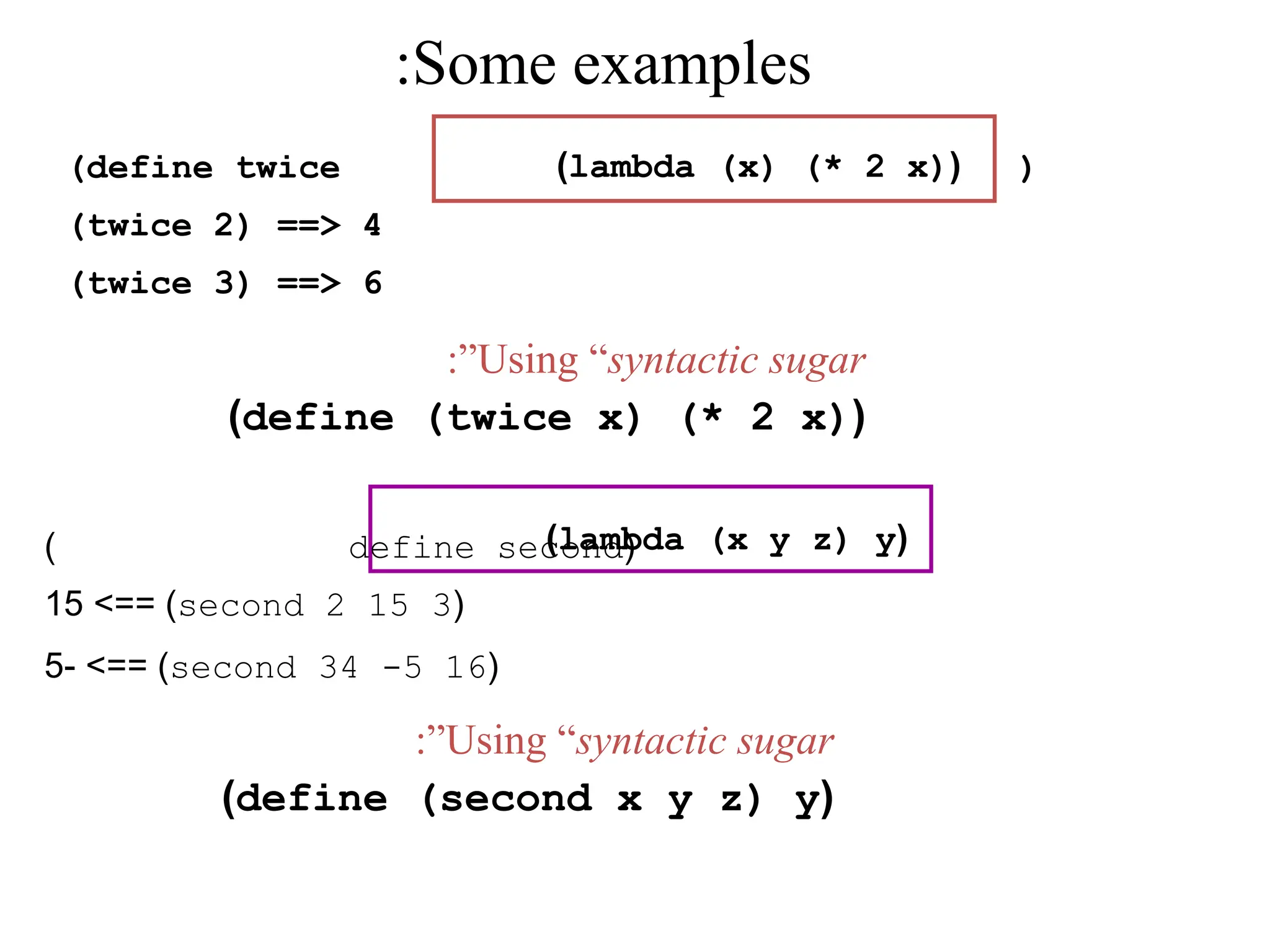
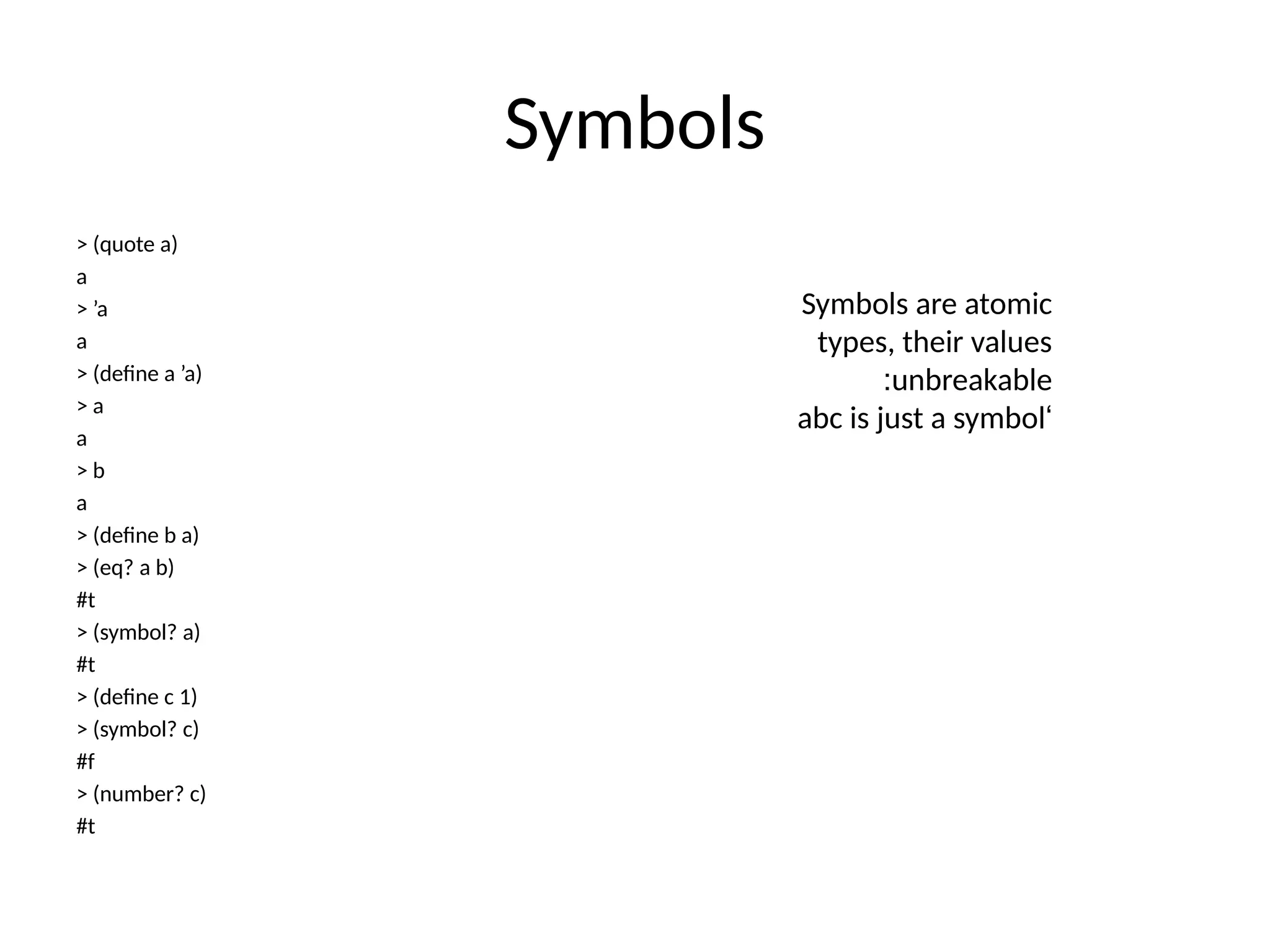
The document introduces principles of programming languages, focusing on modeling computational processes and differentiating between programming paradigms such as functional, logic, and imperative programming. Topics covered include types, semantics, language features, and specific languages like Scheme, ML, and Prolog, along with the mechanics of the Scheme interpreter and evaluation processes. Administrative issues, such as assessment methods and class materials, are also addressed.



![4
To find an approximation of x:
• Make a guess G
• Improve the guess by averaging G and x/G
• Keep improving the guess until it is good enough
Imperative and Functional
Knowledge
“
How to
”
An algorithm due to
:
[
Heron of Alexandria
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppl1-241212063722-3292e240/75/Principles-of-programming-language-intro-4-2048.jpg)




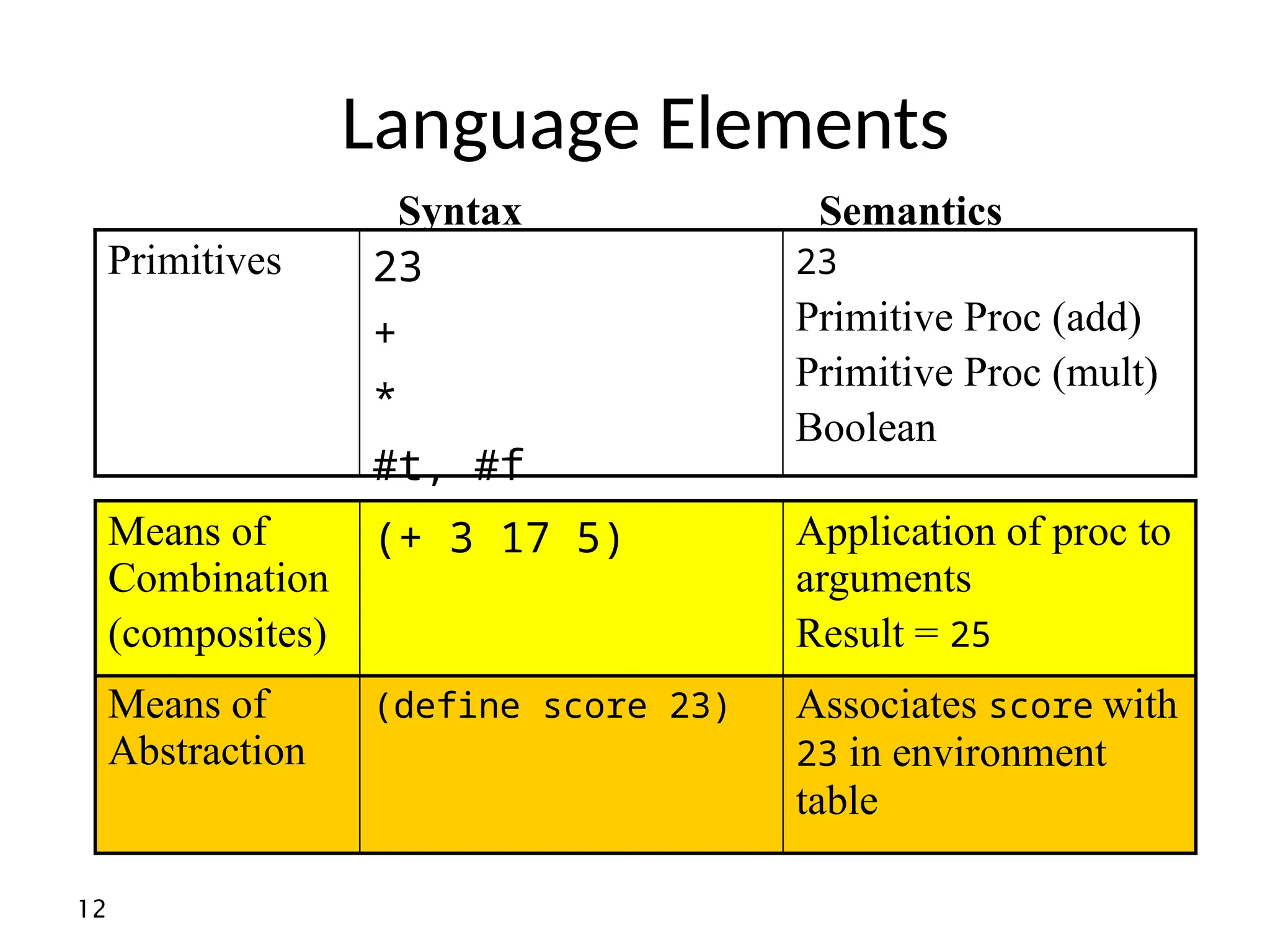
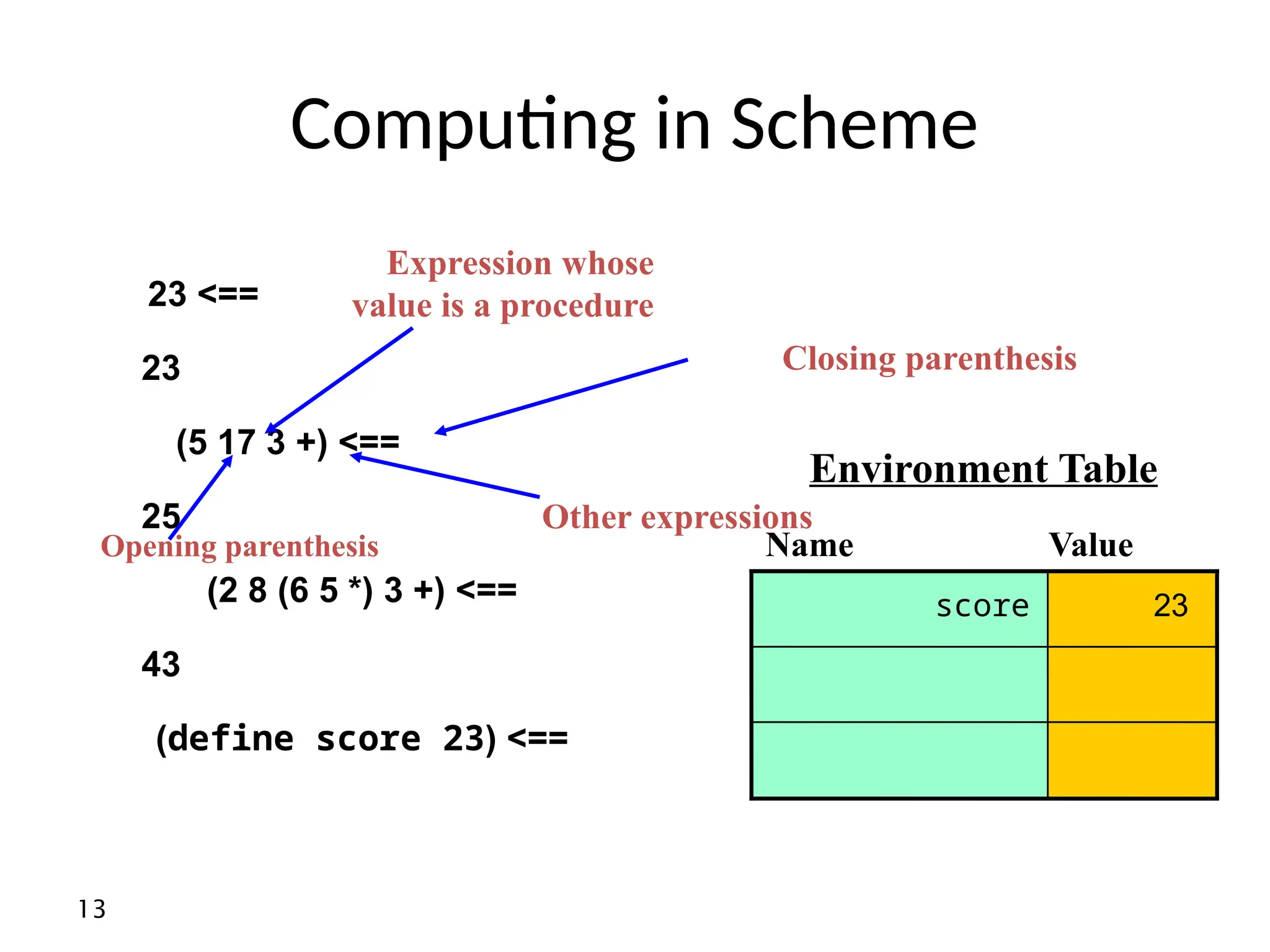
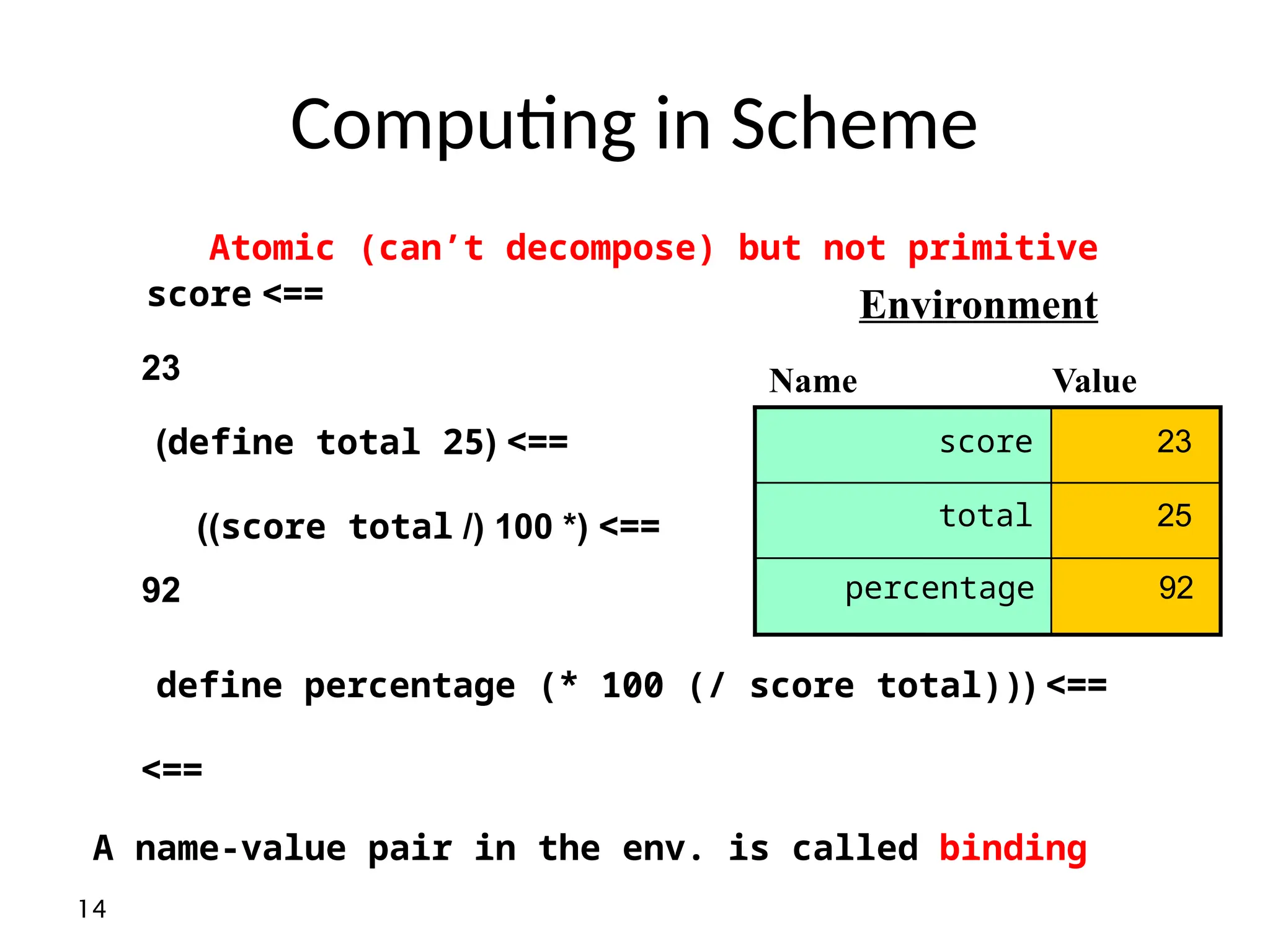

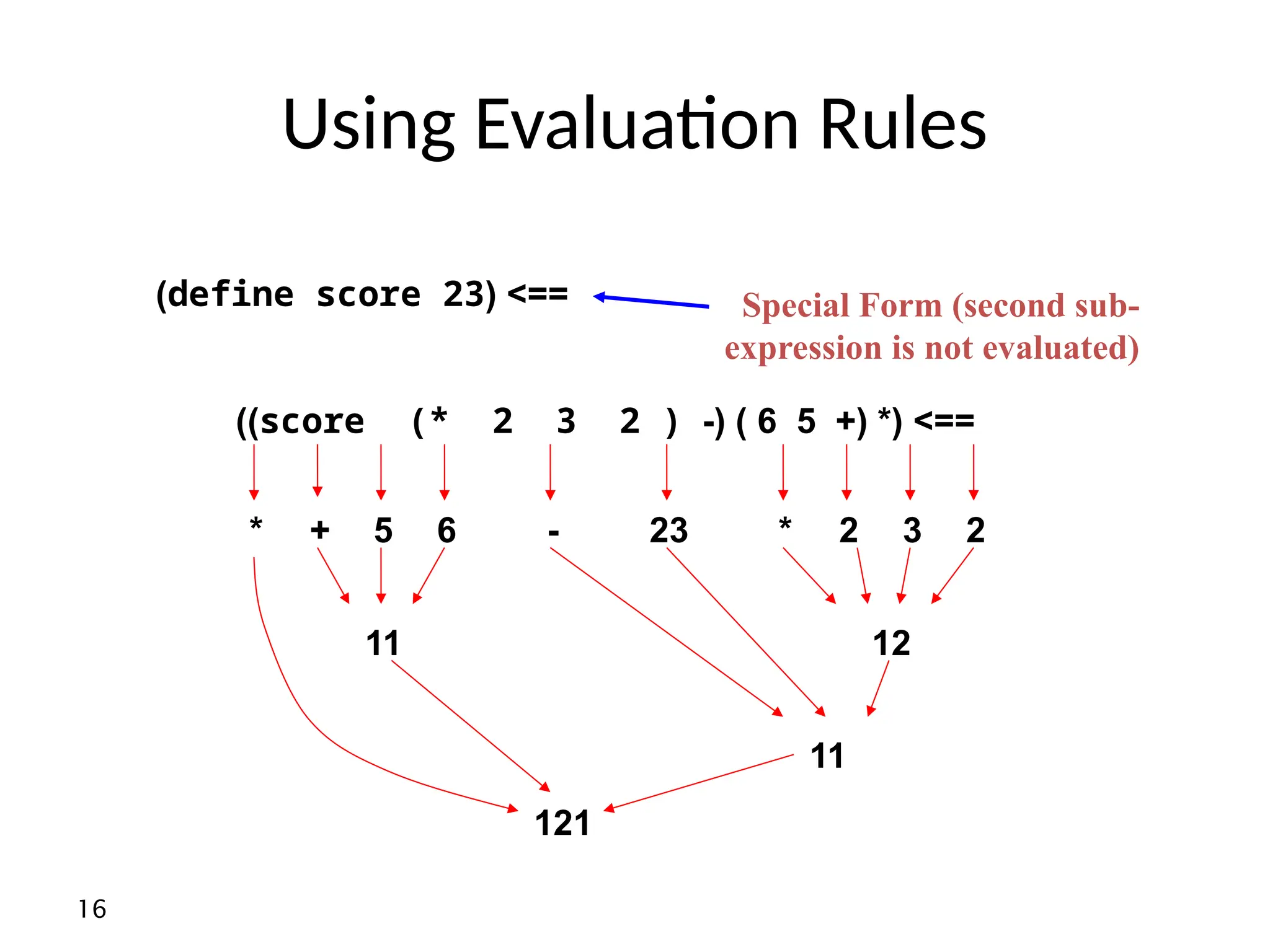





![29
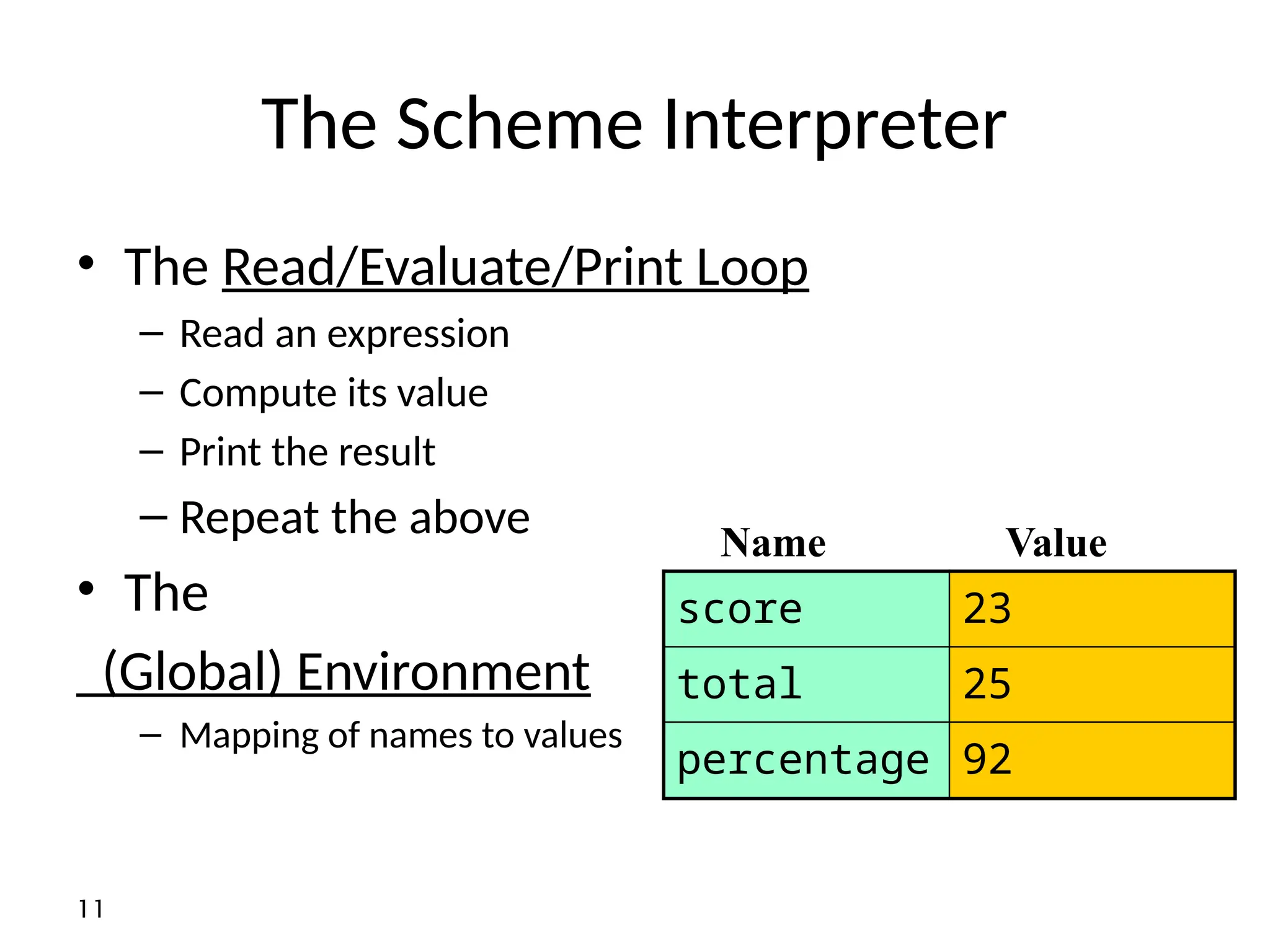
No Value
?
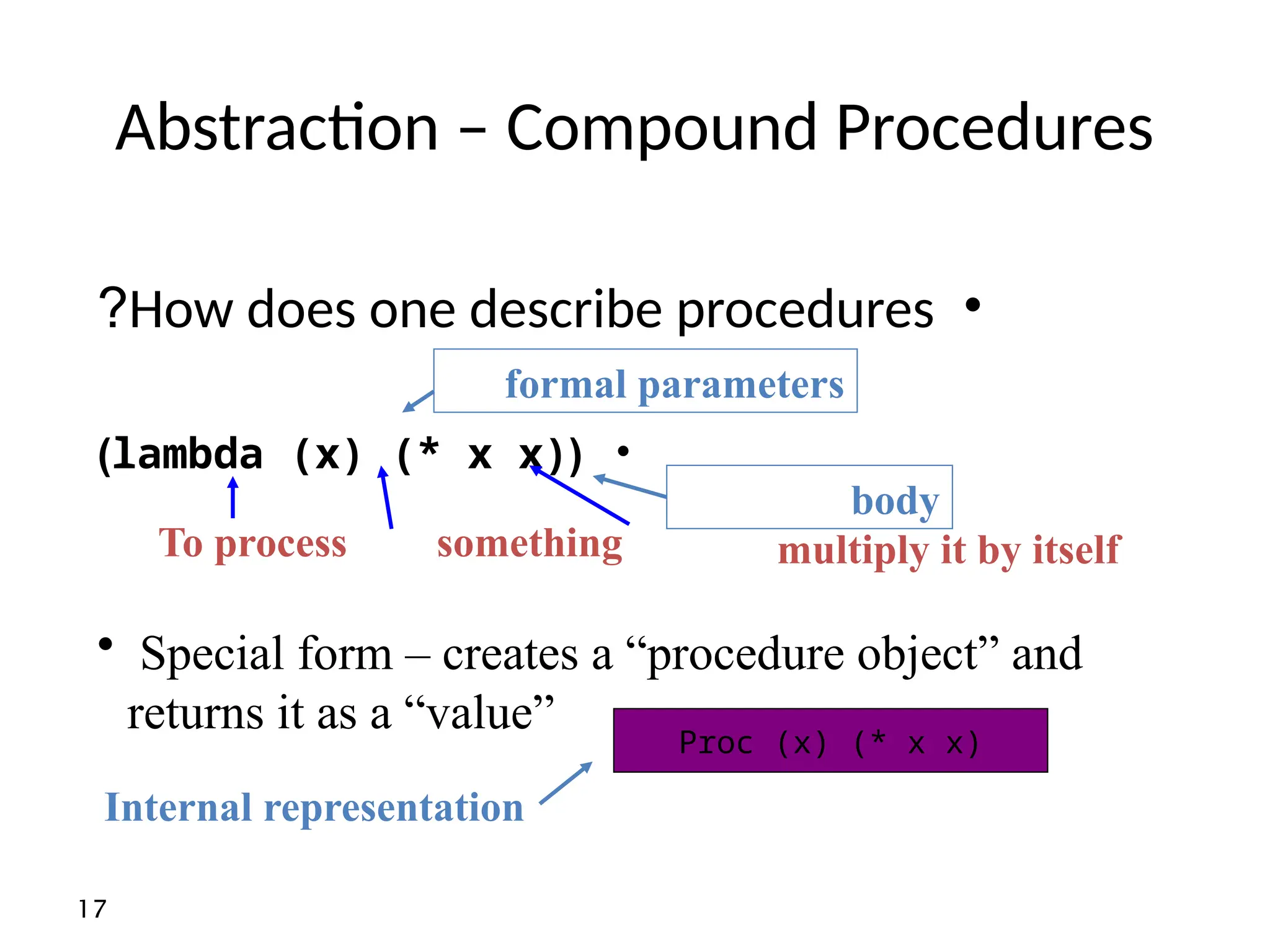
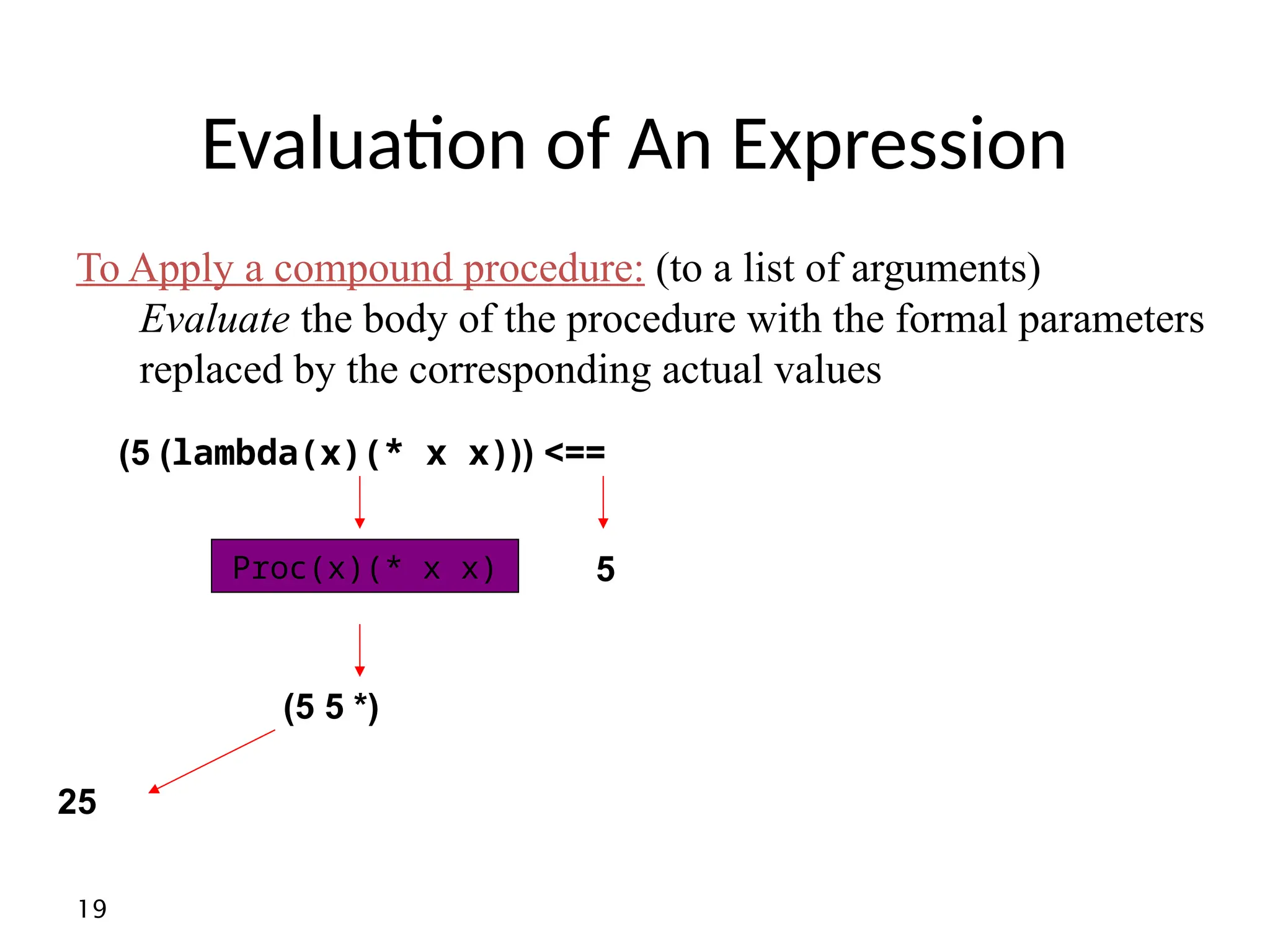
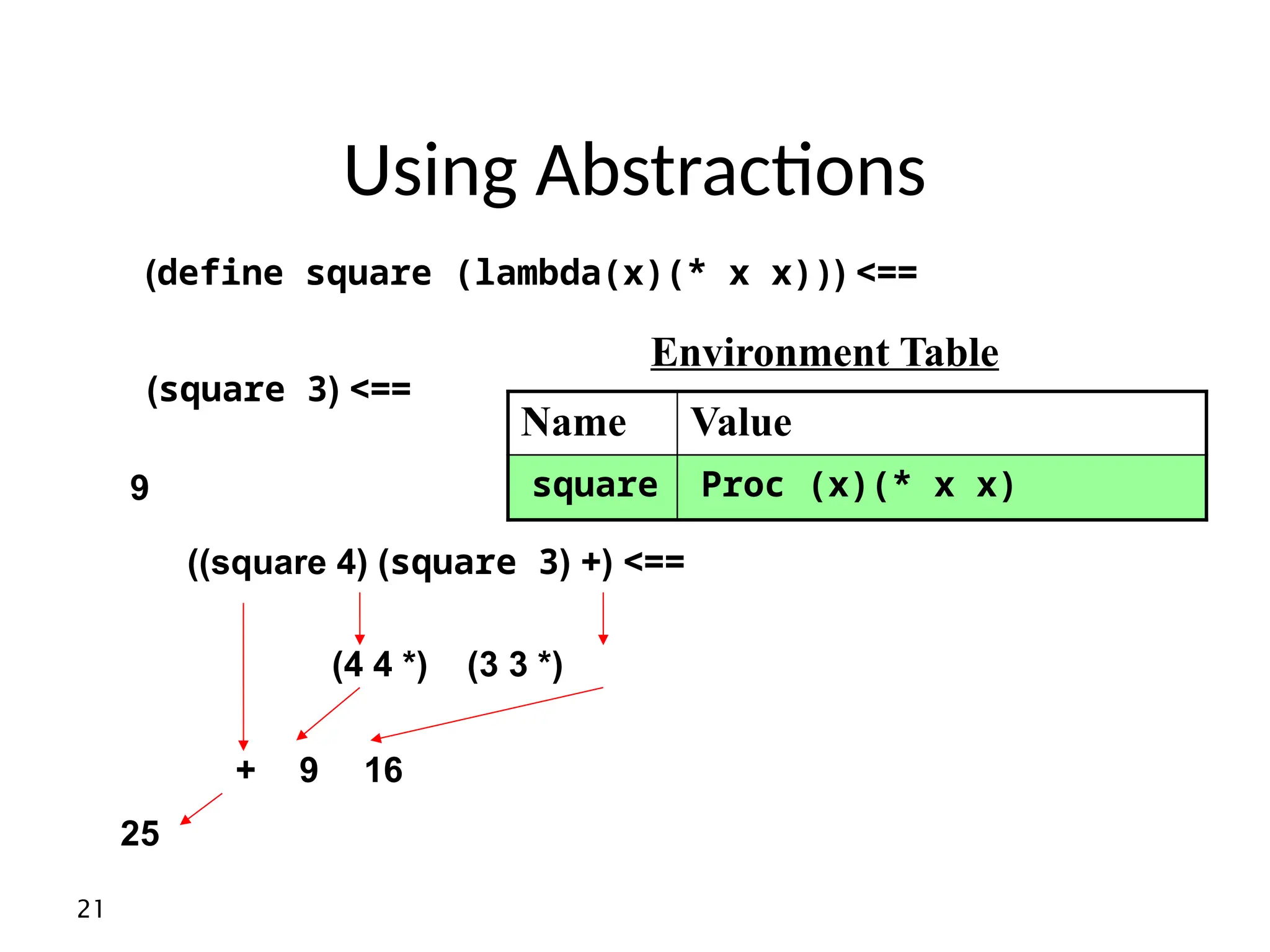
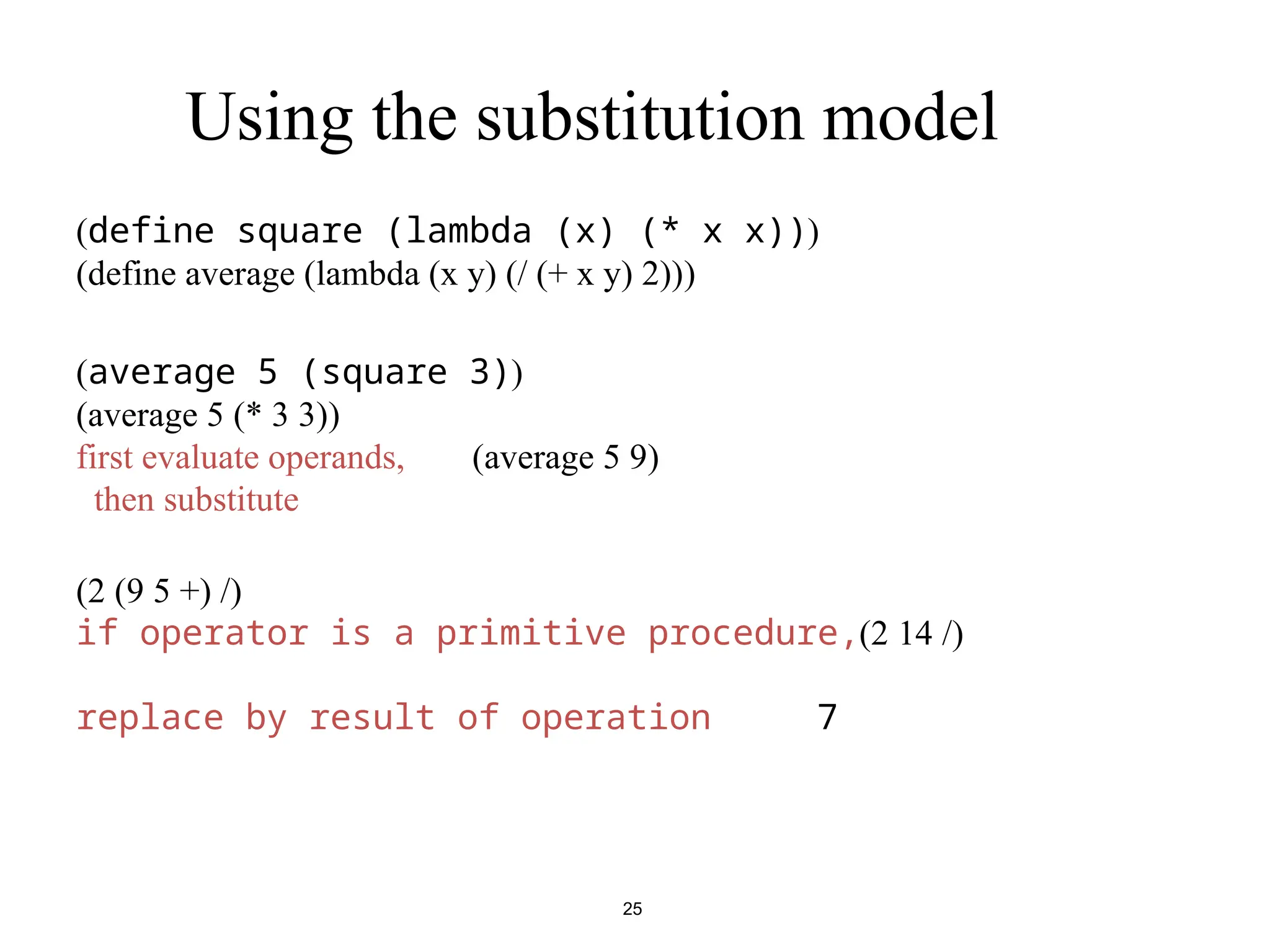
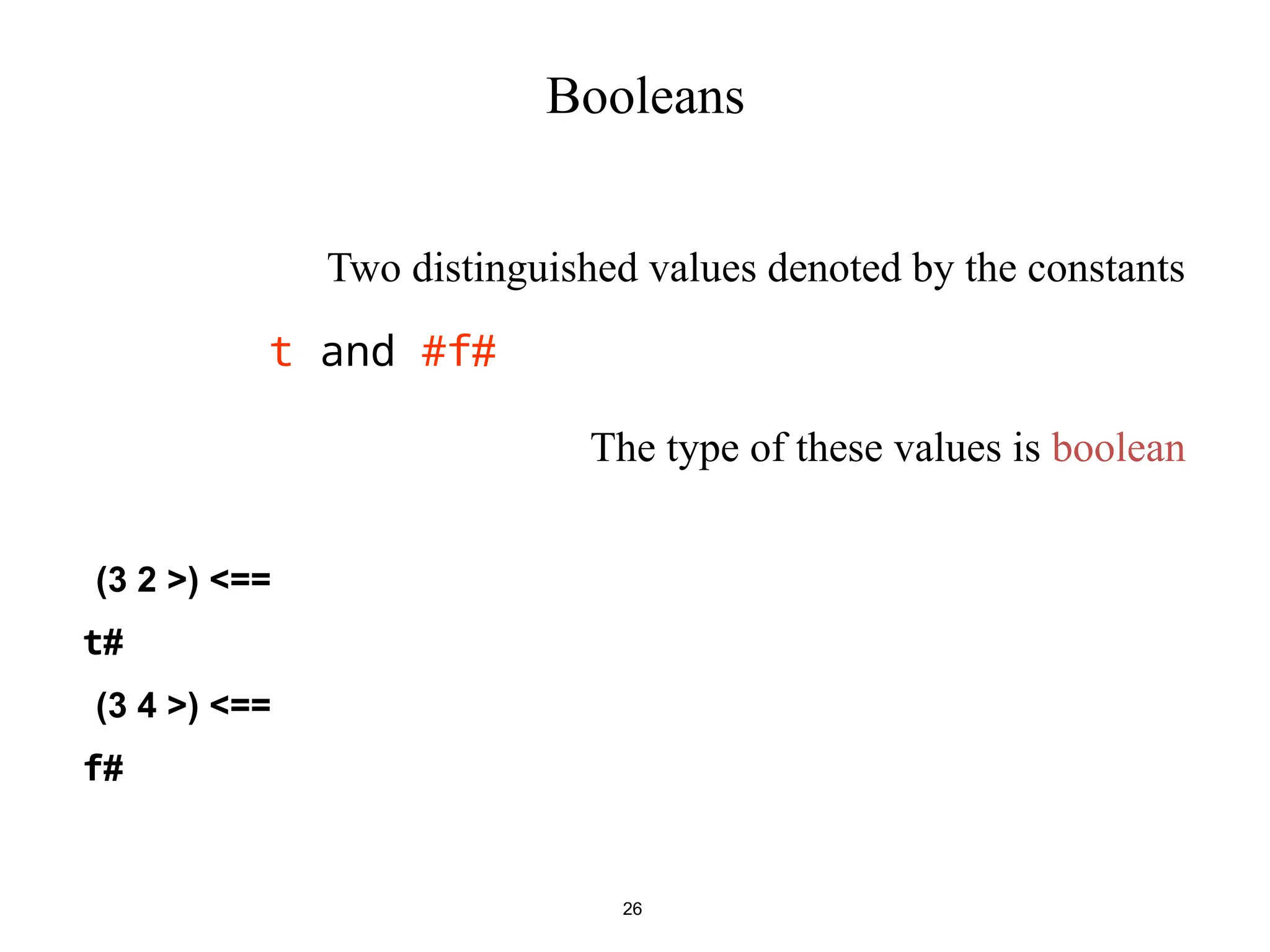
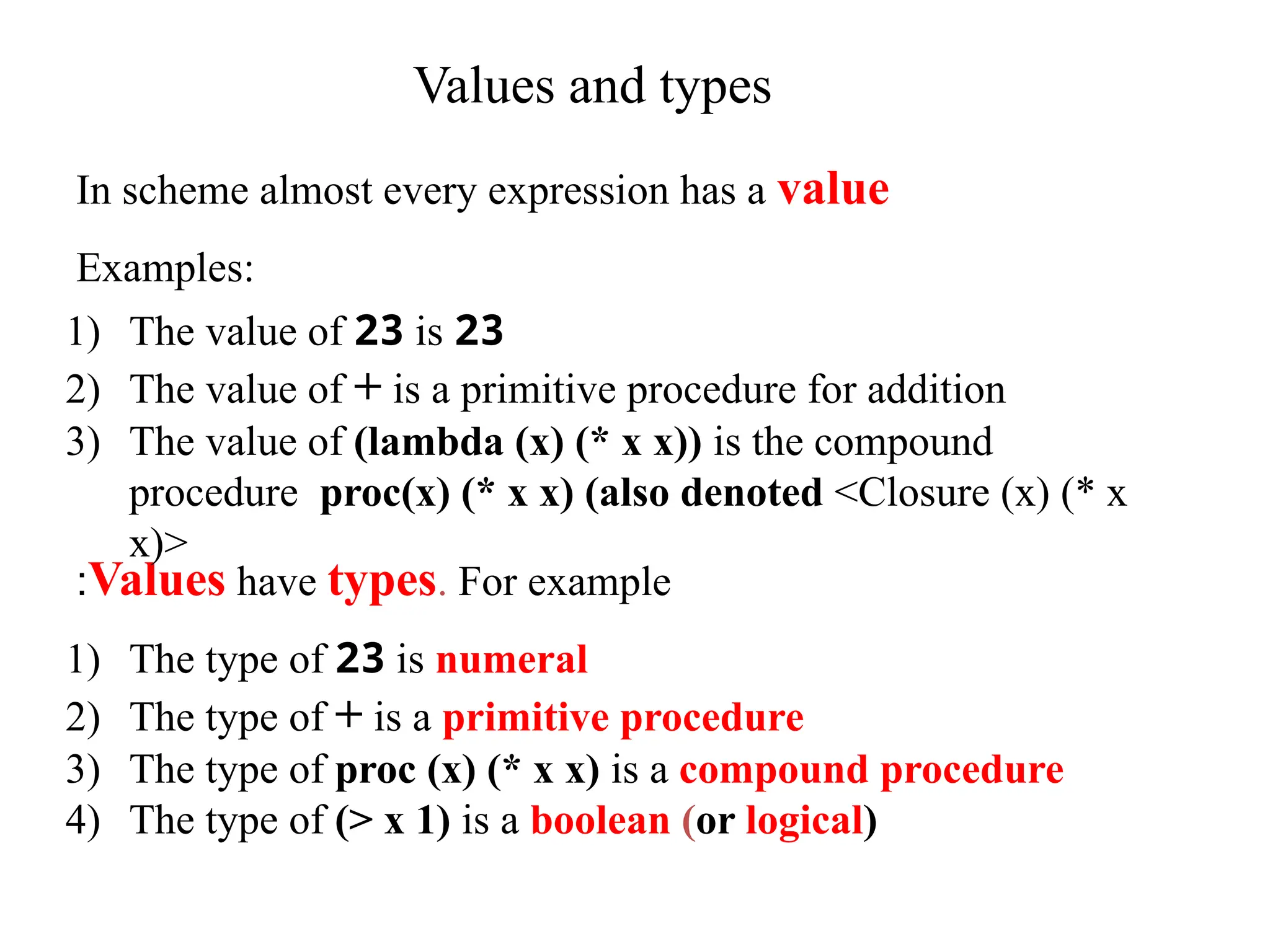
• In scheme most expressions have values
• Not all! Those that don’t usually have side effects
Example : what is the value of the expression
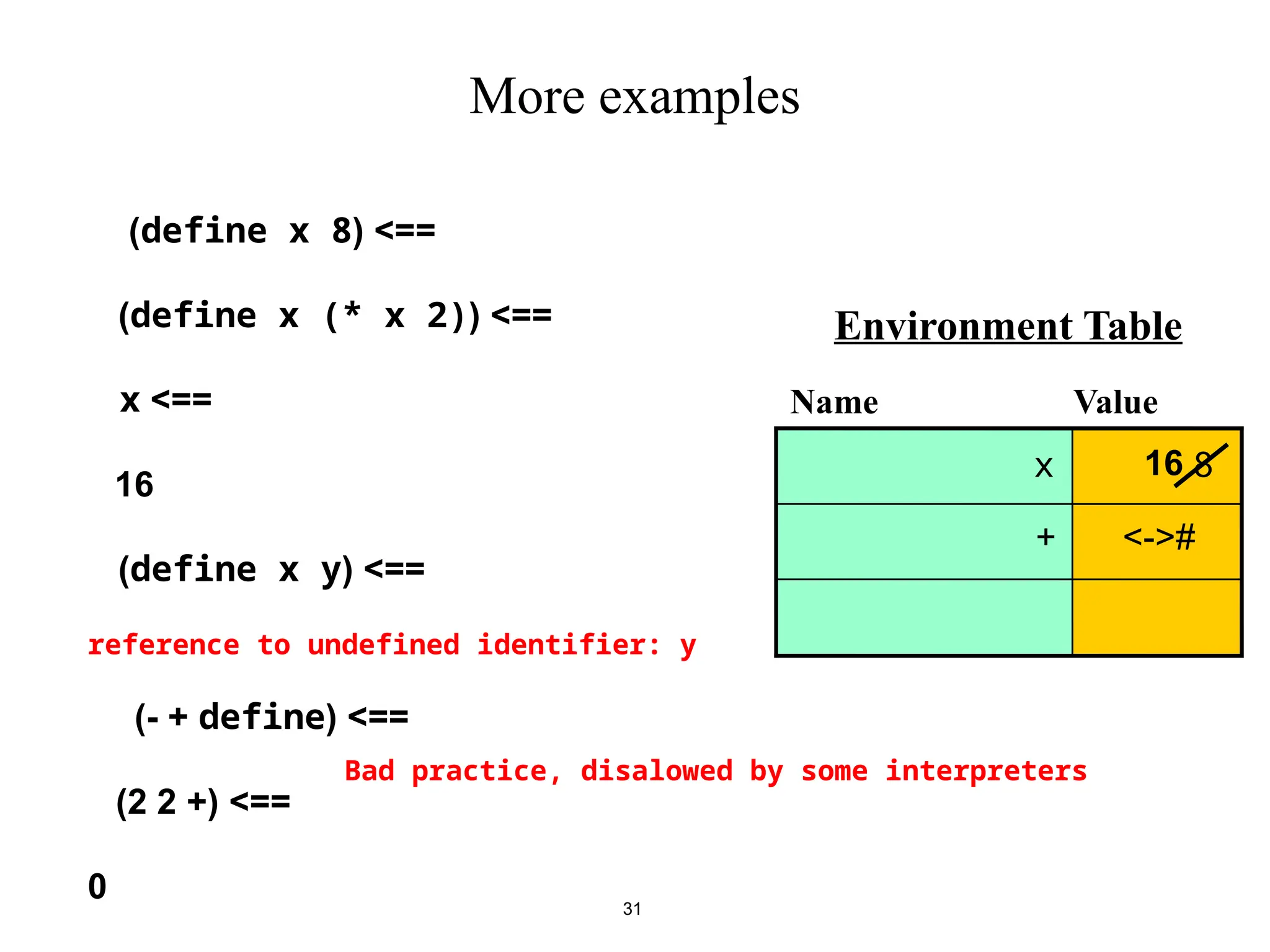
(define x 8)
And of
(display x)
[display is a primitive func., prints the value of its
argument to the screen]
• In scheme, the value of a define, display expression is
“undefined” . This means “implementation-dependent”
• Never write code that relies on such value!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppl1-241212063722-3292e240/75/Principles-of-programming-language-intro-29-2048.jpg)
![Dynamic Typing
• Note that we never specify explicitly types of
variables
• However primitive functions expect values of a
certain type!
– E.g. “+” expects numeral values
• So will our procedures (To be discussed soon)
• The Scheme interpreter checks type correctness
at run-time: dynamic typing
– [As opposed to static typing verified by a compiler ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppl1-241212063722-3292e240/75/Principles-of-programming-language-intro-30-2048.jpg)




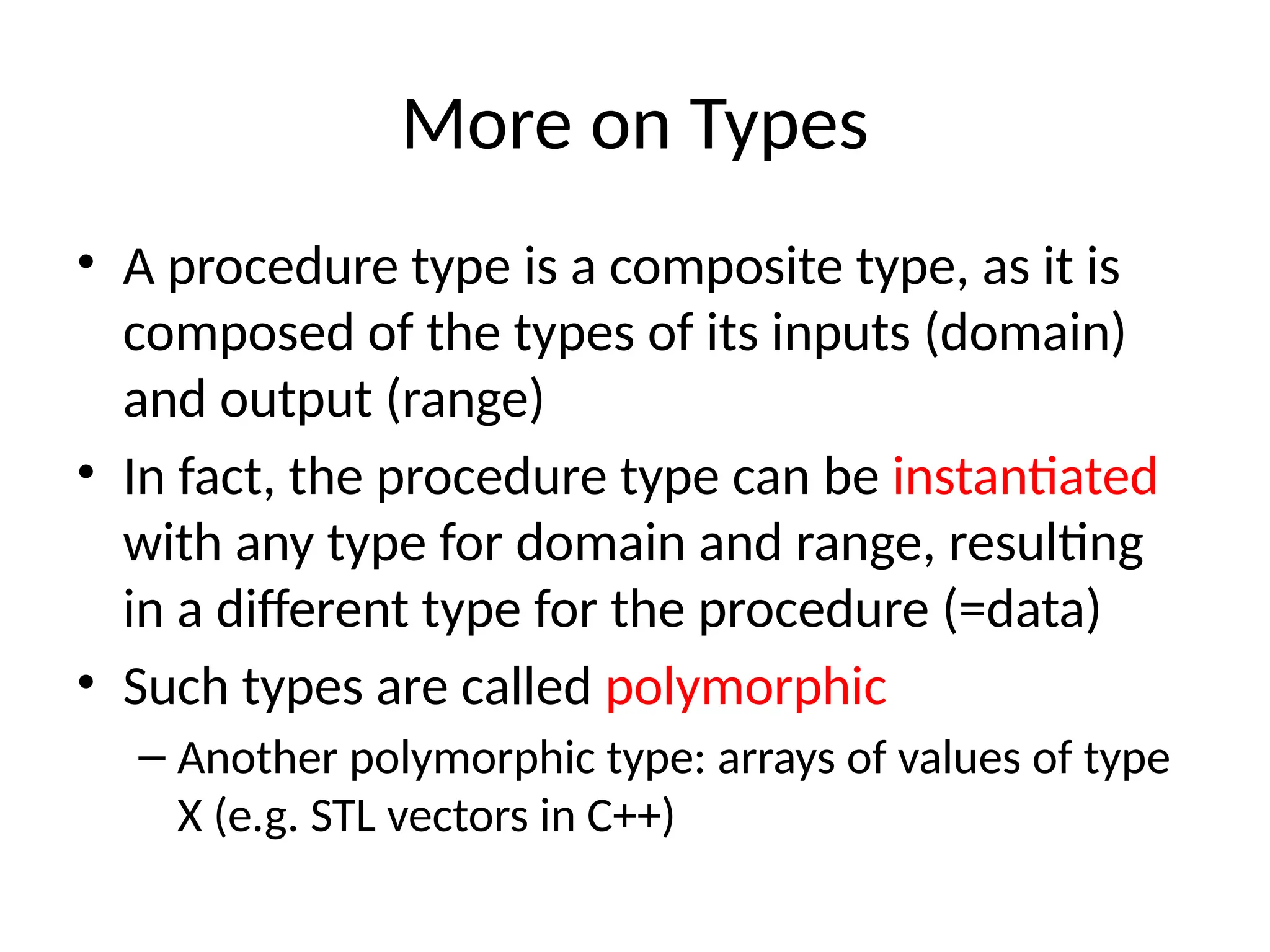
![Type constructor
• Defines a composite type out of other types
• The type constructor for functions is denoted “->”
• Example: [Number X Number –> Number] is the type of all procedures
that get as input two numbers, and return a number
• If all types are allowed we use a type variable:
– [T –> T] is the type of all procs. That return the same type as they get as input
• Note: there is nothing in the syntax for defining types! This is a
convention we manually enforce (for now..).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppl1-241212063722-3292e240/75/Principles-of-programming-language-intro-39-2048.jpg)
![Scheme Type Grammar
Type --> ’Unit’ | Non-Unit [Unit=Void]
Non-unit -> Atomic | Composite | Type-variable
Atomic --> ’Number’ | ’Boolean’ | ’Symbol’
Composite --> Procedure | Union
Procedure --> ’Unit ’->’ Type | ’[’ (Non-Unit ’*’)* Non-
Unit ’->’ Type ’]’
Union --> Type ’union’ Type
Type-variable -> A symbol starting with an upper case
letter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppl1-241212063722-3292e240/75/Principles-of-programming-language-intro-40-2048.jpg)