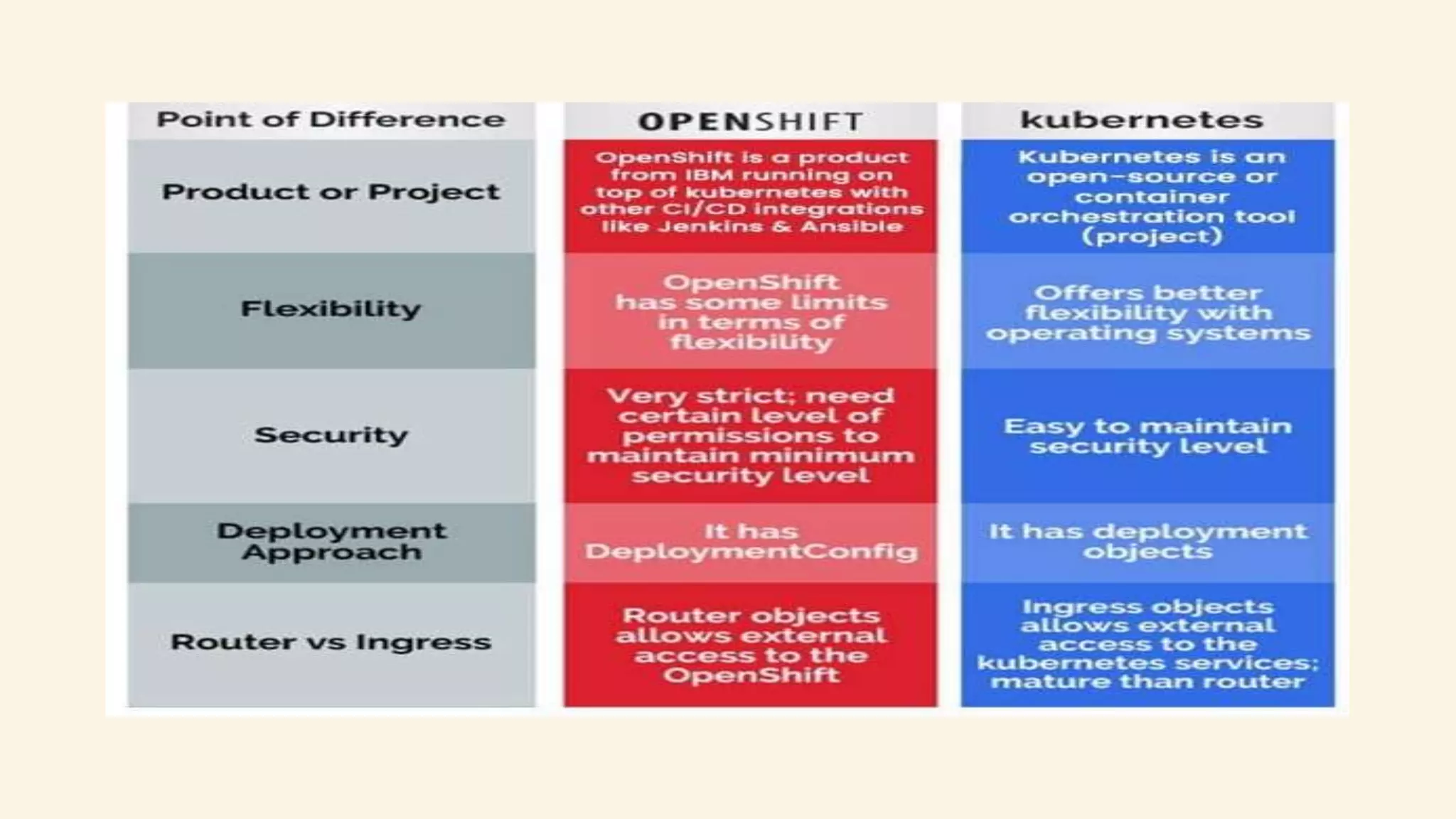
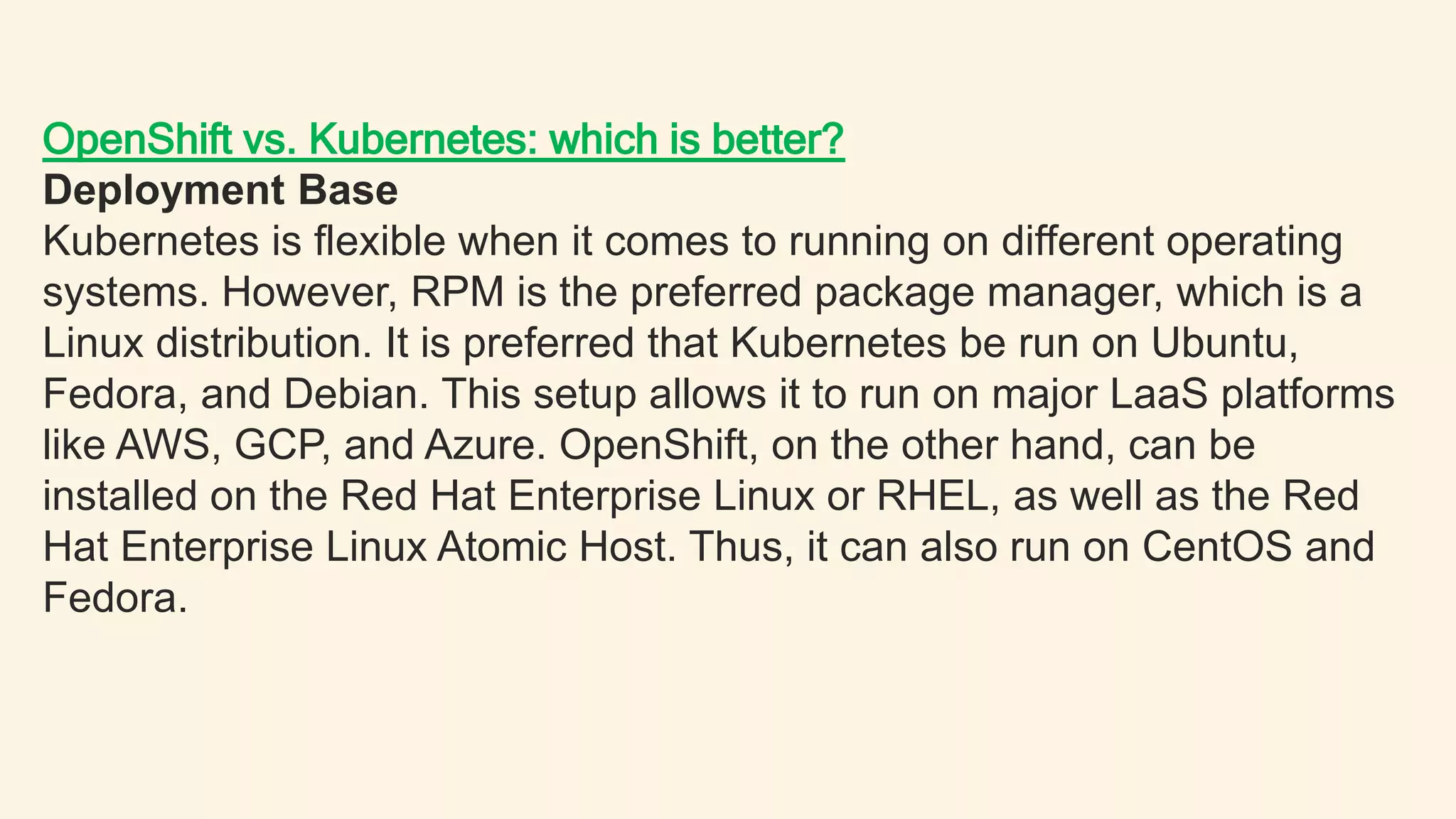
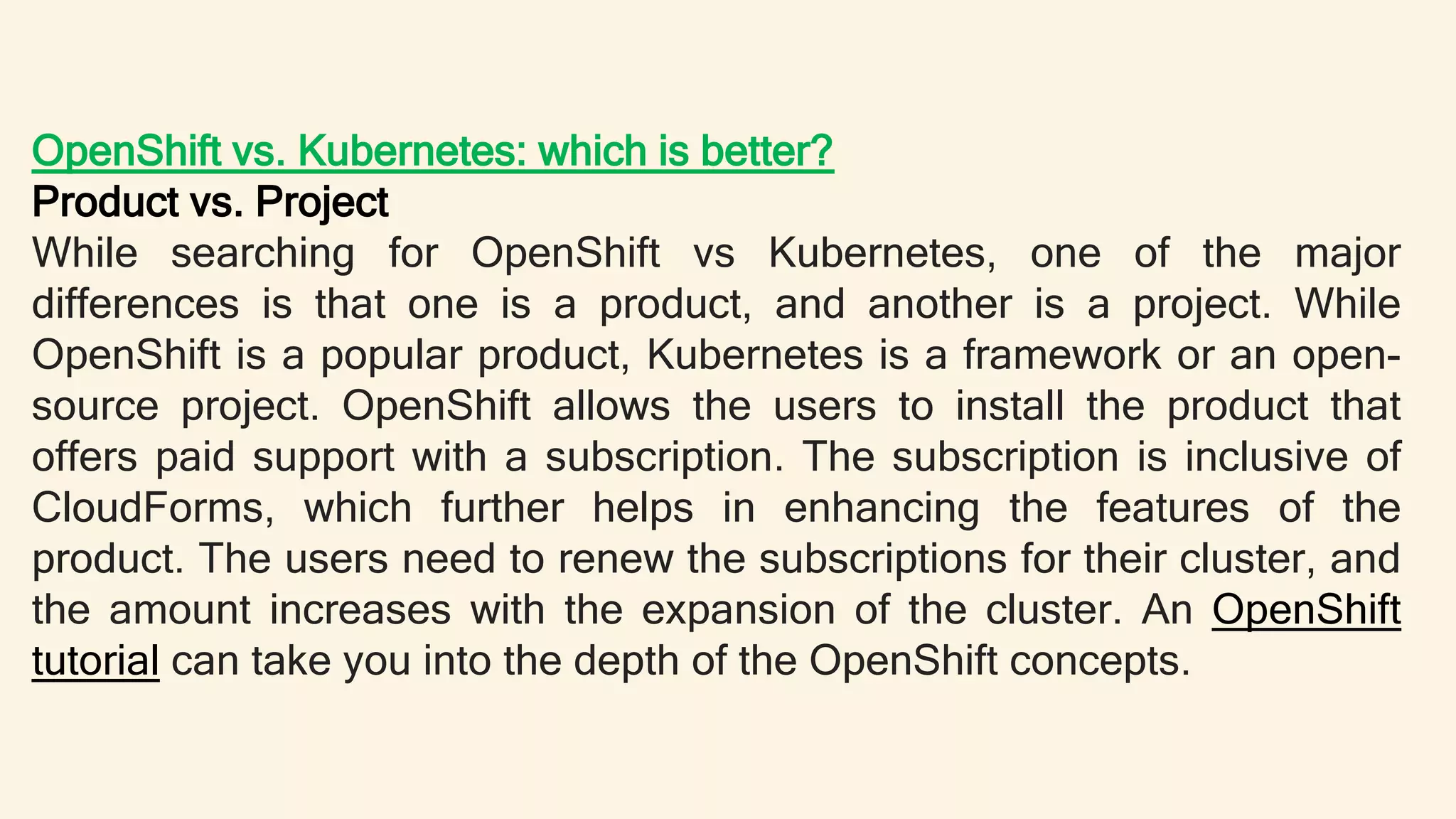
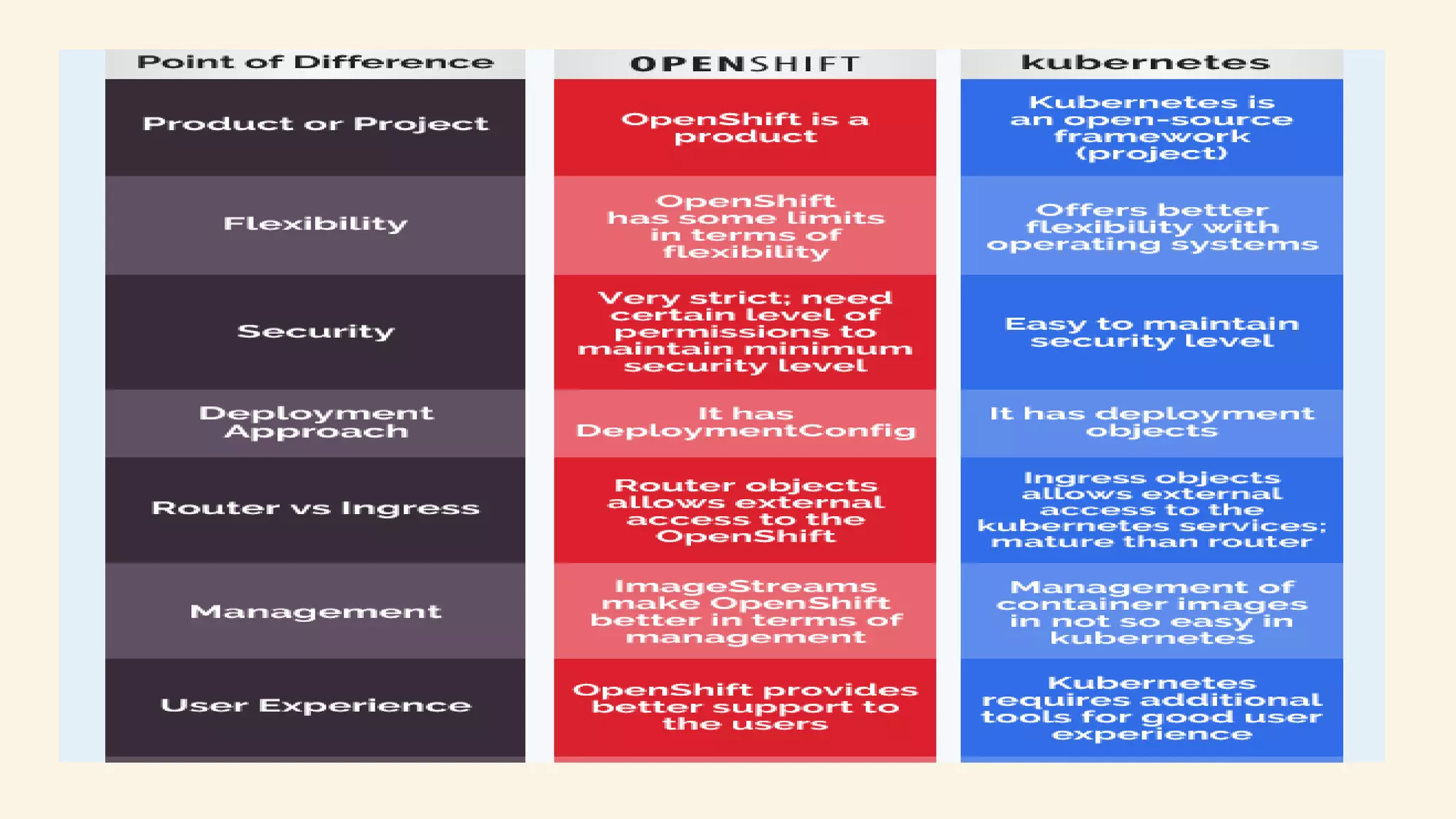
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system that automates deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. OpenShift is a container application platform from Red Hat that is based on Kubernetes but provides additional features such as integrated CI/CD pipelines and a native networking solution. While Kubernetes provides more flexibility in deployment environments and is open source, OpenShift offers easier management, stronger security policies, and commercial support but is limited to Red Hat Linux distributions. Both are excellent for building and deploying containerized apps, with OpenShift providing more out-of-the-box functionality and Kubernetes offering more flexibility.