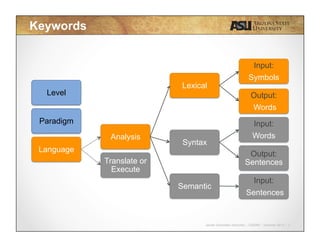
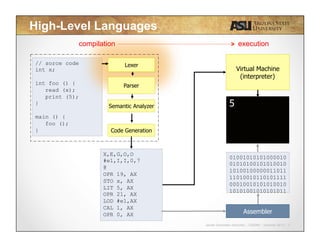
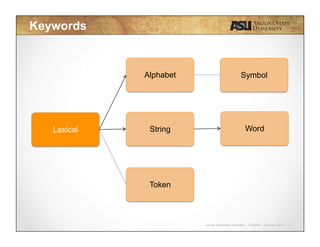
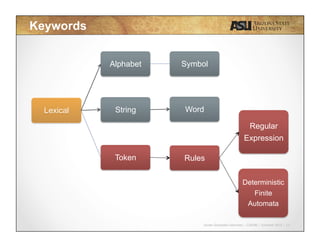
This document contains lecture slides for CSE340 - Principles of Programming Languages. It introduces lexical analysis and discusses how it is used to break source code into individual tokens by identifying strings and words. The key steps of lexical analysis are described, including reading the text line by line, grouping characters into strings, and verifying strings as valid words to create a vector of tokens. Regular expressions and deterministic finite automata are also introduced as techniques for defining token rules. Students are assigned to review these topics for lexical analysis in the provided textbook.