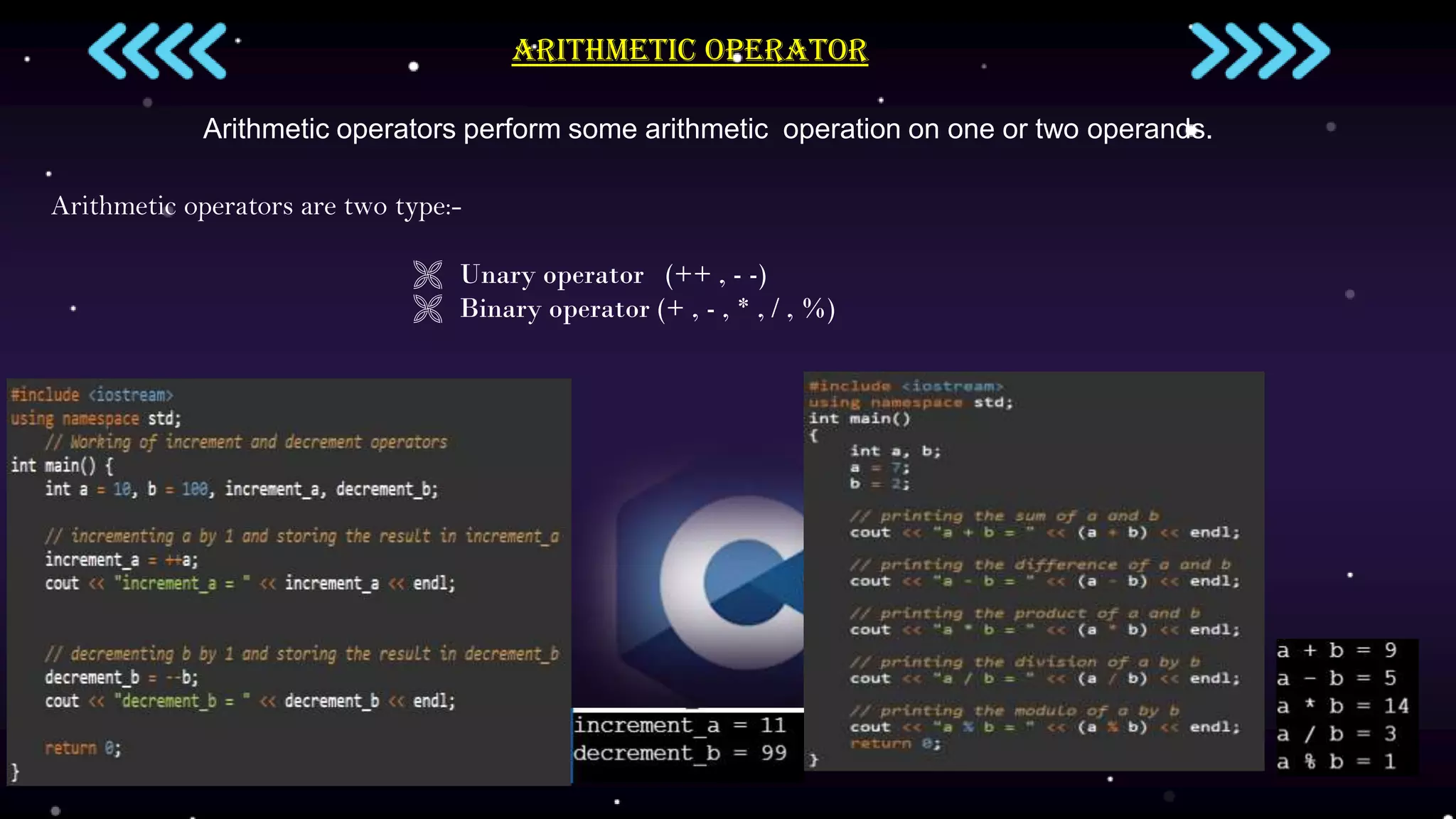
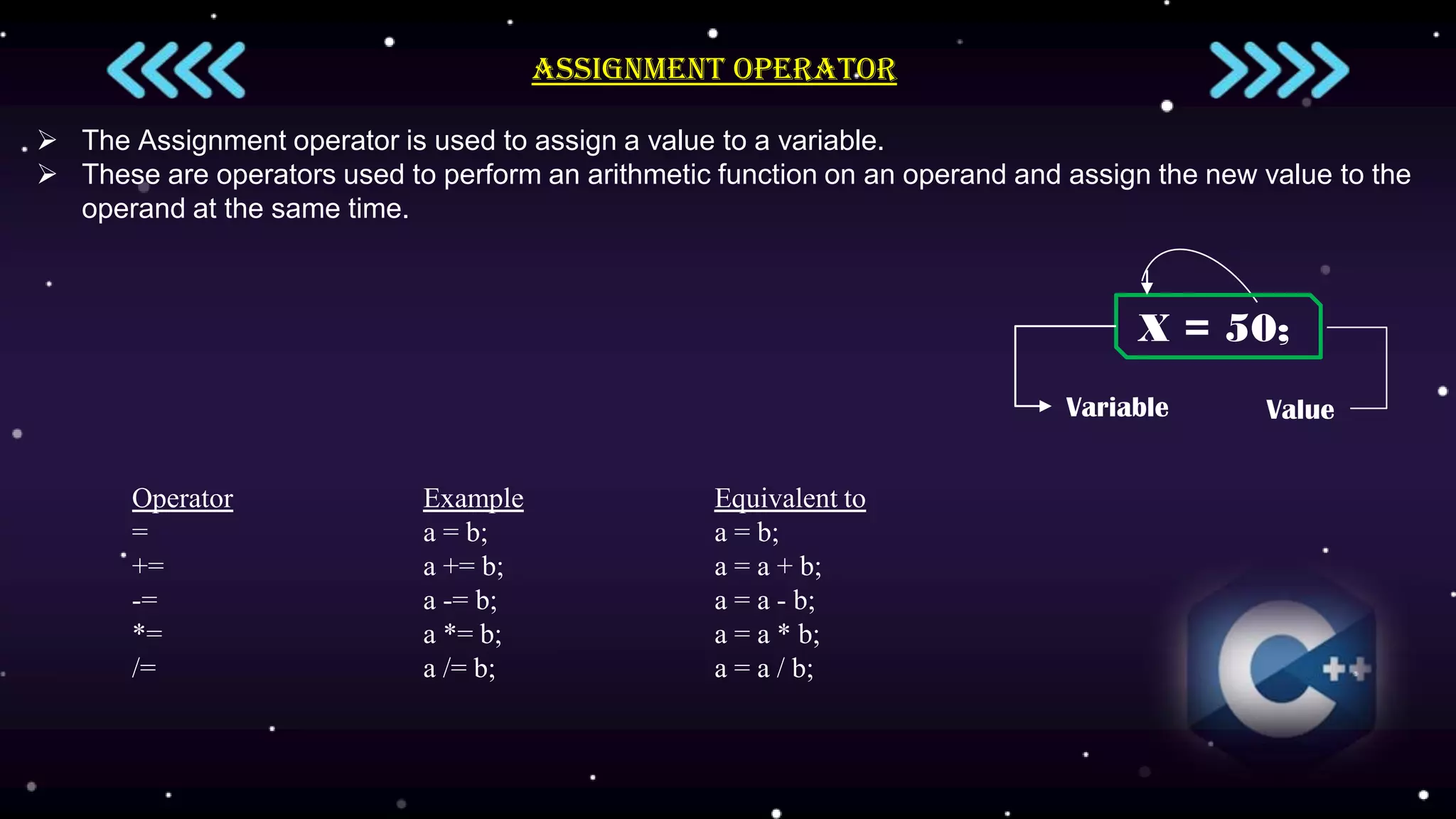
Operators are symbols that perform computations on operands and are essential to C++ programming. There are several types of operators including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, and assignment. Arithmetic operators perform math operations, relational operators define relations between operands and return Boolean values, logical operators combine conditions and return Boolean values, bitwise operators perform bit-level operations, and assignment operators assign values to variables.