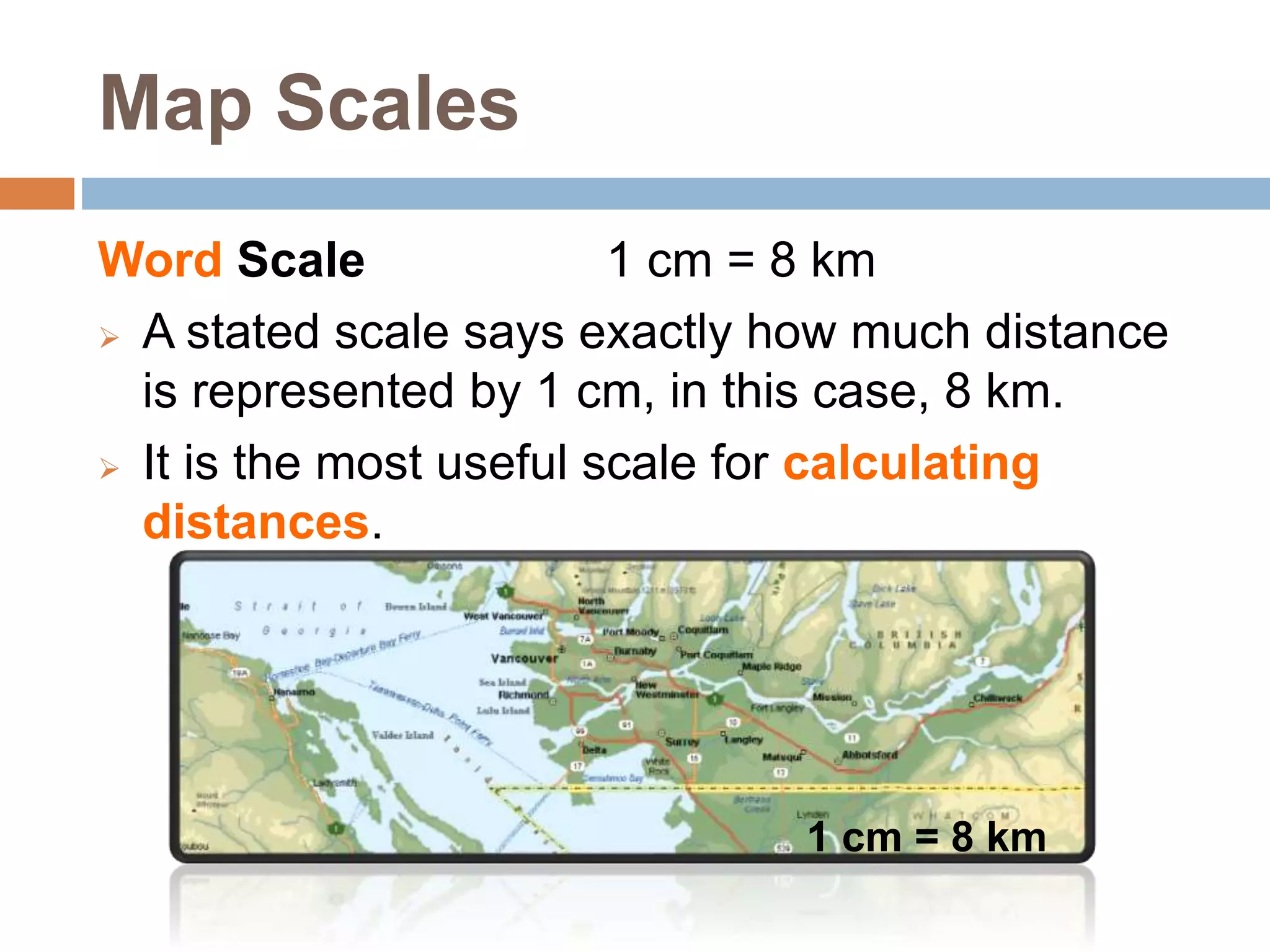
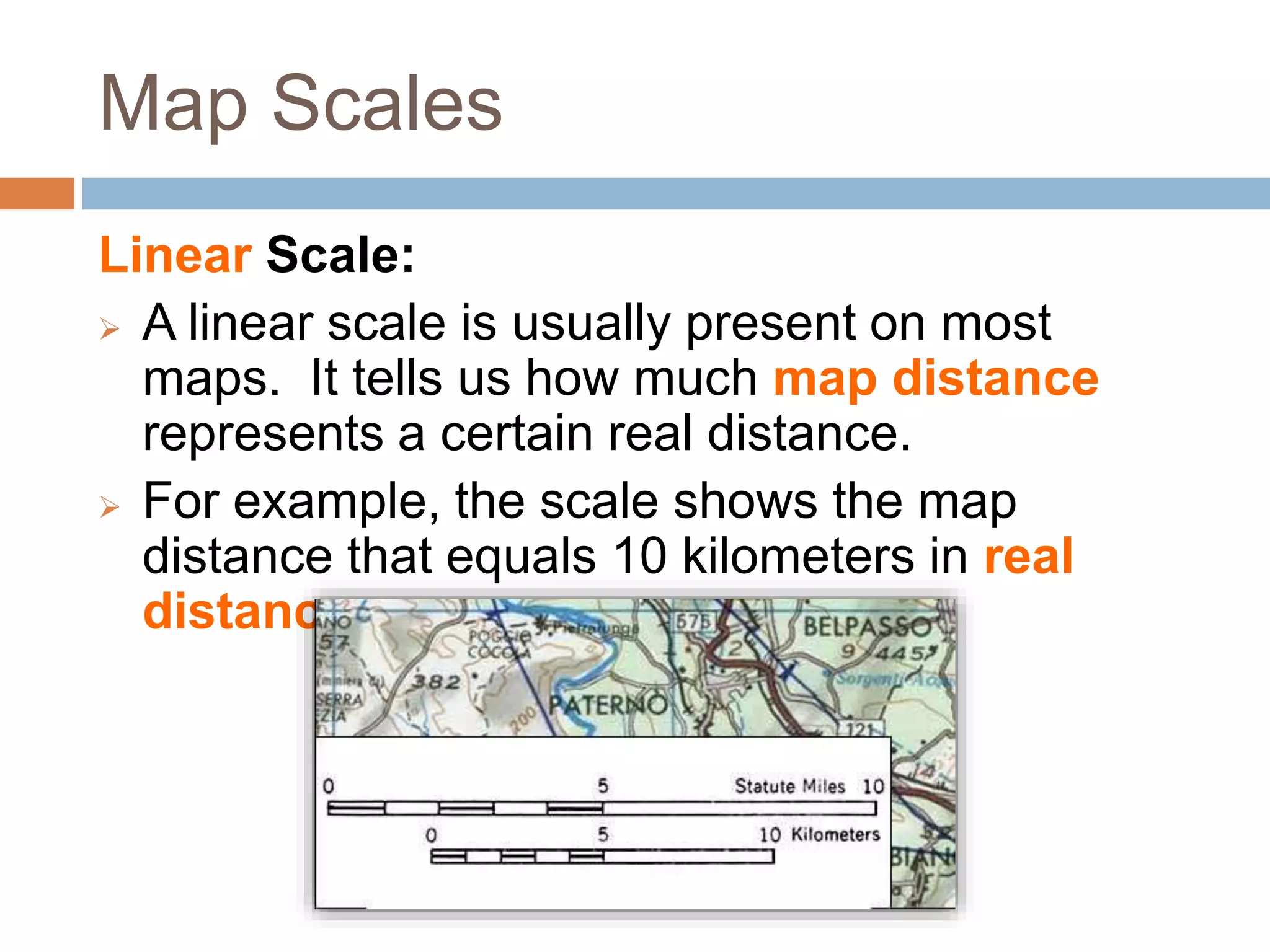
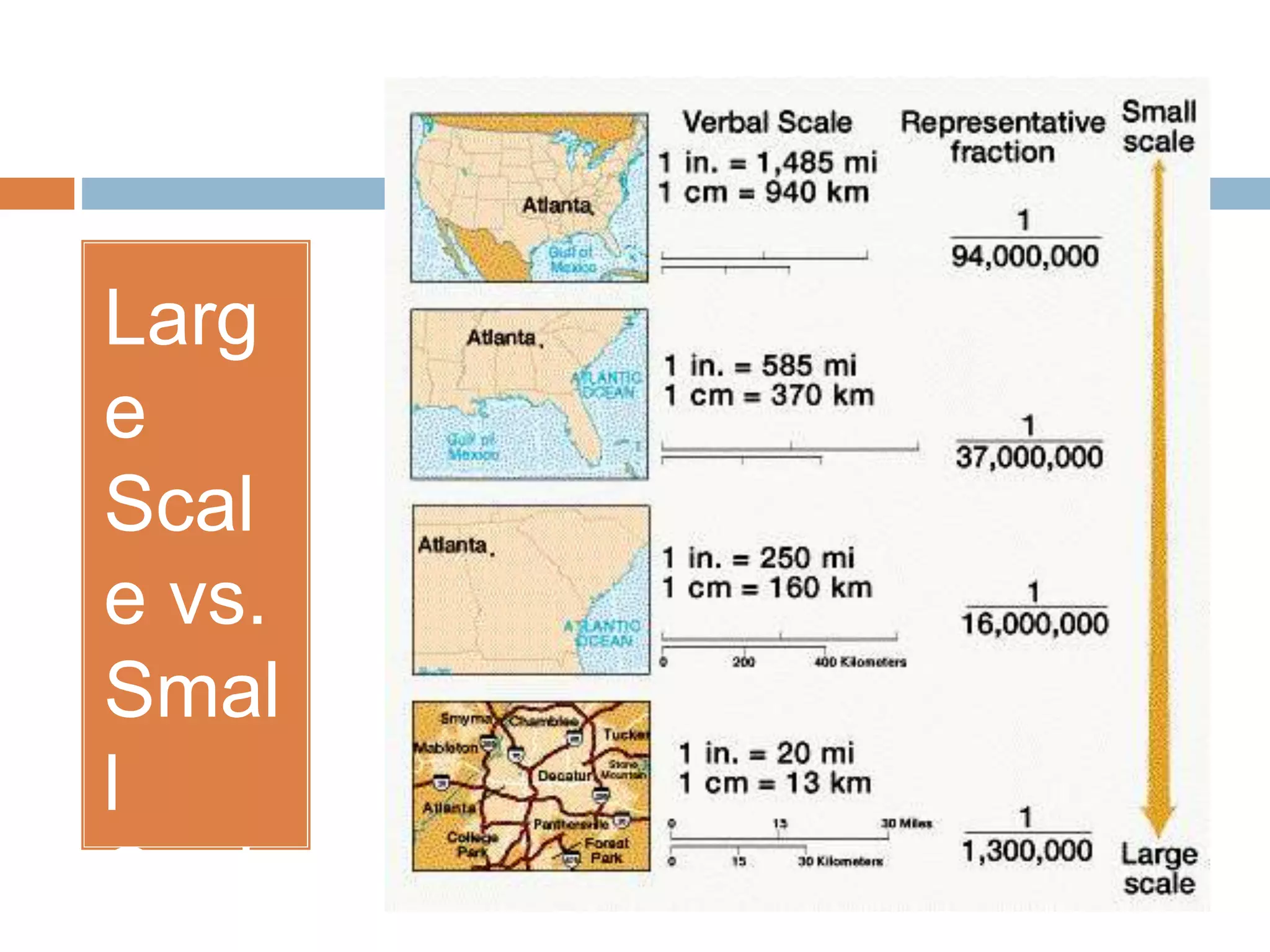
- A map scale indicates the relationship between distances on a map and in real life, allowing for accurate representations though smaller or larger than reality.
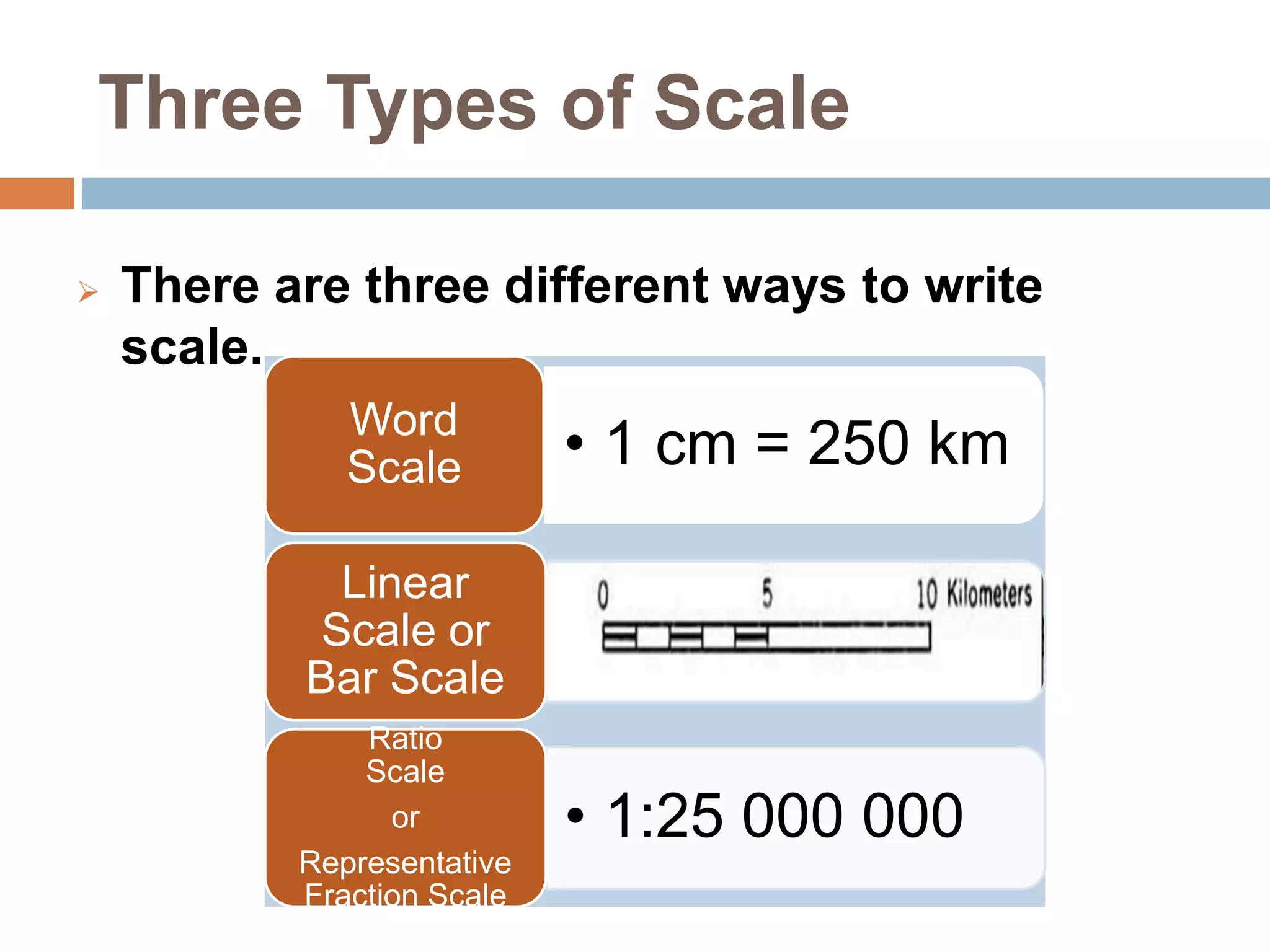
- There are three types of map scales: word scale, linear scale, and ratio scale. A word scale states the distance represented by 1 cm, a linear scale graphically shows a distance, and a ratio scale compares map units to real-world units.
- Ratio scales can be difficult to comprehend, so they are often converted to a word scale using a system like metrics. For example, 1:25,000,000 could be changed to 1 cm = 250 km.
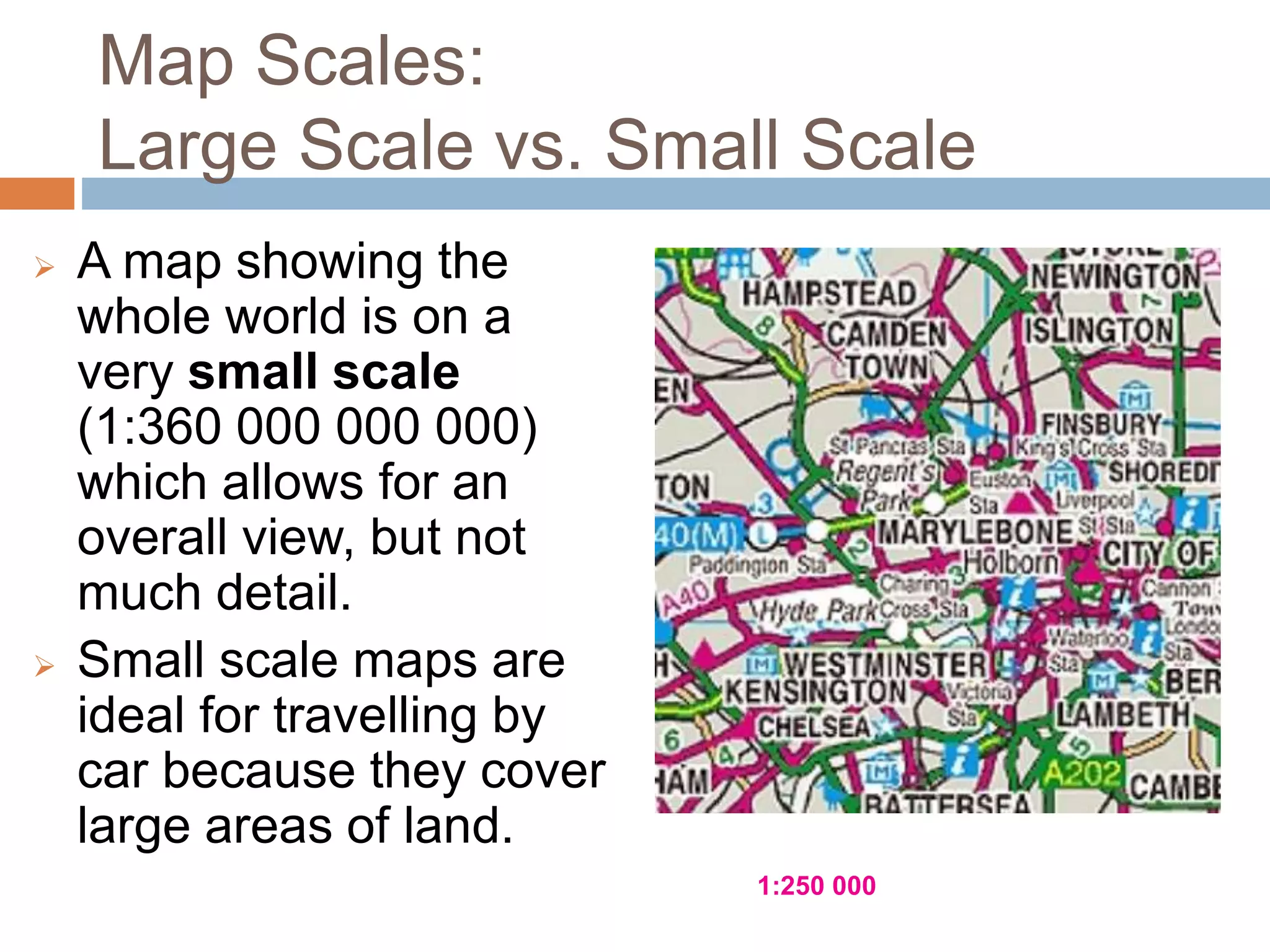
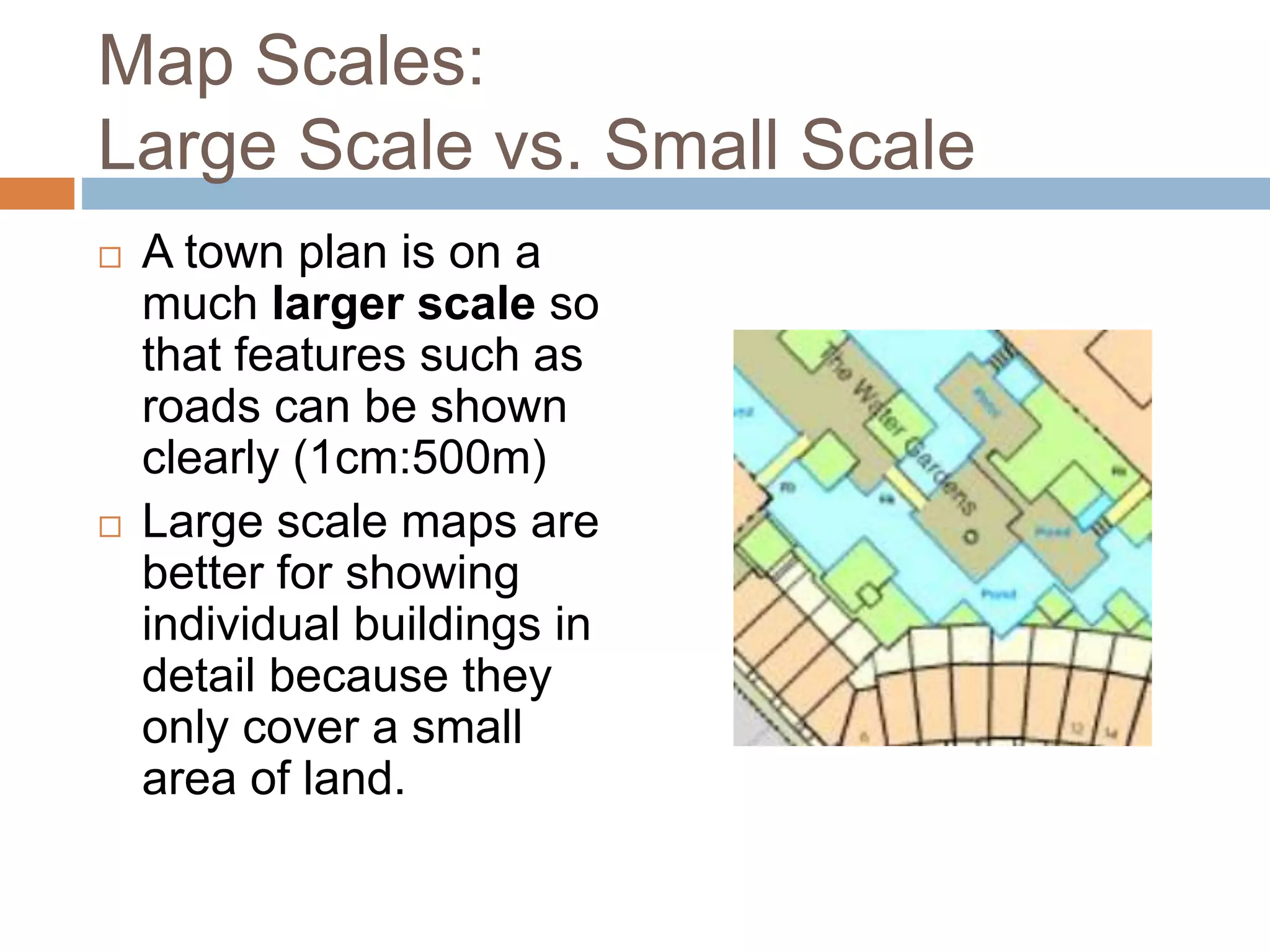
- Maps are categorized as large or small scale depending on the level of detail. Small scale