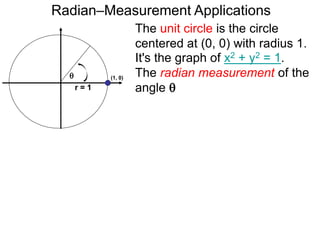
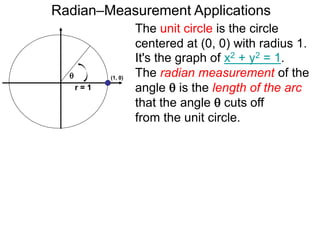
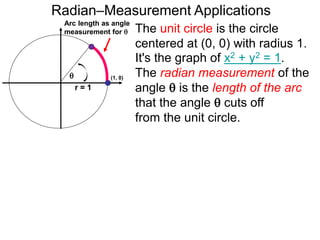
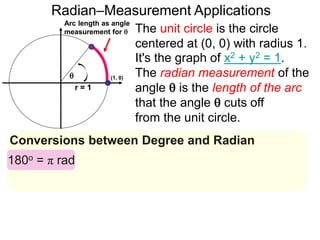
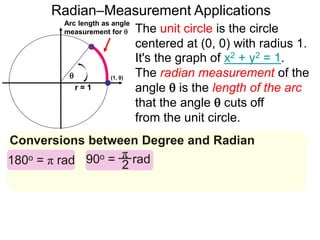
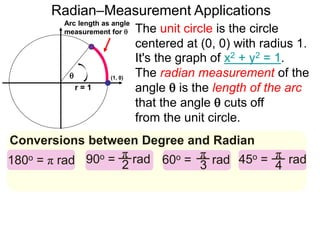
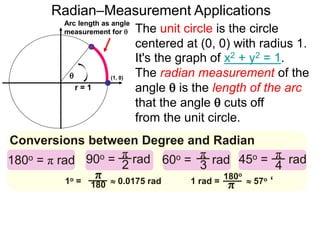
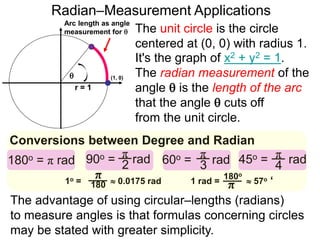
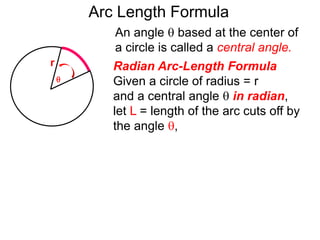
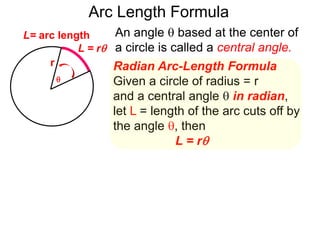
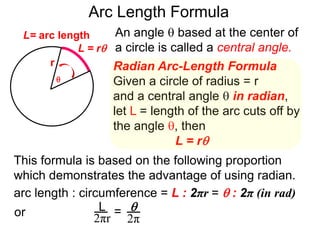
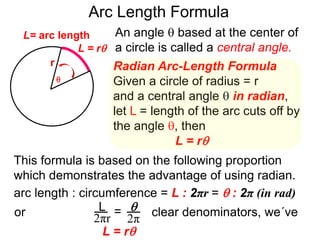
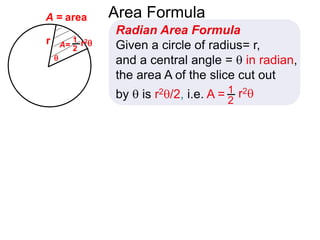
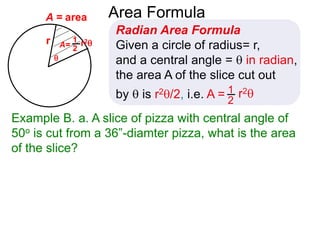
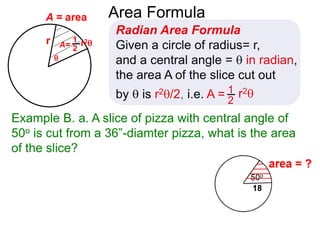
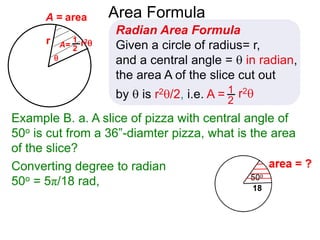
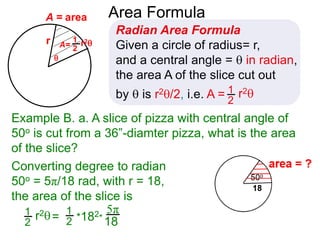
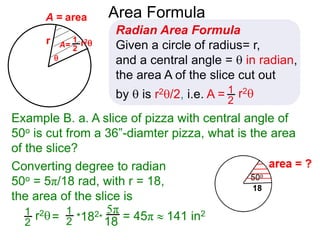
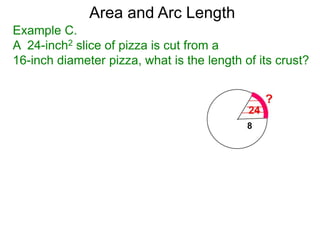
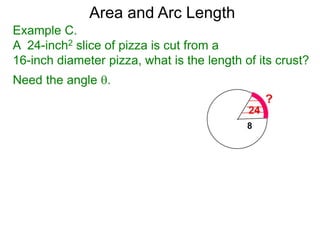
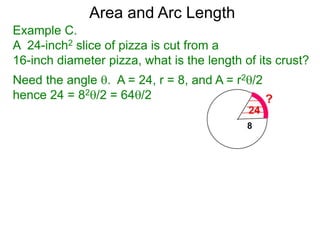
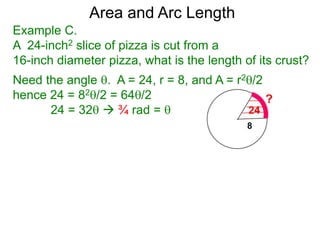
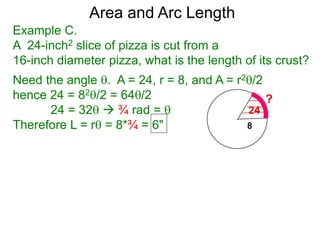
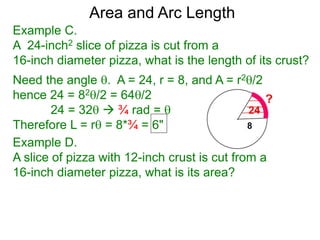
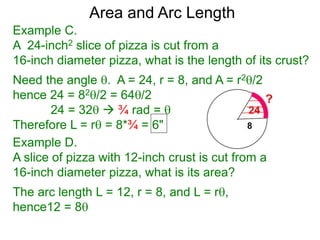
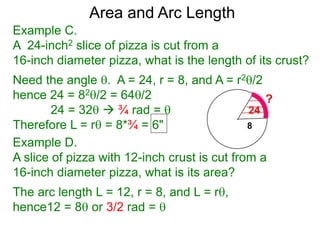
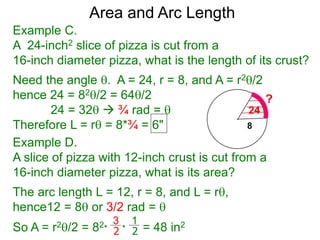
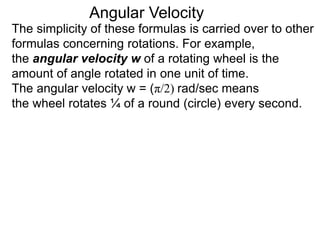
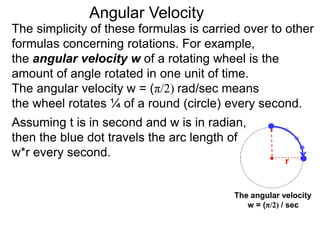
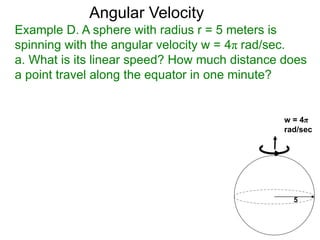
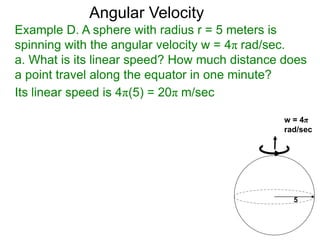
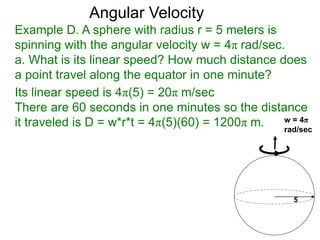
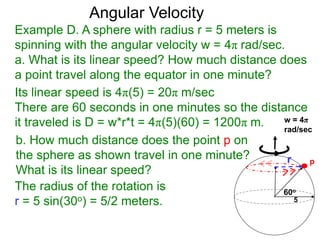
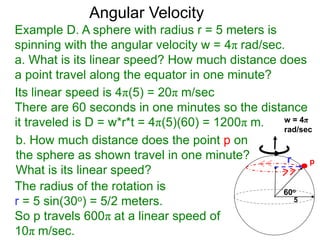
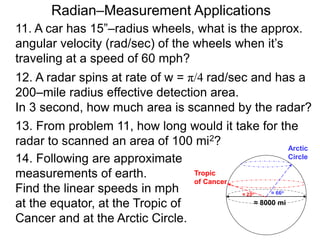
The document discusses radian measurement as it relates to angles on a unit circle. It defines the unit circle as having a radius of 1 centered at the origin, and explains that the radian measurement of an angle θ is the length of the arc cut off by θ on the unit circle. It provides conversions between radians and degrees for common angles. It then presents formulas for finding arc length and area of a sector on a circle using radian measurements of the central angle. Examples applying these formulas to find the crust length and area of a pizza slice are also included.