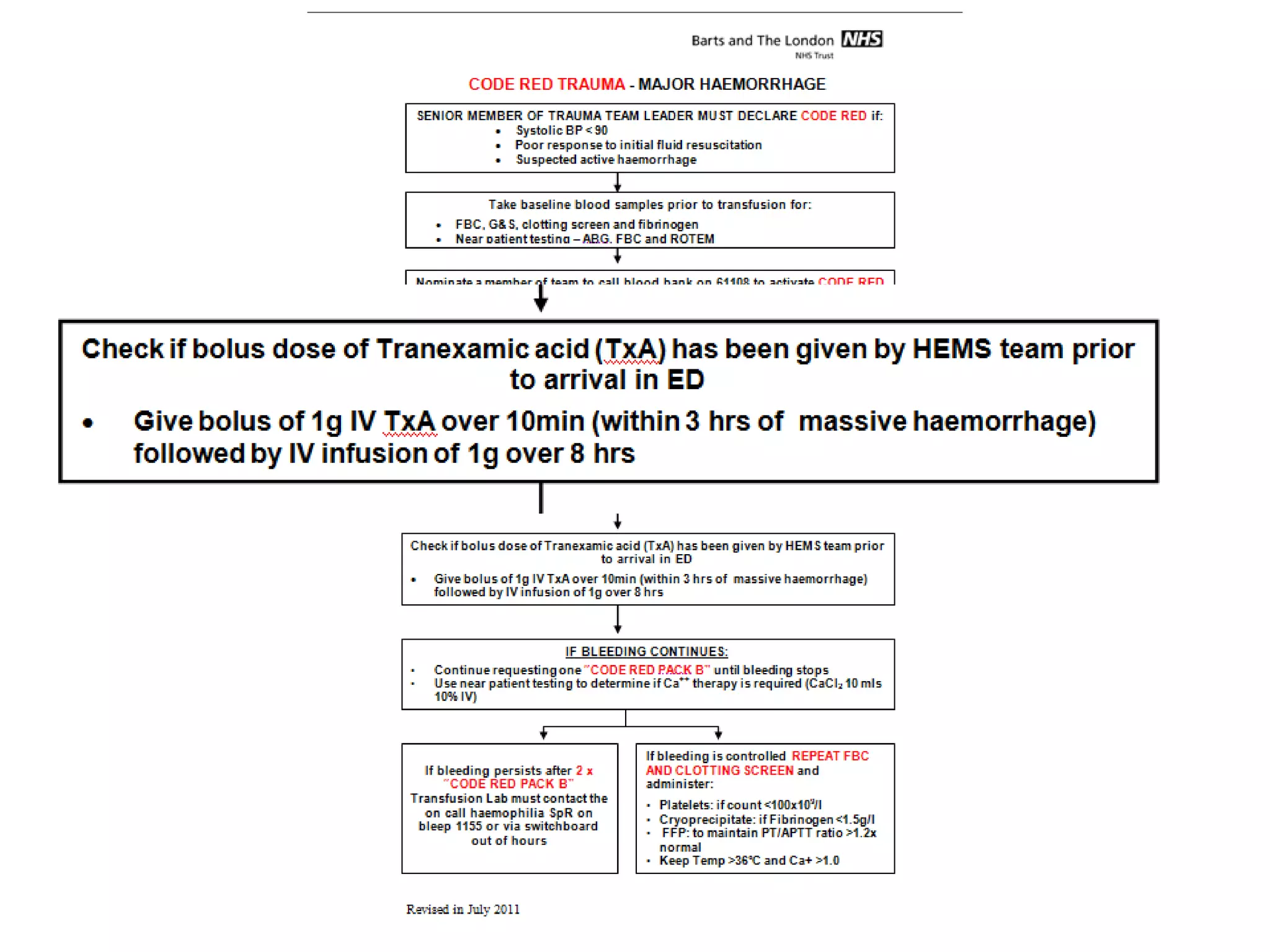
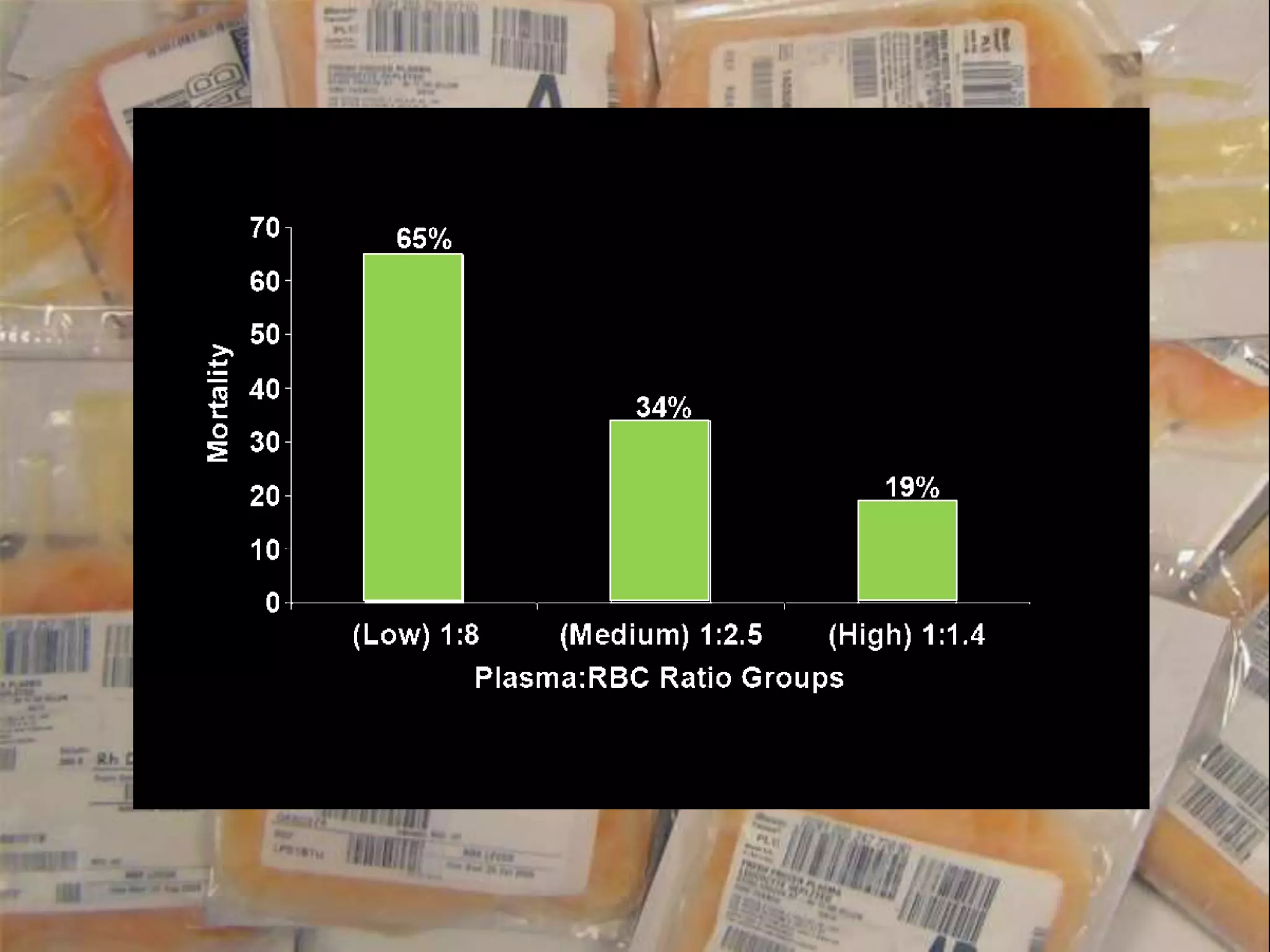
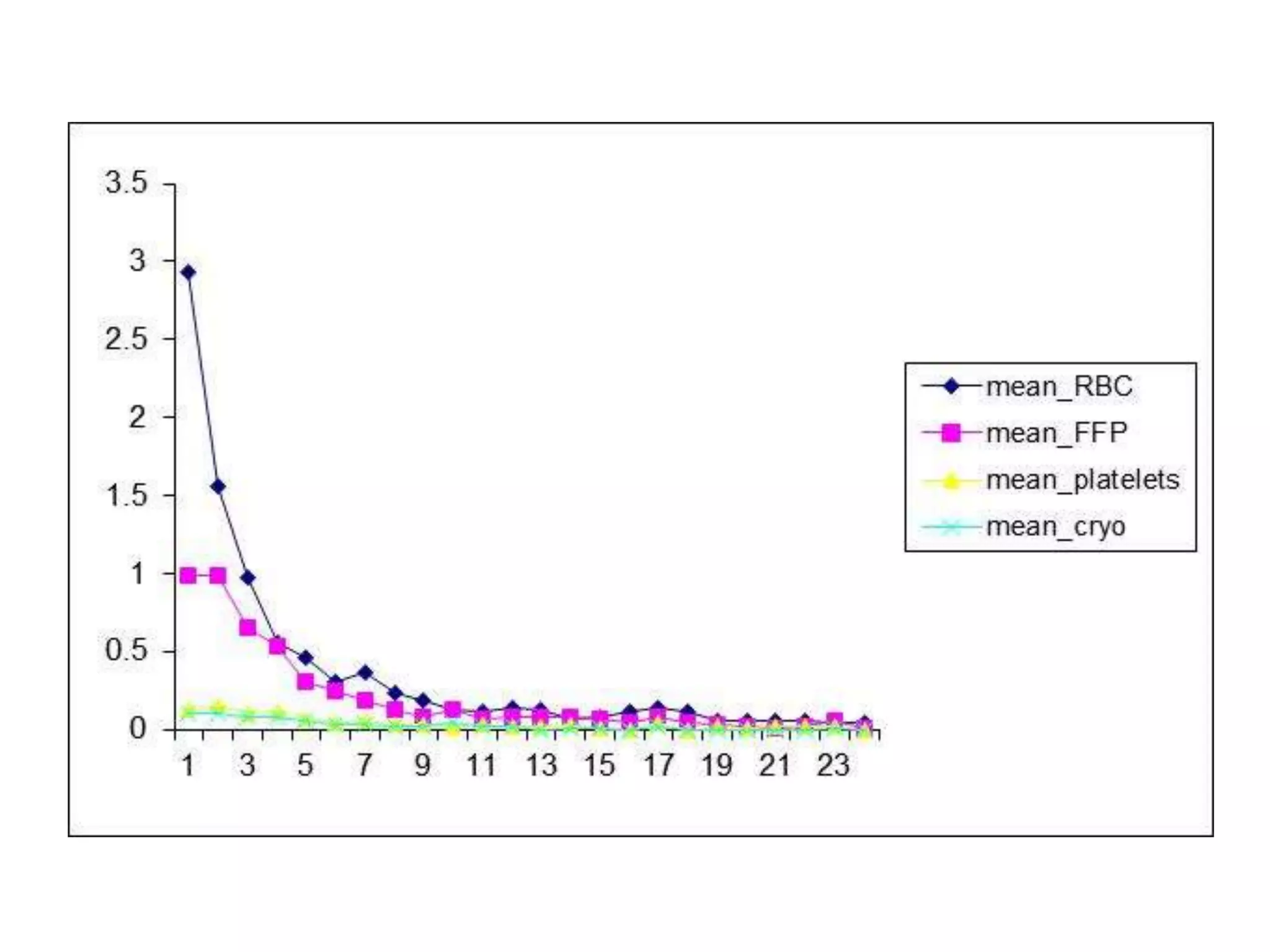
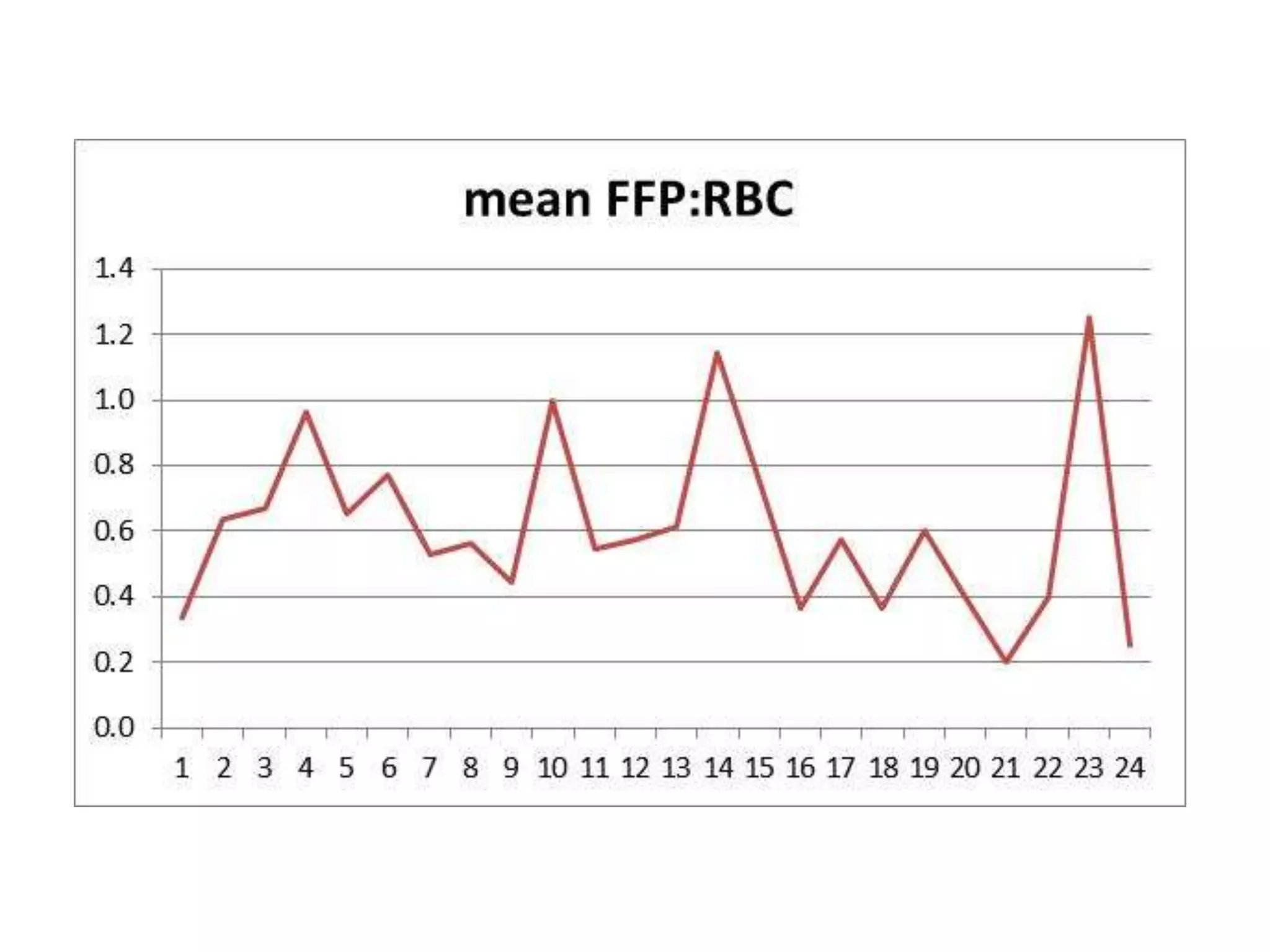
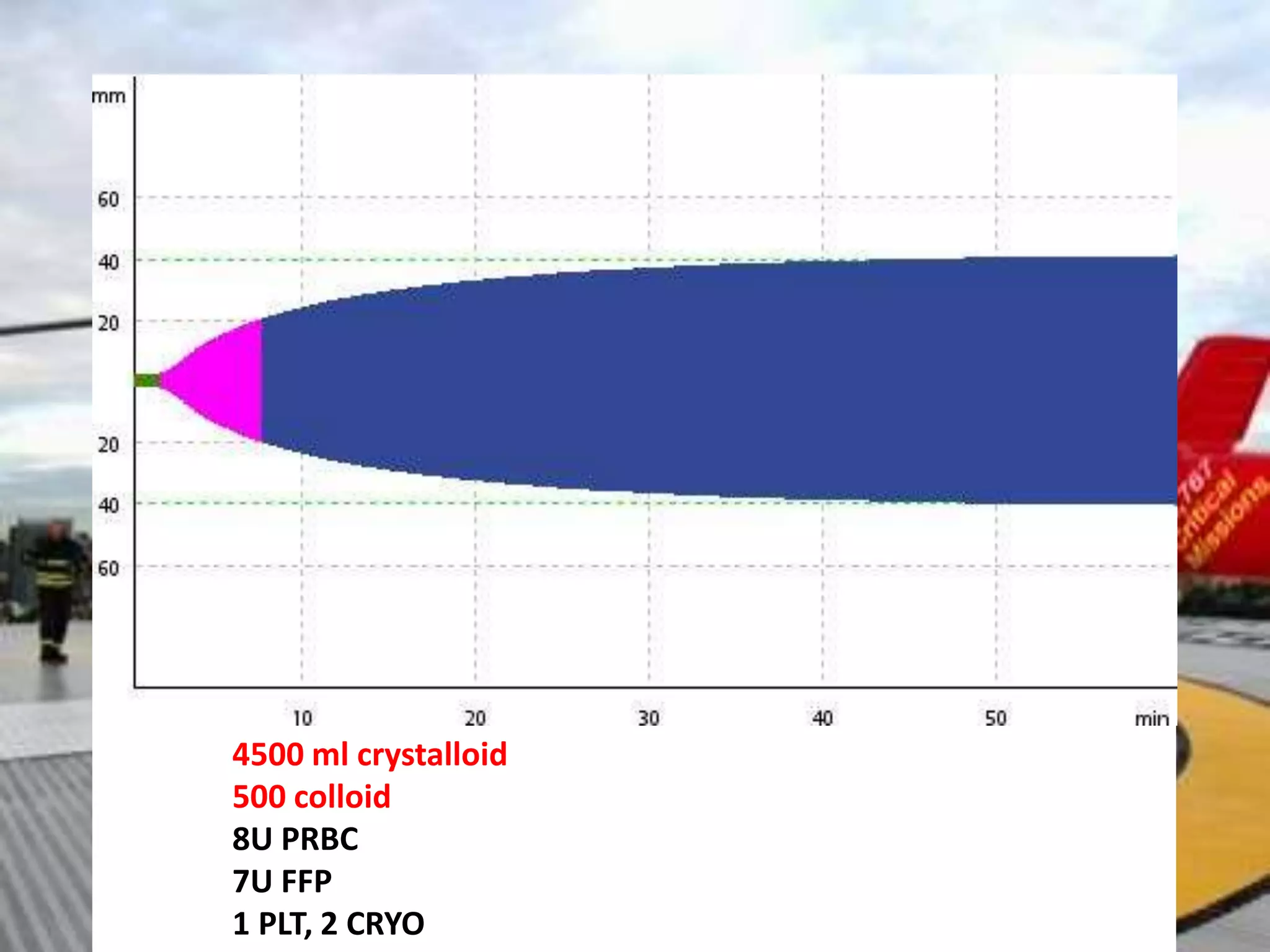
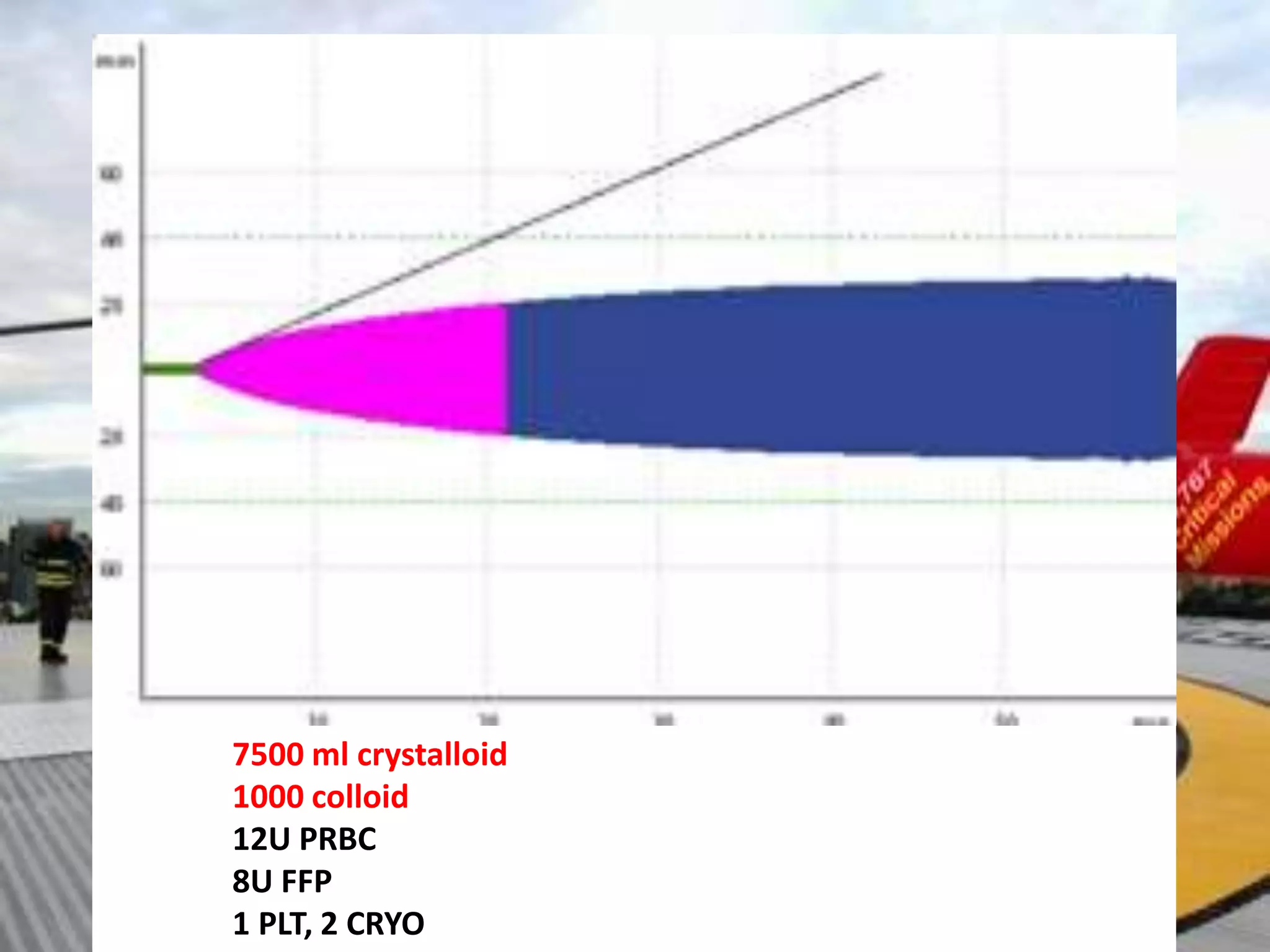
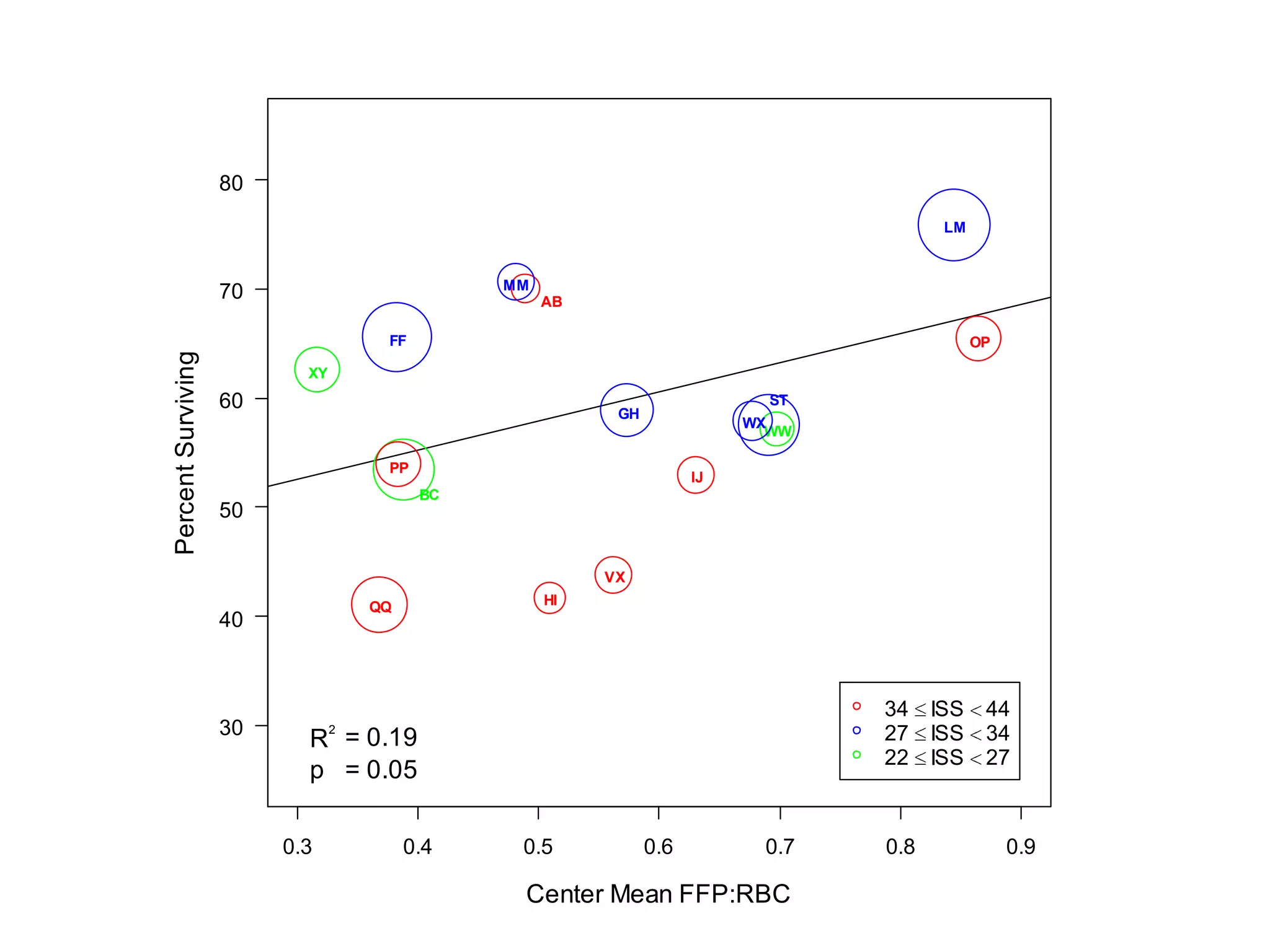
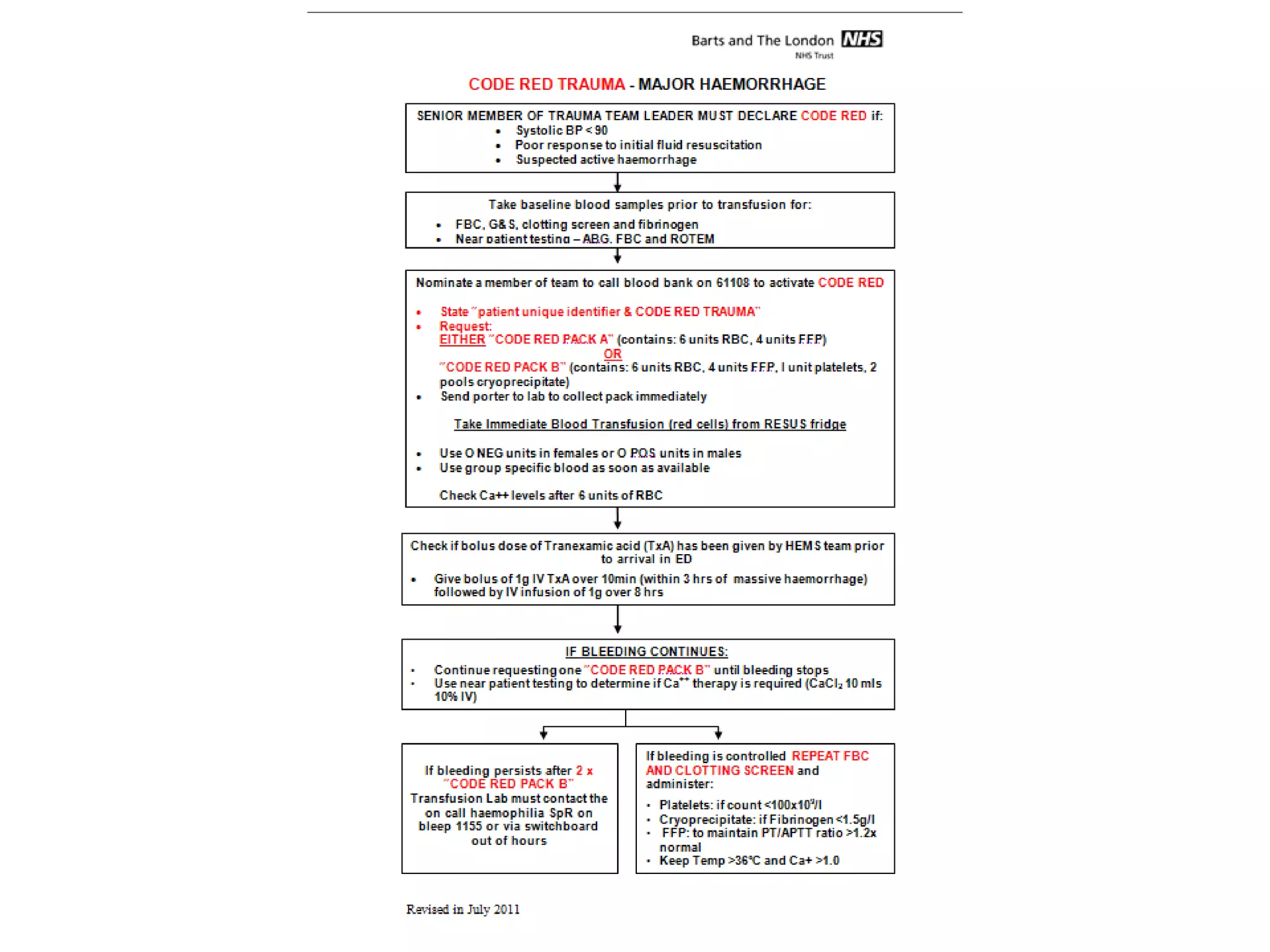
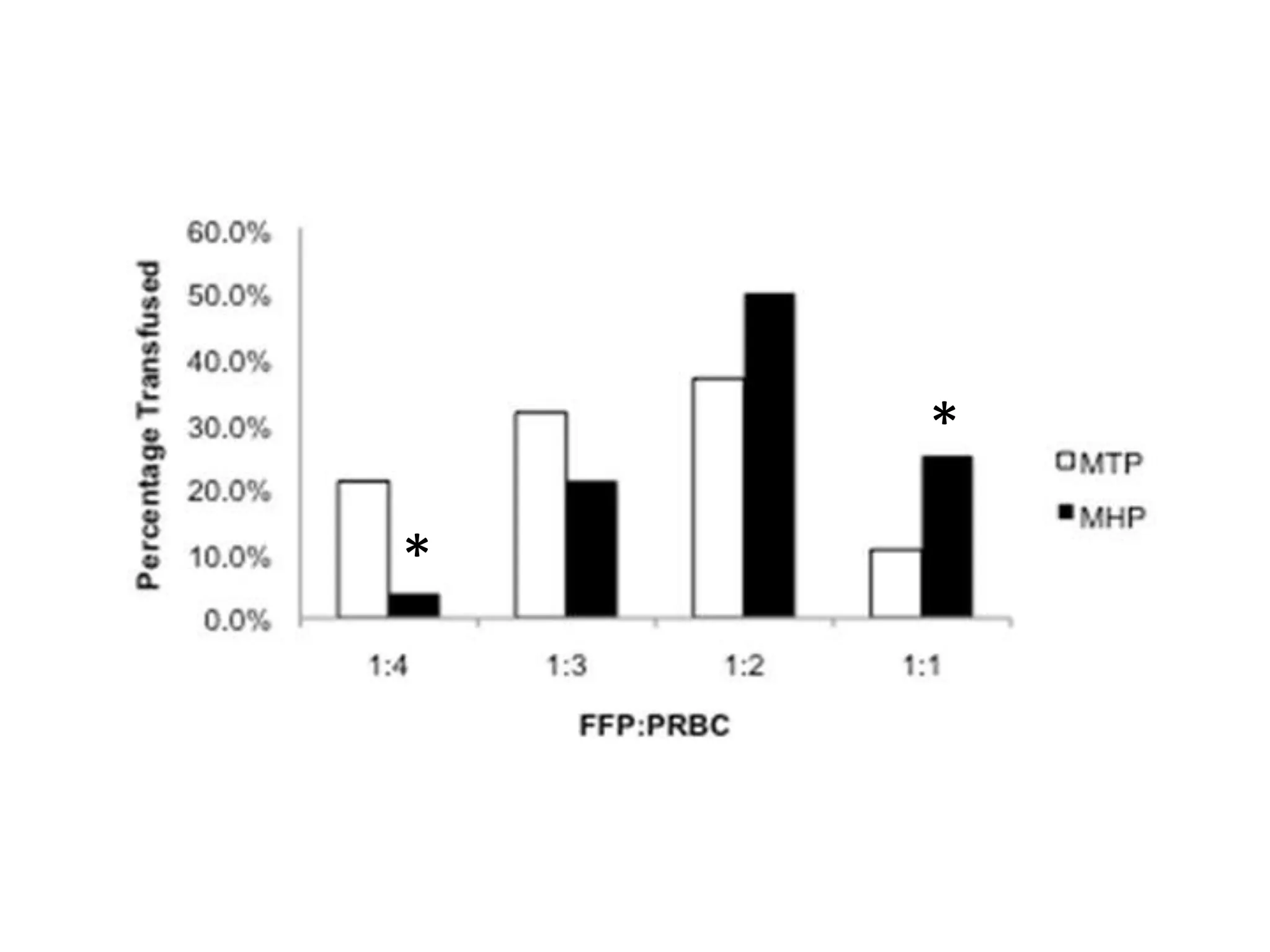
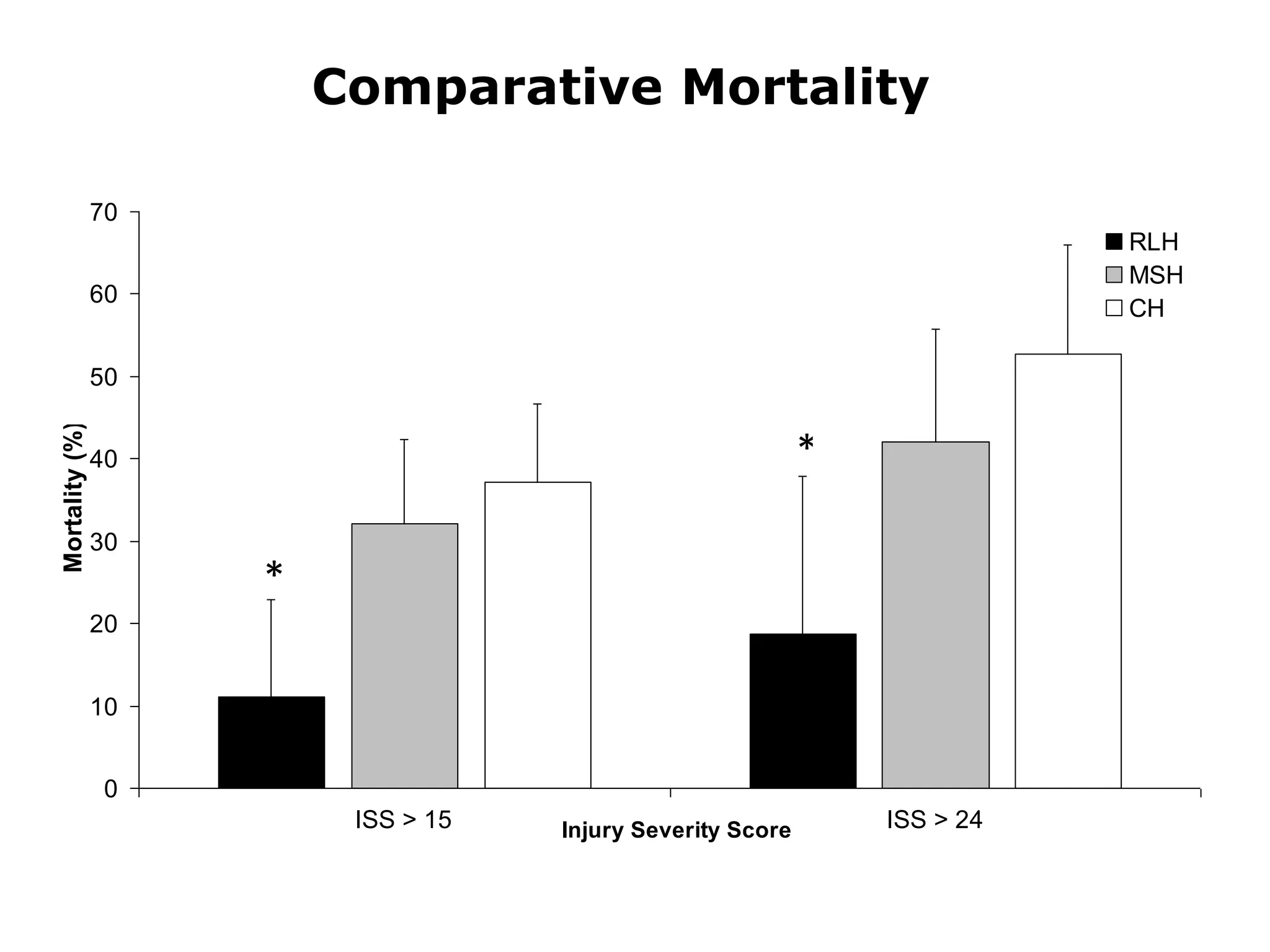
The document discusses damage control resuscitation (DCR) strategies for trauma care, emphasizing early hemorrhage control, permissive hypotension, limited fluid infusions, and targeting coagulopathy to improve survival rates. It highlights that trauma patients are more prone to die from metabolic failure during surgery rather than from incomplete repairs. The data presented suggests a correlation between high injury severity scores and increased mortality rates.