Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times





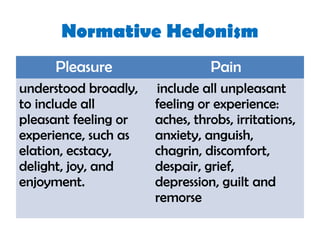



Hedonism is the belief that pleasure is the most important thing in life. There are two main types of hedonism - psychological hedonism and ethical hedonism. Psychological hedonism claims that pleasure and pain alone motivate us or determine what is valuable. Ethical hedonism holds that our fundamental moral duty is to maximize pleasure and happiness, as advocated by Epicurus who taught that all actions should aim to minimize pain and maximize pleasure.







