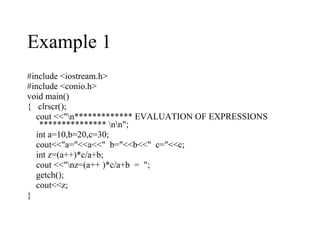
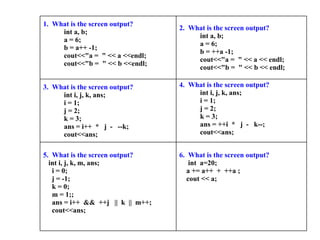
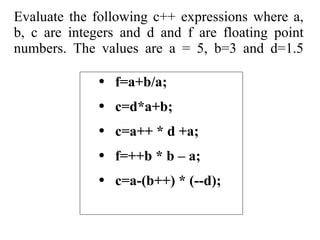
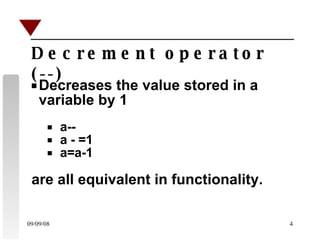
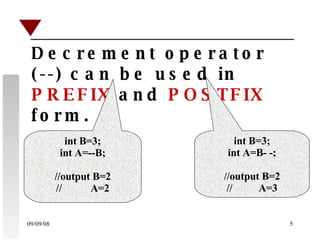
The document discusses increment and decrement operators in C++. It provides examples of using these operators in both prefix and postfix form and evaluates expressions involving these operators. Several examples are given that demonstrate evaluating expressions with increment and decrement operators. Questions involving the output of code snippets using these operators are also provided.
![Priority of Operators and Associativity Left Comma , 11 Right Assignment = += -= *= /= %= 10 Right Conditional ?: 9 Left Logical Op. && || 8 Left Relational Op. == != 7 Left Relational Op. < <= >= > 6 Left Arithmetic Op. + - 5 Left Arithmetic Op. * / % 4 Right ++ -- ! & * (type) + - 3 Left ()[]->sizeof 2 Left Scope :: 1 associativity Description Operator Priority](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prefix-postfix-1220980481065867-9/85/Prefix-Postfix-6-320.jpg)