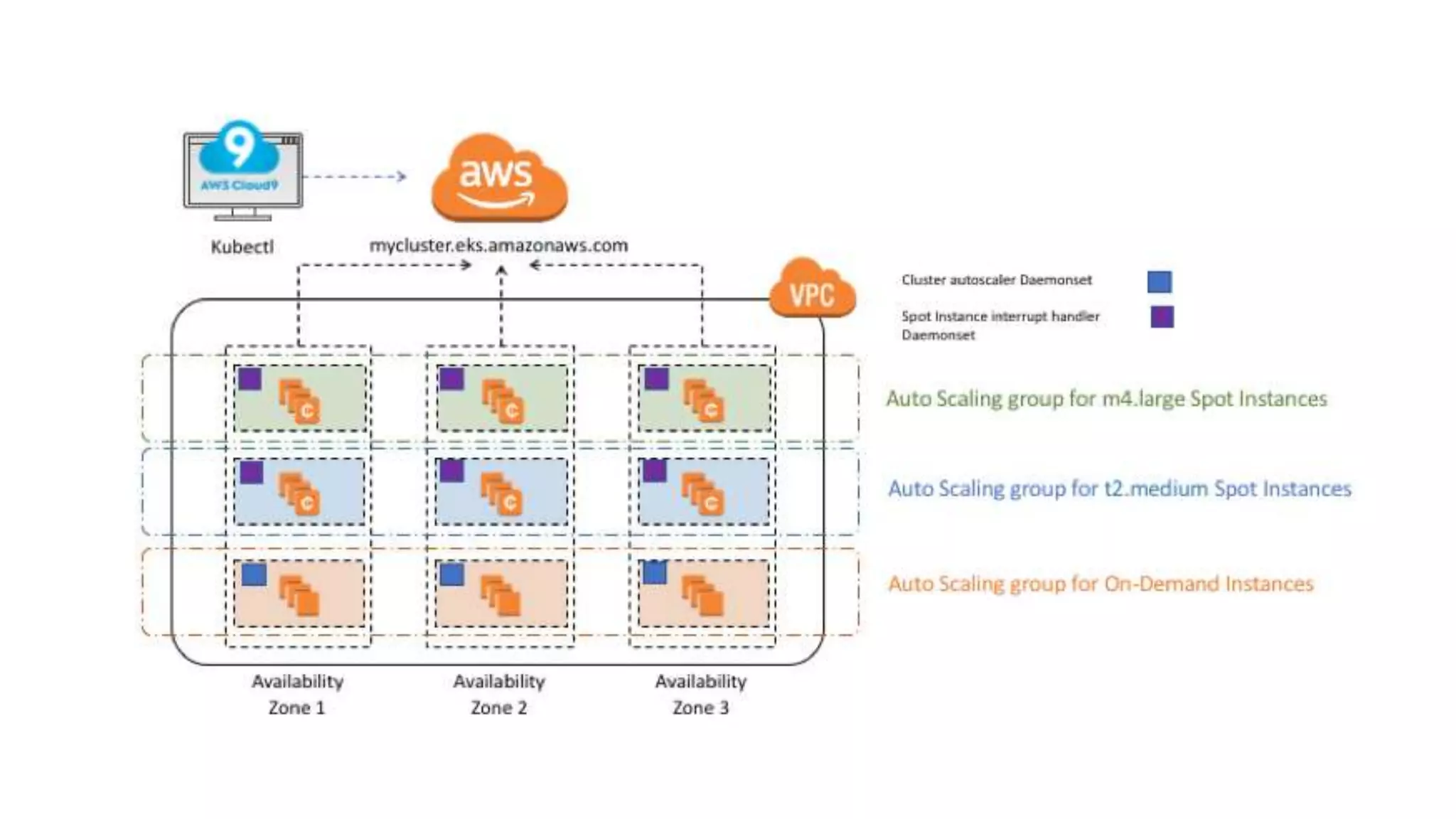
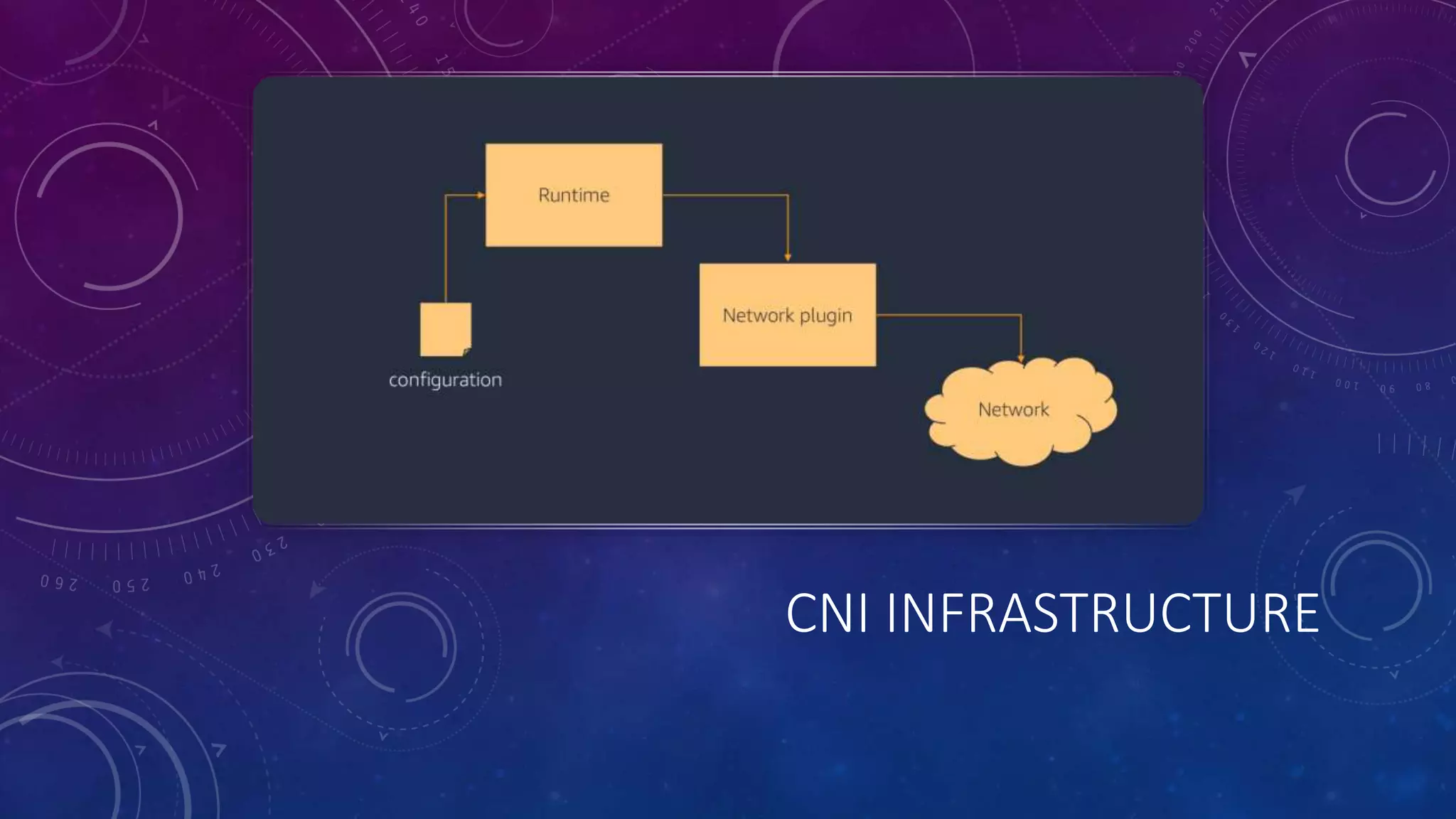
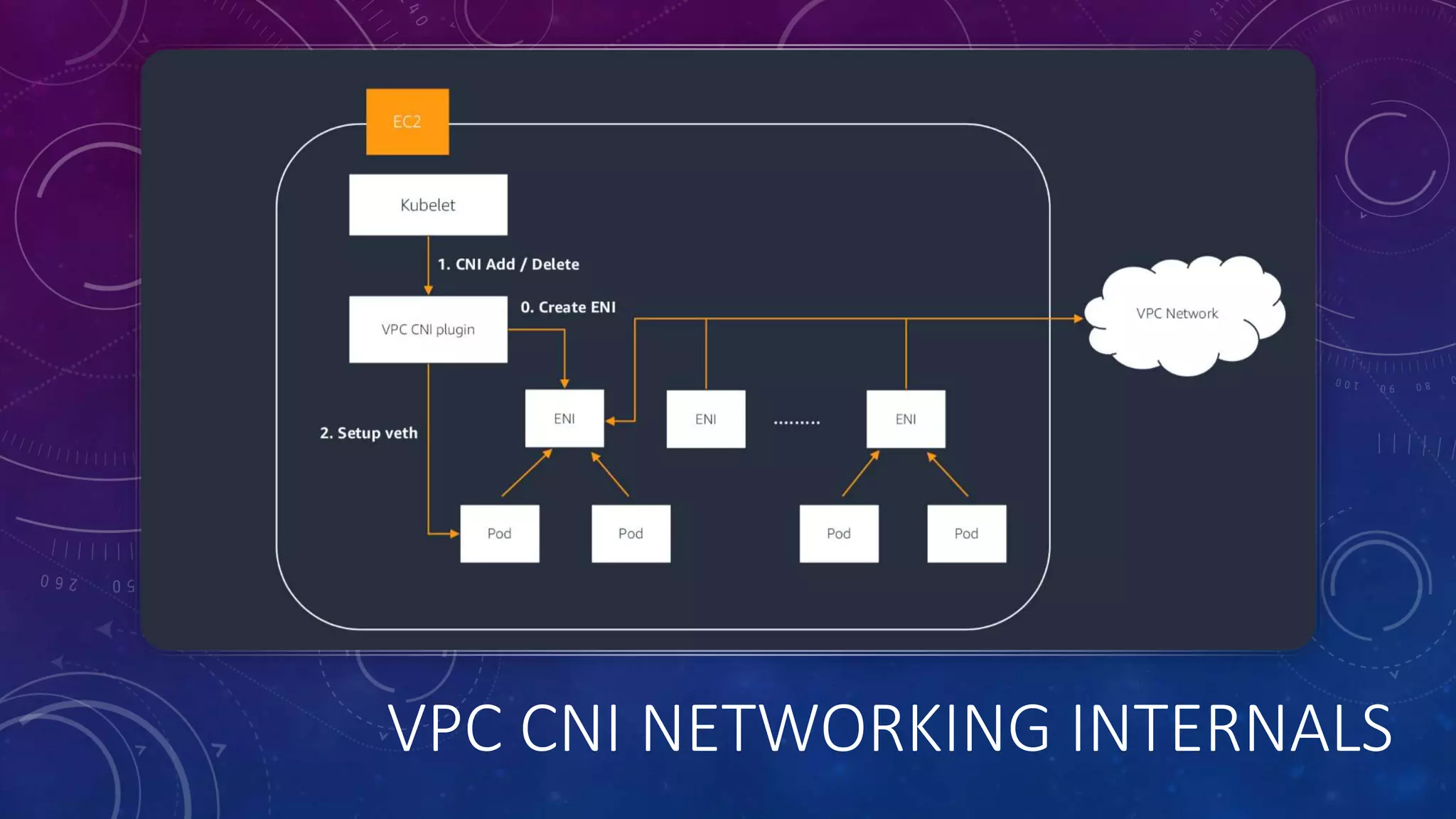
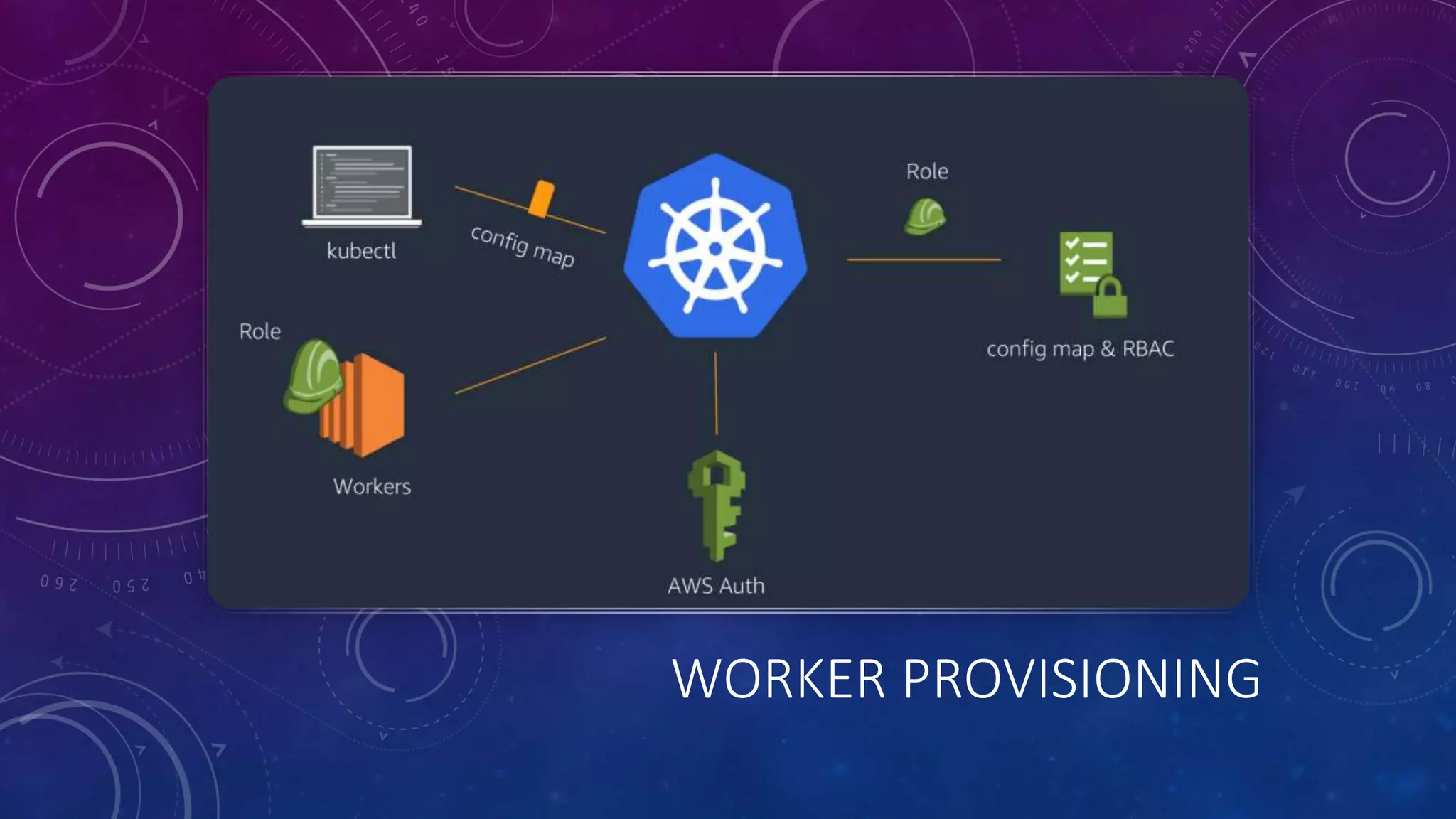
The document provides a detailed overview of Amazon EKS, including platform versions, shared responsibility models, worker node management, and load balancing configurations. It discusses the integration of Kubernetes with AWS features such as IAM authentication, networking plugins, and CI/CD options, while also highlighting the use of EC2 spot instances for cost optimization and resilience. The information is geared towards DevOps architects and Kubernetes practitioners looking to leverage Amazon EKS for scalable container orchestration solutions.


















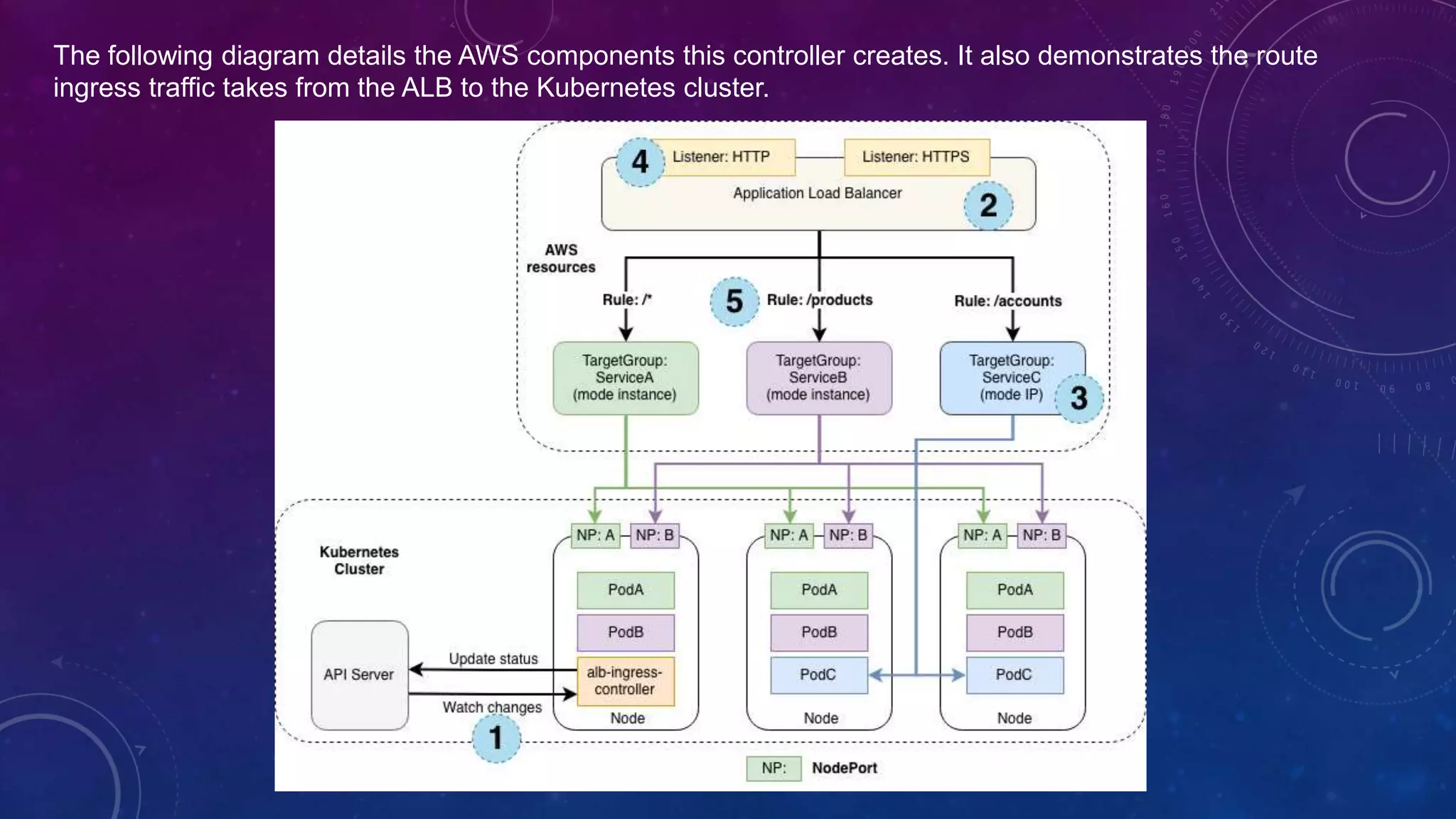
![Ingress Creation
This section describes each step (circle) above. This example demonstrates satisfying 1 ingress resource.
[1]: The controller watches for ingress events from the API server. When it finds ingress resources that satisfy its
requirements, it begins the creation of AWS resources.
[2]: An ALB (ELBv2) is created in AWS for the new ingress resource. This ALB can be internet-facing or internal.
You can also specify the subnets it's created in using annotations.
[3]: Target Groups are created in AWS for each unique Kubernetes service described in the ingress resource.
[4]: Listeners are created for every port detailed in your ingress resource annotations. When no port is specified,
sensible defaults (80 or 443) are used. Certificates may also be attached via annotations.
[5]: Rules are created for each path specified in your ingress resource. This ensures traffic to a specific path is
routed to the correct Kubernetes Service.
Along with the above, the controller also...
•deletes AWS components when ingress resources are removed from k8s.
•modifies AWS components when ingress resources change in k8s.
•assembles a list of existing ingress-related AWS components on start-up, allowing you to recover if the controller
were to be restarted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amazoneksdeepdive-181107034532/75/Amazon-EKS-Deep-Dive-33-2048.jpg)