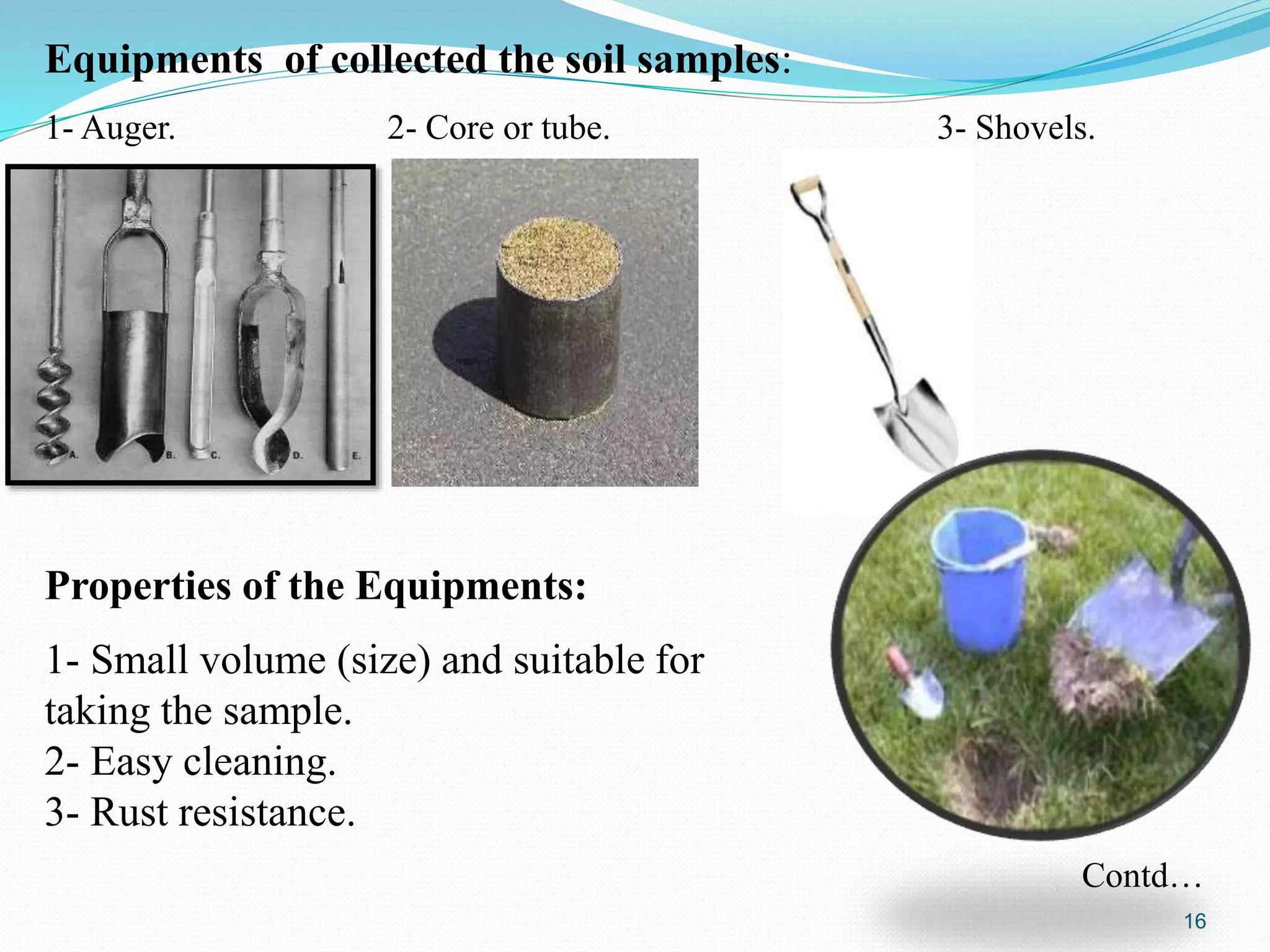
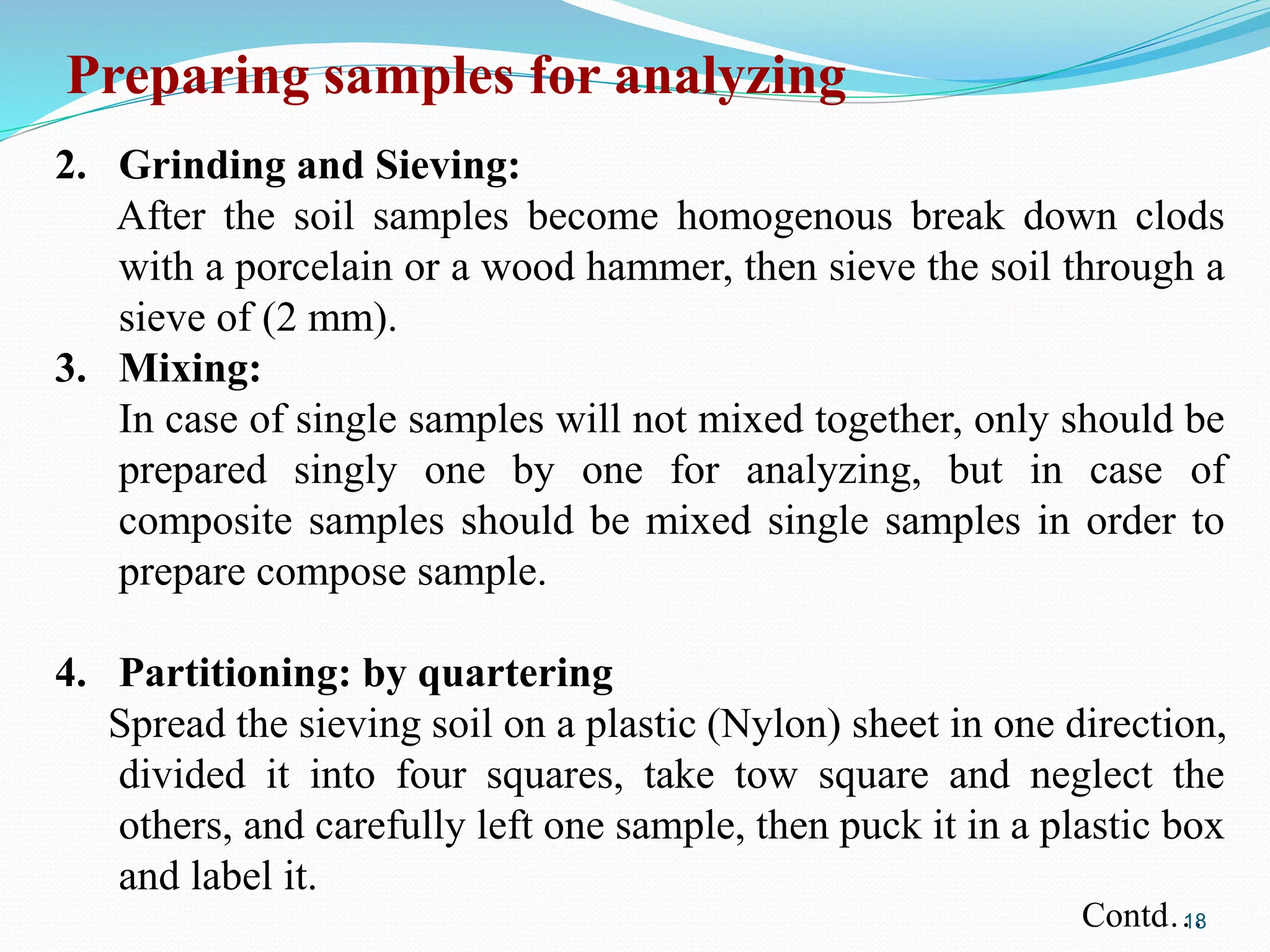
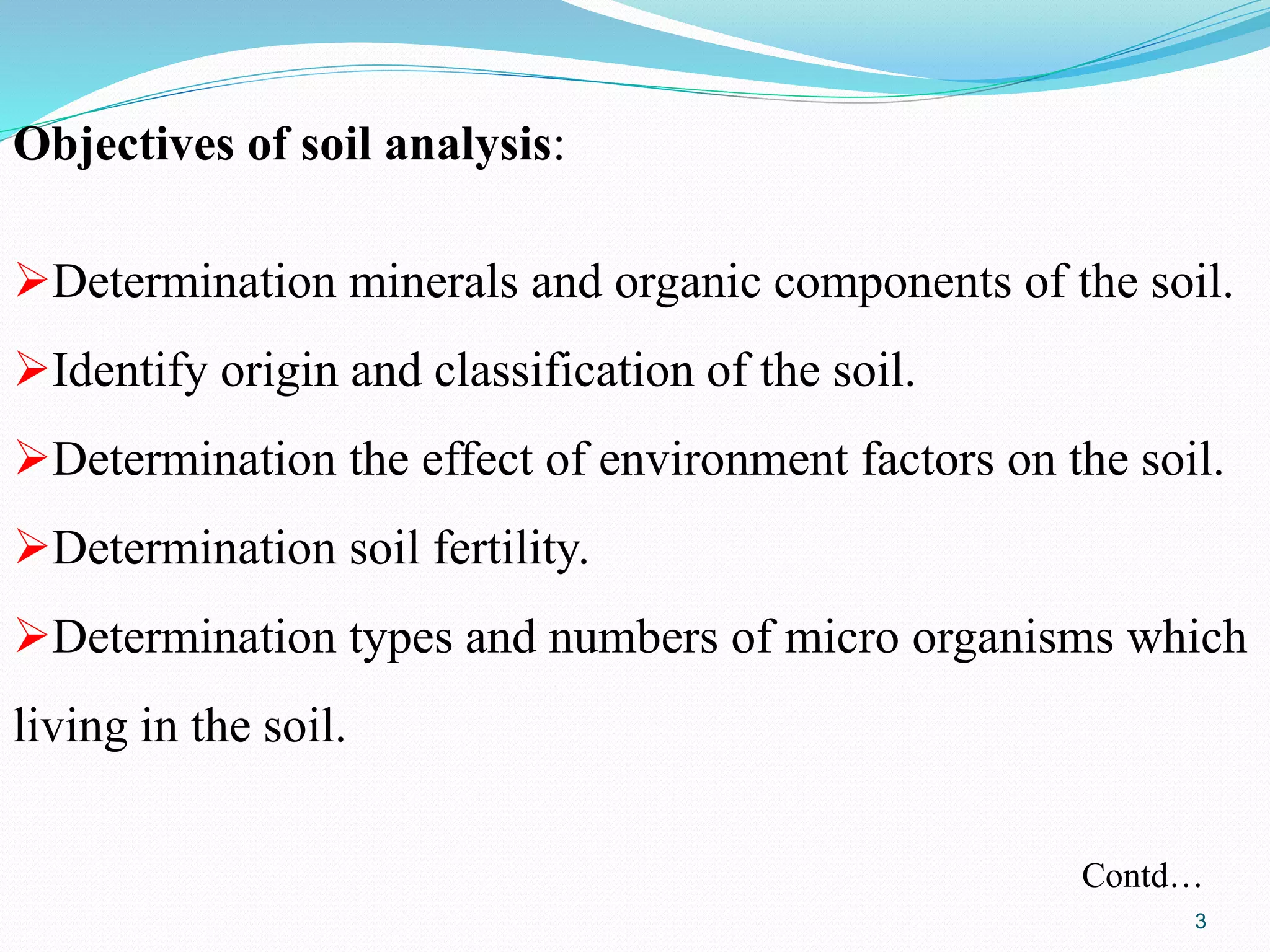
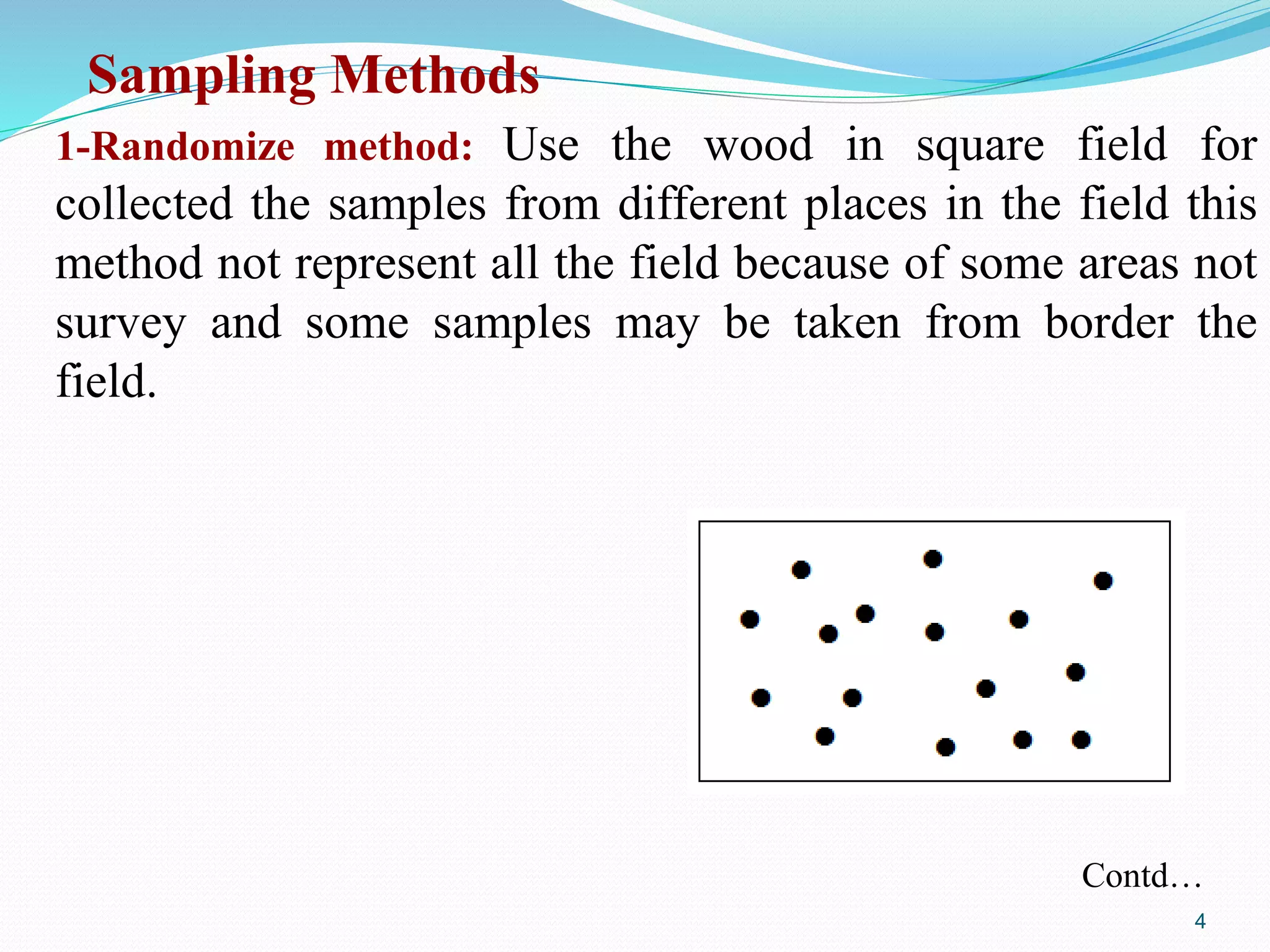
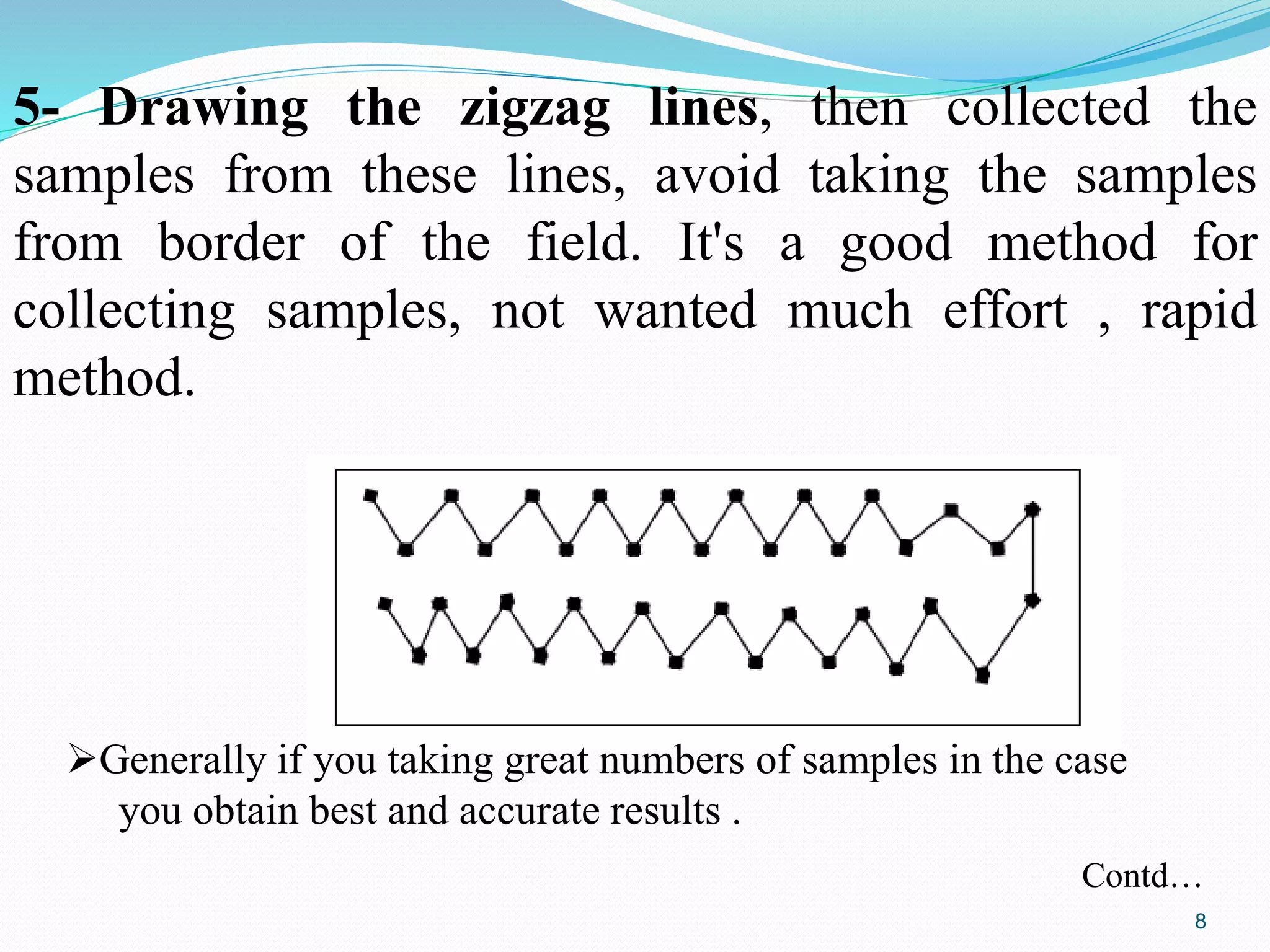
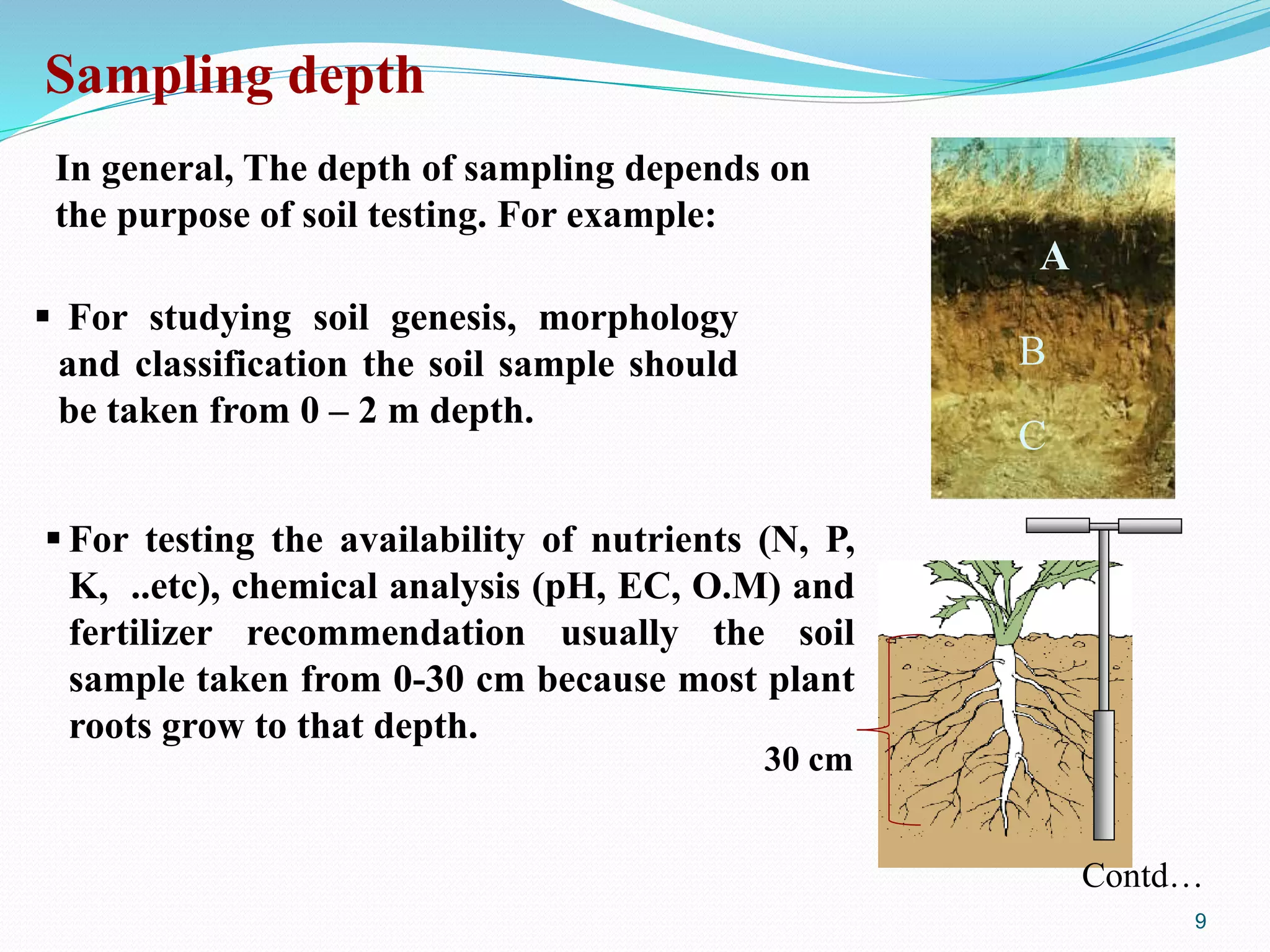
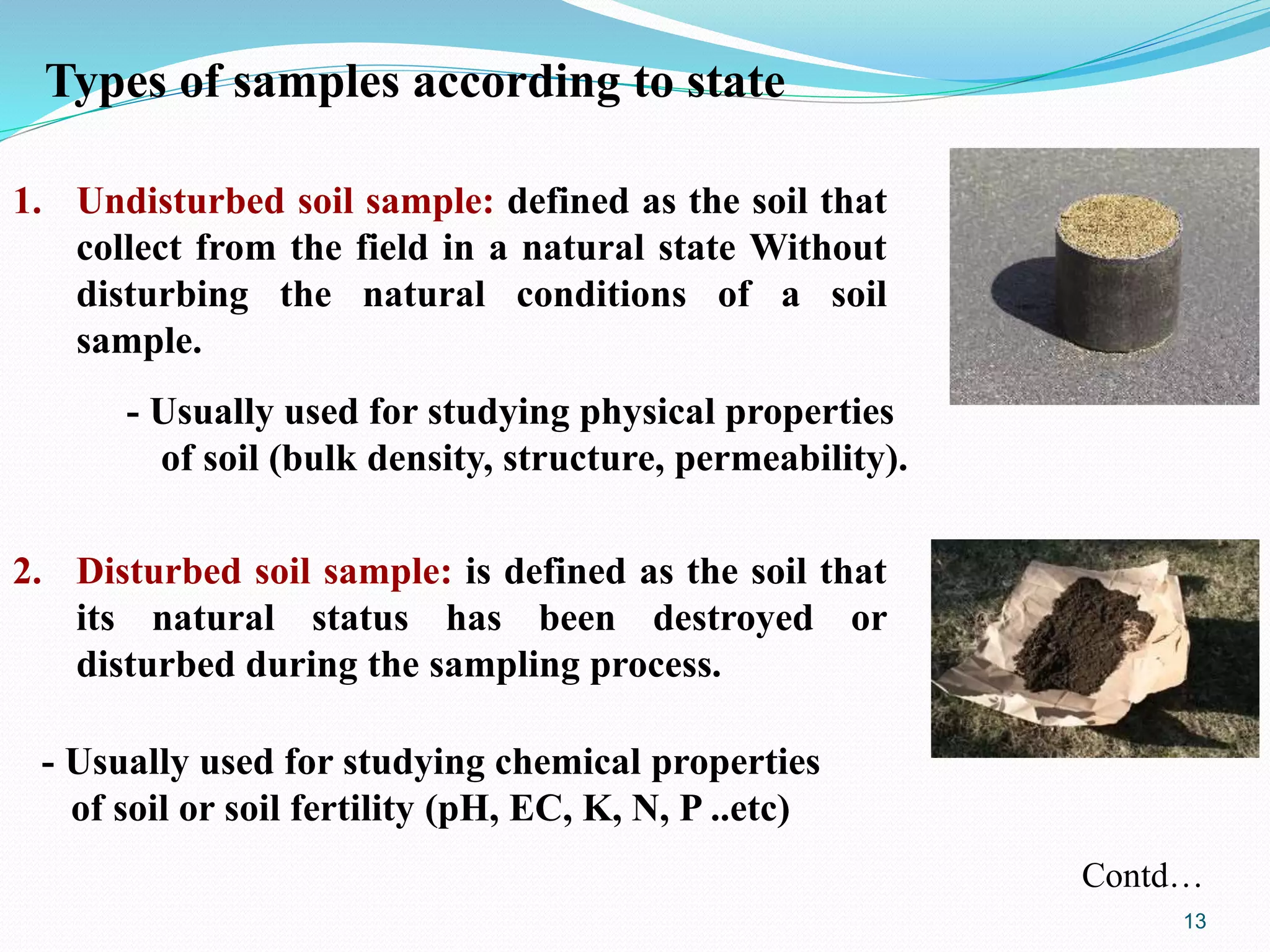
The document discusses soil sampling methods and procedures for soil analysis. It describes various sampling methods like random sampling, dividing fields into squares or triangles, and zigzag patterns. Samples should be collected from a depth of 0-30 cm for nutrient analysis and 0-200 cm for classification. Composite samples consist of mixing several single samples. Undisturbed samples preserve the soil's natural structure while disturbed samples have been altered. Key steps in sample preparation are drying, grinding, sieving, mixing or partitioning samples, and storing them at 4°C until analysis.


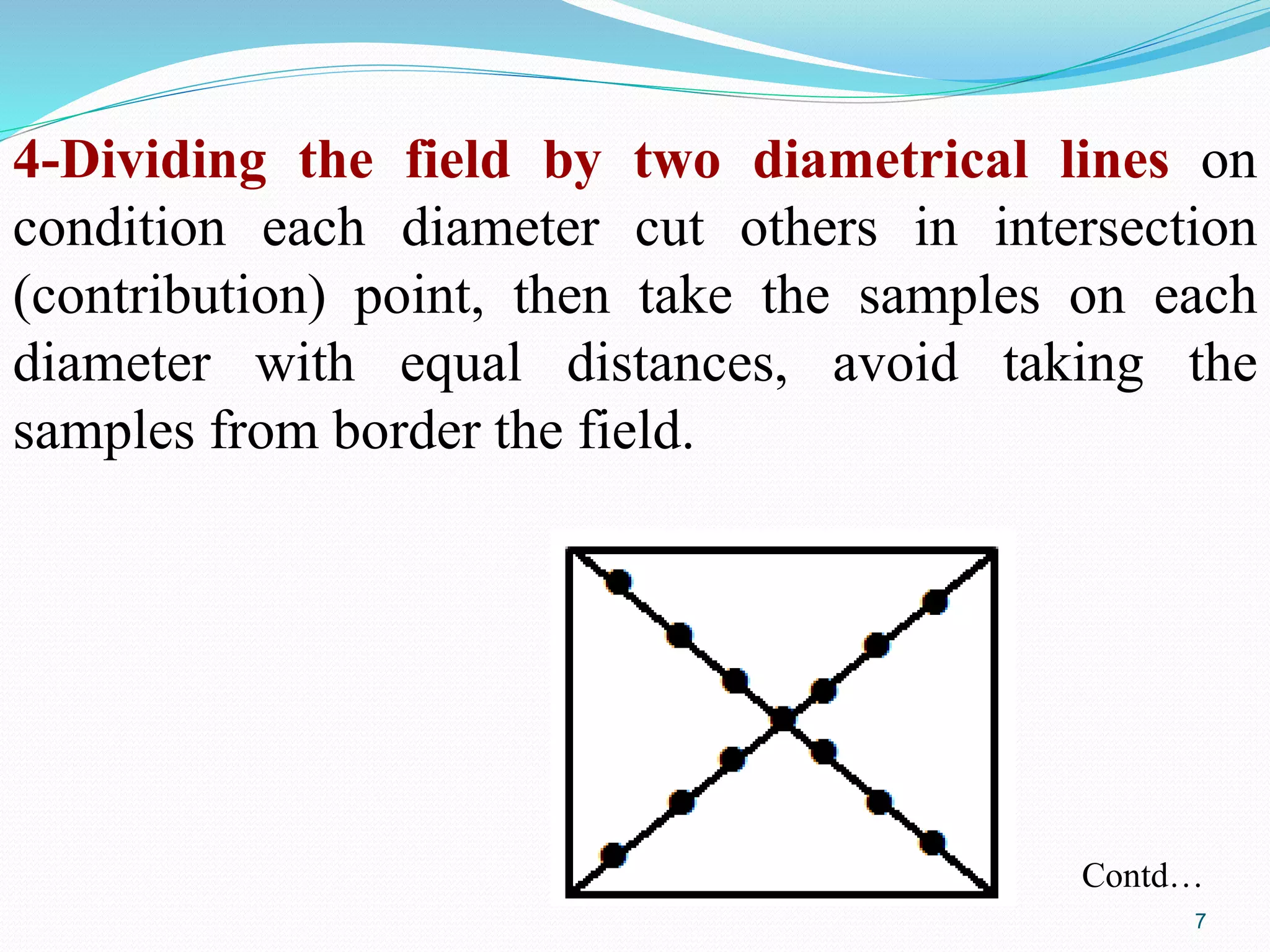
![3- Dividing the field to triangles: Dividing the field to
squares then dividing these squares by slope lines on
condition slope lines passing through the intersection point
of width and length lines [vertical and horizontal lines] of
squares after that take the samples on the slope lines with
equal distances , avoid taking the samples from border the
field.
Contd…
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-141103113811-conversion-gate01/75/Soil-Sampling-6-2048.jpg)
![Notes must be followed when collecting the
samples:
Sample volume must be equal of each layer or horizon.
Avoid taking the samples from region which contain disturbed
soil, Wet soil [Irrigated soil], saline regions in the field.
Avoid taking the samples from up to the hill and down to the hill.
Avoid taking the samples near the roads in the field, fertilizer stores.
Samples must be collected at the same time.
Contd…
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-141103113811-conversion-gate01/75/Soil-Sampling-14-2048.jpg)