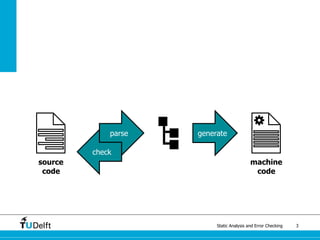
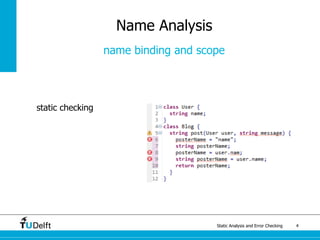
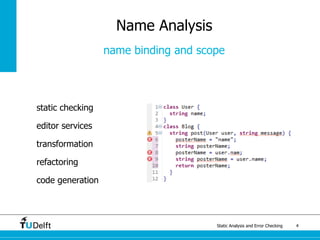
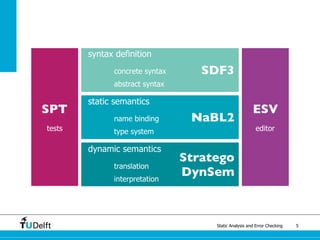
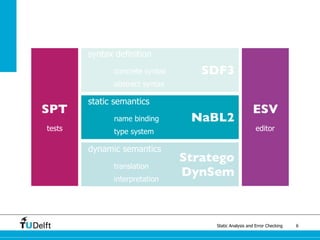
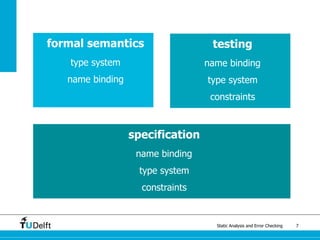
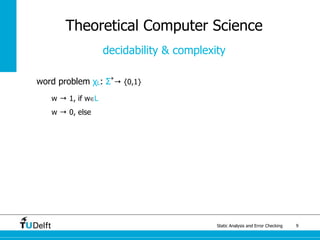
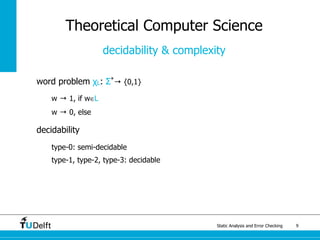
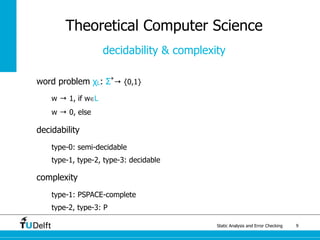
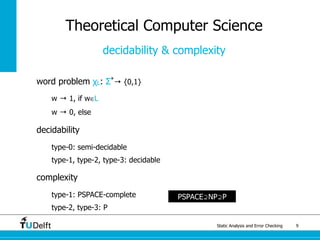
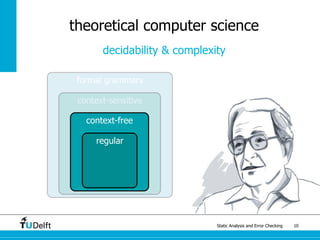
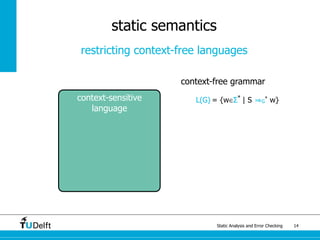
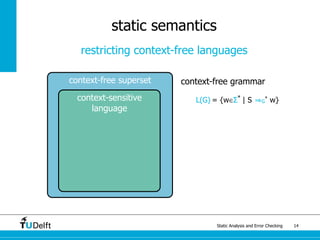
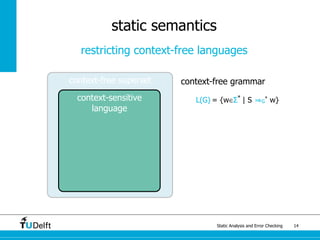
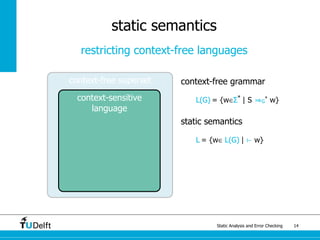
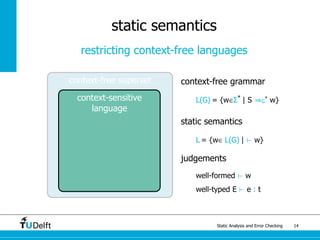
The document discusses static analysis and error checking in compiler construction. It introduces key concepts like parsing source code, performing static semantic checks, and generating machine code. Specific techniques covered include name analysis, type systems, formal semantics, and testing static analysis. Examples are provided using Tiger, a simple imperative language, to illustrate type rules and name binding. The document also discusses theoretical foundations in formal language theory and decidability/complexity.







![Static Analysis and Error Checking 13
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Fac().fac(10));
}
}
class Fac {
public int fac(int num) {
int num_aux;
if (num < 1)
num_aux = 1;
else
num_aux = num * this.fac(num - 1);
return num_aux;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticanalysis-170116145405/85/Static-Analysis-29-320.jpg)

![Static Analysis and Error Checking 18
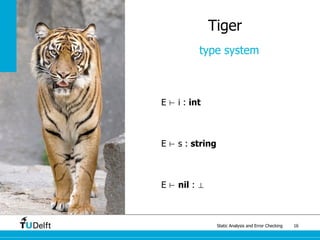
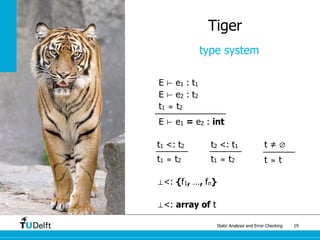
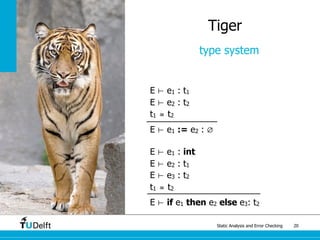
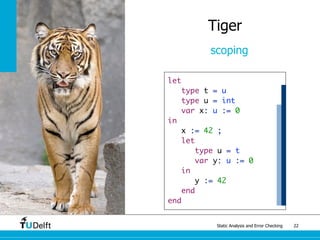
Tiger
type system
E ⊢ e1 : int
E ⊢ e2 : int
E ⊢ e1 + e2 : int
E ⊢ e1 : int
E ⊢ e2 : int
E ⊢ e1 < e2 : int
E ⊢ e1 : string
E ⊢ e2 : string
E ⊢ e1 < e2 : int
E ⊢ e1 : array of t
E ⊢ e2 : int
E ⊢ e1[e2] : t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticanalysis-170116145405/85/Static-Analysis-38-320.jpg)







![Static Analysis and Error Checking 26
test outer name [[
let type t = u
type [[u]] = int
var x: [[u]] := 0
in
x := 42 ;
let type u = t
var y: u := 0
in
y := 42
end
end
]] resolve #2 to #1
test inner name [[
let type t = u
type u = int
var x: u := 0
in
x := 42 ;
let type [[u]] = t
var y: [[u]] := 0
in
y := 42
end
end
]] resolve #2 to #1
Testing
name binding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticanalysis-170116145405/85/Static-Analysis-50-320.jpg)
![Static Analysis and Error Checking 27
test integer constant [[
let type t = u
type u = int
var x: u := 0
in
x := 42 ;
let type u = t
var y: u := 0
in
y := [[42]]
end
end
]] run get-type to IntTy()
test variable reference [[
let type t = u
type u = int
var x: u := 0
in
x := 42 ;
let type u = t
var y: u := 0
in
y := [[x]]
end
end
]] run get-type to IntTy()
Testing
type system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticanalysis-170116145405/85/Static-Analysis-51-320.jpg)
![Static Analysis and Error Checking 28
test undefined variable [[
let type t = u
type u = int
var x: u := 0
in
x := 42 ;
let type u = t
var y: u := 0
in
y := [[z]]
end
end
]] 1 error
test type error [[
let type t = u
type u = string
var x: u := 0
in
x := 42 ;
let type u = t
var y: u := 0
in
y := [[x]]
end
end
]] 1 error
Testing
constraints](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticanalysis-170116145405/85/Static-Analysis-52-320.jpg)