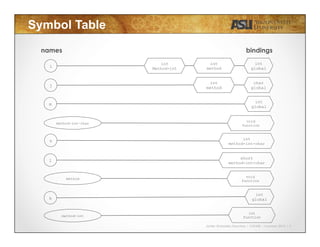
This document contains slides from a lecture on semantic analysis in programming languages. It discusses the key aspects of semantic analysis, including declaration and unicity, variable types, array indexes, condition types, return types, and parameter matching. It provides examples of code snippets and uses symbol tables to illustrate how semantic analysis would work for each example. The document is intended to teach students about semantic analysis and have them practice it through examples and exercises.



![Javier Gonzalez-Sanchez | CSE340 | Summer 2015 | 4
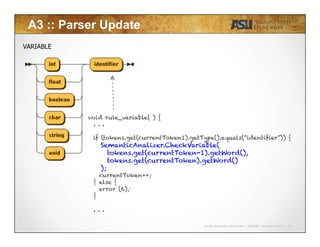
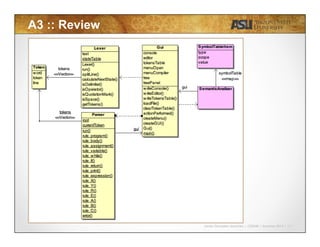
Case 1:
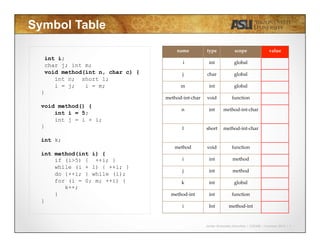
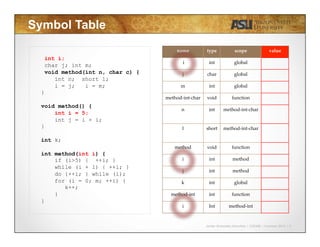
int i;
char j; int m;
void method(int n, char c) {
int n; short l;
i = j; i = m;
}
Case 2:
int i, j;
void method() {
int i = 5;
int j = i + i;
int i = i + i;
}
Case 3:
int i, m, k; boolean j;
void main() {
if (i>5) { ++i; }
while (i + 1) { ++i; }
do {++i; } while (i);
for (i = 0; m; ++i) {
k++;
}
}
Case 4:
int a; int b; int c, d;
char c1, c2;
int test1(int x, int y) {
return x+y;
}
void main() {
int i; i = a++;
i = test1(a, b);
i = test1(c1, c2);
i = test1(a, c1);
} }
Case 5:
int i, m; boolean j;
public void main() {
int m; int a[];
a = new int[j];
}
Case 6:
int i;
void main(int m) {
i++; return i;
}
Study Cases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cse34017semantic1-150624082402-lva1-app6891/85/201506-CSE340-Lecture-17-4-320.jpg)






![Javier Gonzalez-Sanchez | CSE340 | Summer 2015 | 14
Grammar
<PROGRAM> à '{' <BODY> '}’
<BODY> à {<PRINT>';'|<ASSIGNMENT>';'|<VARIABLE>';’|<WHILE>|<IF>|<RETURN>';'}
<ASSIGNMENT> à identifier '=' <EXPRESSION>
<VARIABLE> à ('int'|'float'|'boolean'|'char’|'string'|'void')identifier
<WHILE> à 'while' '(' <EXPRESSION> ')' <PROGRAM>
<IF> à 'if' '(' <EXPRESSION> ')' <PROGRAM> ['else' <PROGRAM>]
<RETURN> à 'return'
<PRINT> à ’print’ ‘(‘ <EXPRESSION> ‘)’
<EXPRESSION> à <X> {'|' <X>}
<X> à <Y> {'&' <Y>}
<Y> à ['!'] <R>
<R> à <E> {('>'|'<'|'=='|'!=') <E>}
<E> à <A> {(’+'|'-’) <A>}
<A> à <B> {('*'|'/') <B>}
<B> à ['-'] <C>
<C> à integer | octal | hexadecimal | binary | true | false |
string | char | float | identifier|'(' <EXPRESSION> ')'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cse34017semantic1-150624082402-lva1-app6891/85/201506-CSE340-Lecture-17-14-320.jpg)