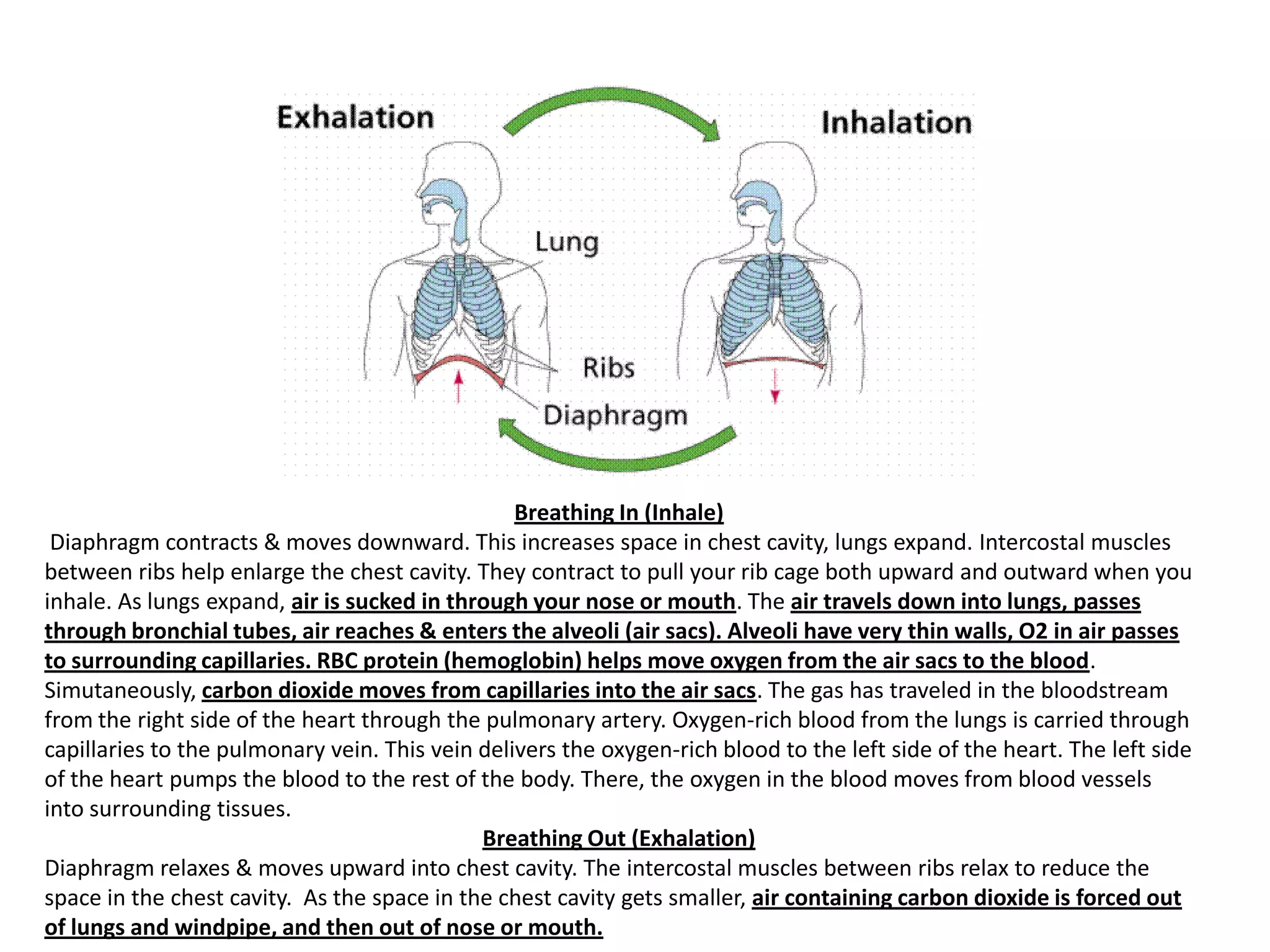
During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward which increases the space in the chest cavity, causing the lungs to expand and suck air in through the nose or mouth. The air travels through bronchial tubes into alveoli where oxygen passes into blood cells and carbon dioxide moves out. Oxygen-rich blood is then pumped by the heart to tissues throughout the body. During exhalation, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, reducing the chest cavity space and forcing carbon dioxide-rich air out of the lungs and mouth or nose.