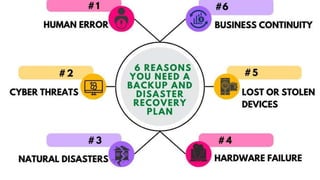
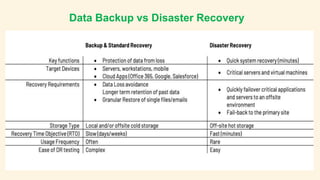
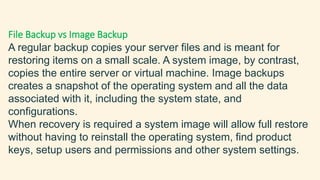
Data backup involves making copies of data to protect against accidental deletion, corruption, or issues with software upgrades. Disaster recovery refers to processes for quickly restoring access and operations after an outage by switching to redundant servers and storage. While backups protect against data loss, disaster recovery ensures business continuity through tested plans to restore full systems and infrastructure. It is crucial for companies to have both backup and disaster recovery plans in place to avoid costly downtime and lost revenue from data or system loss.