The document discusses hip dislocations, including:
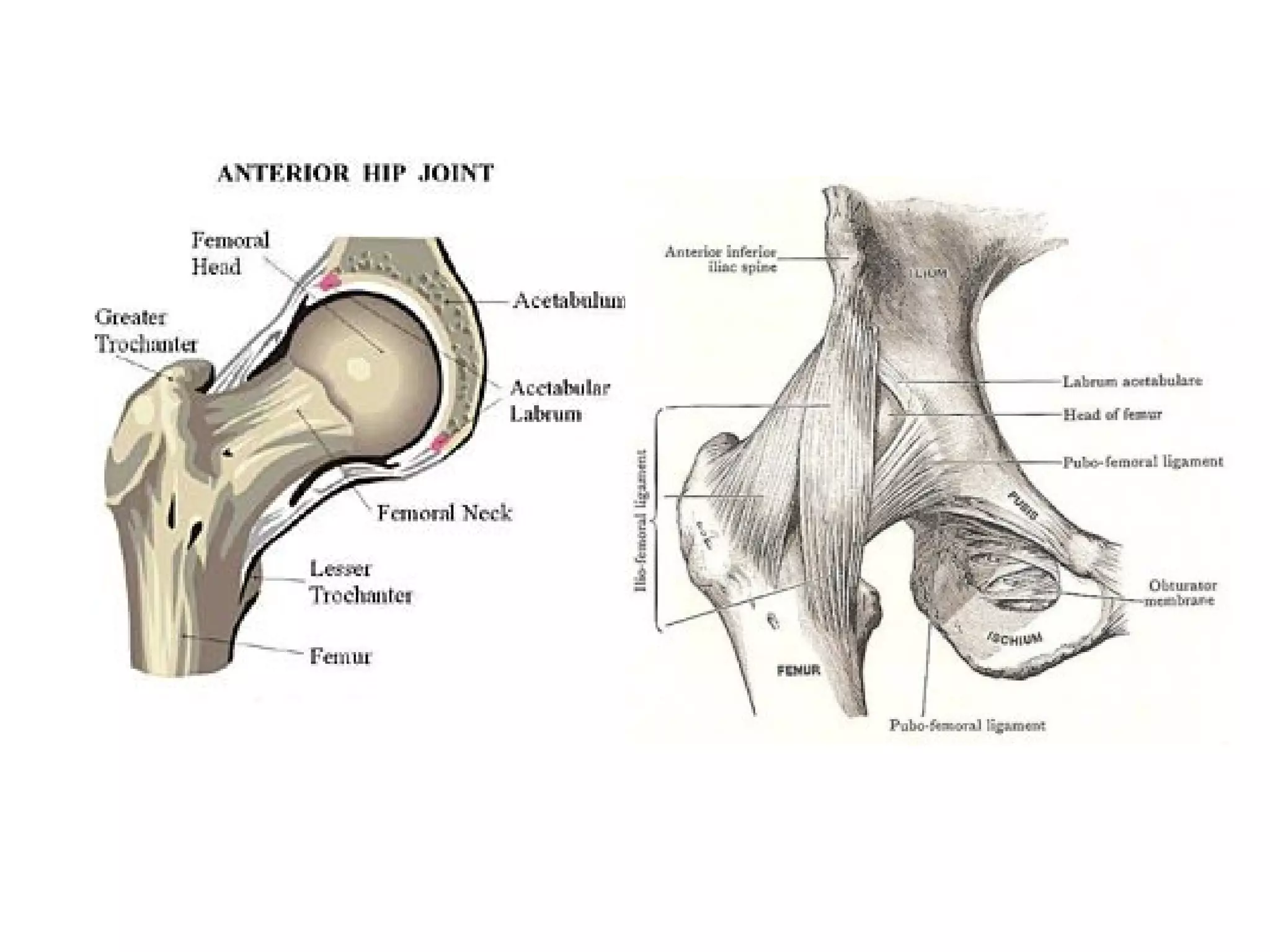
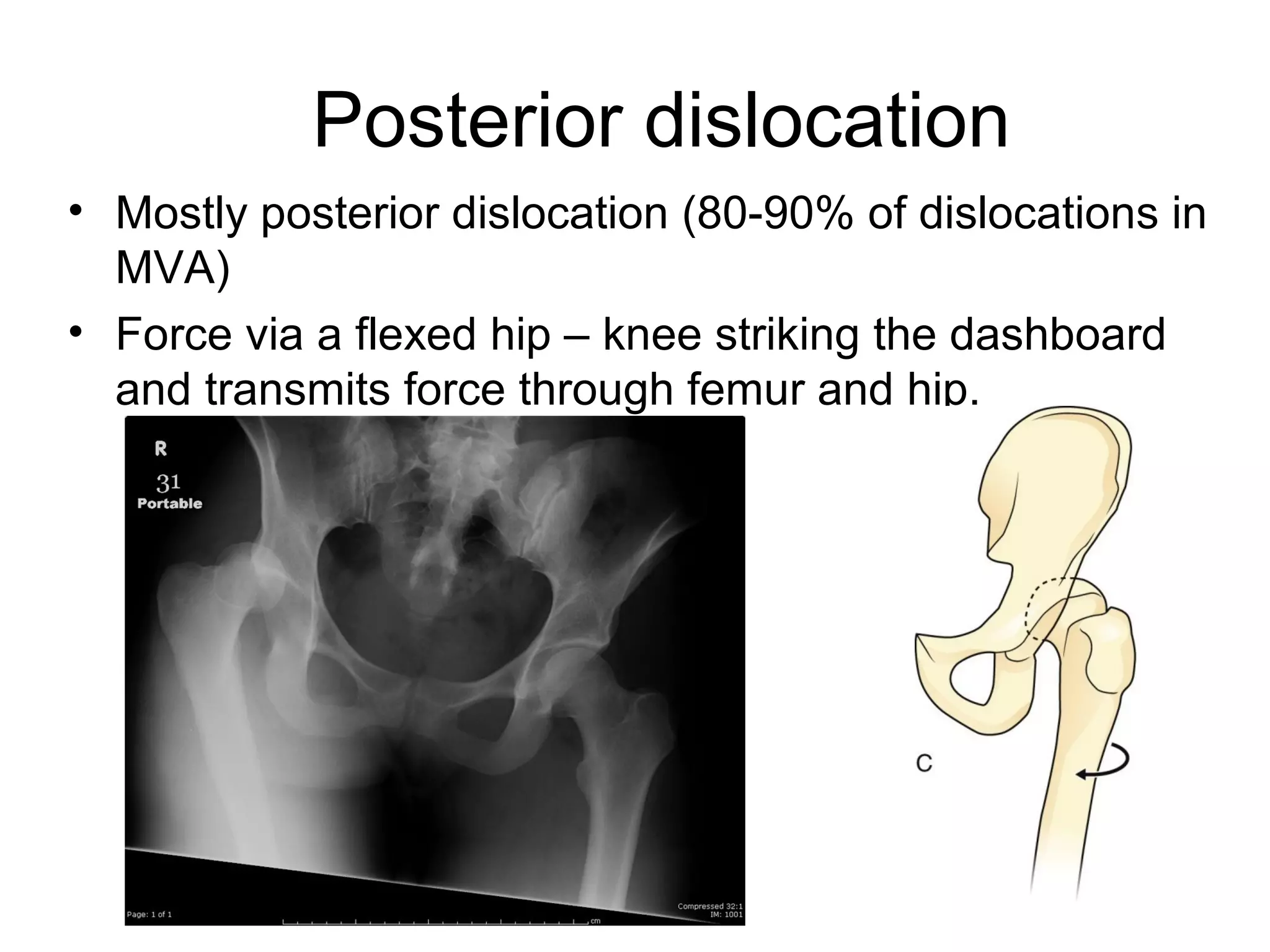
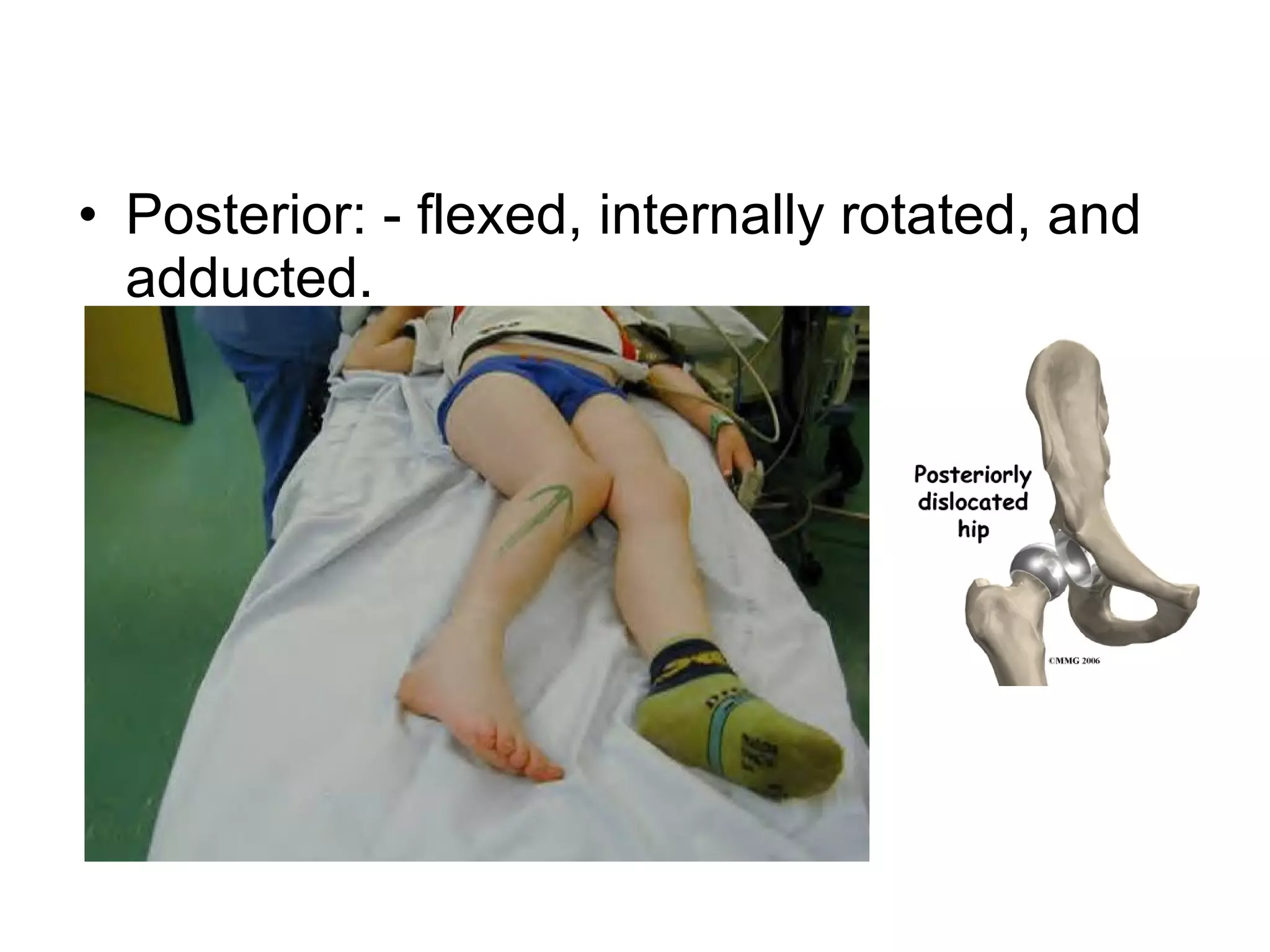
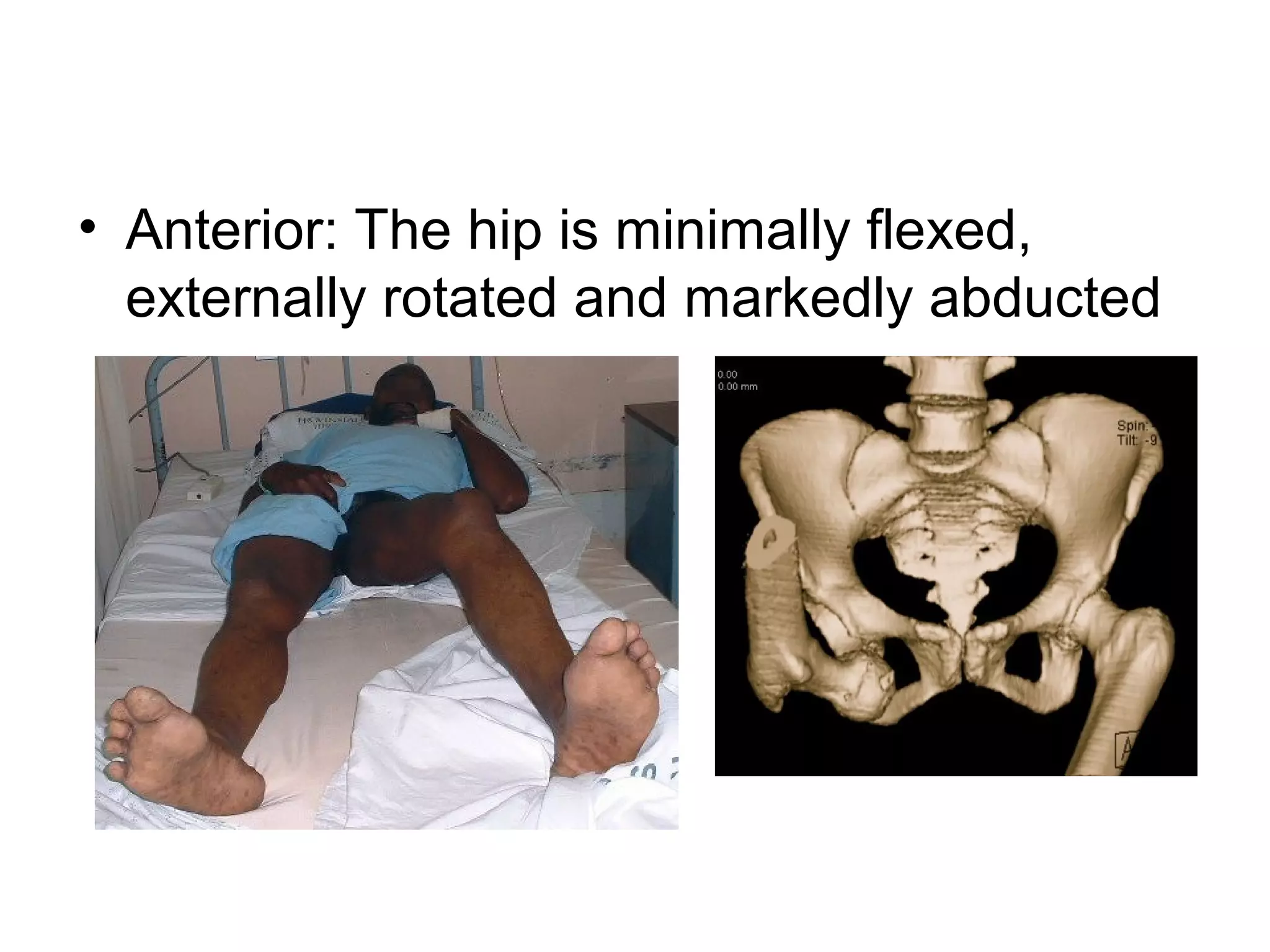
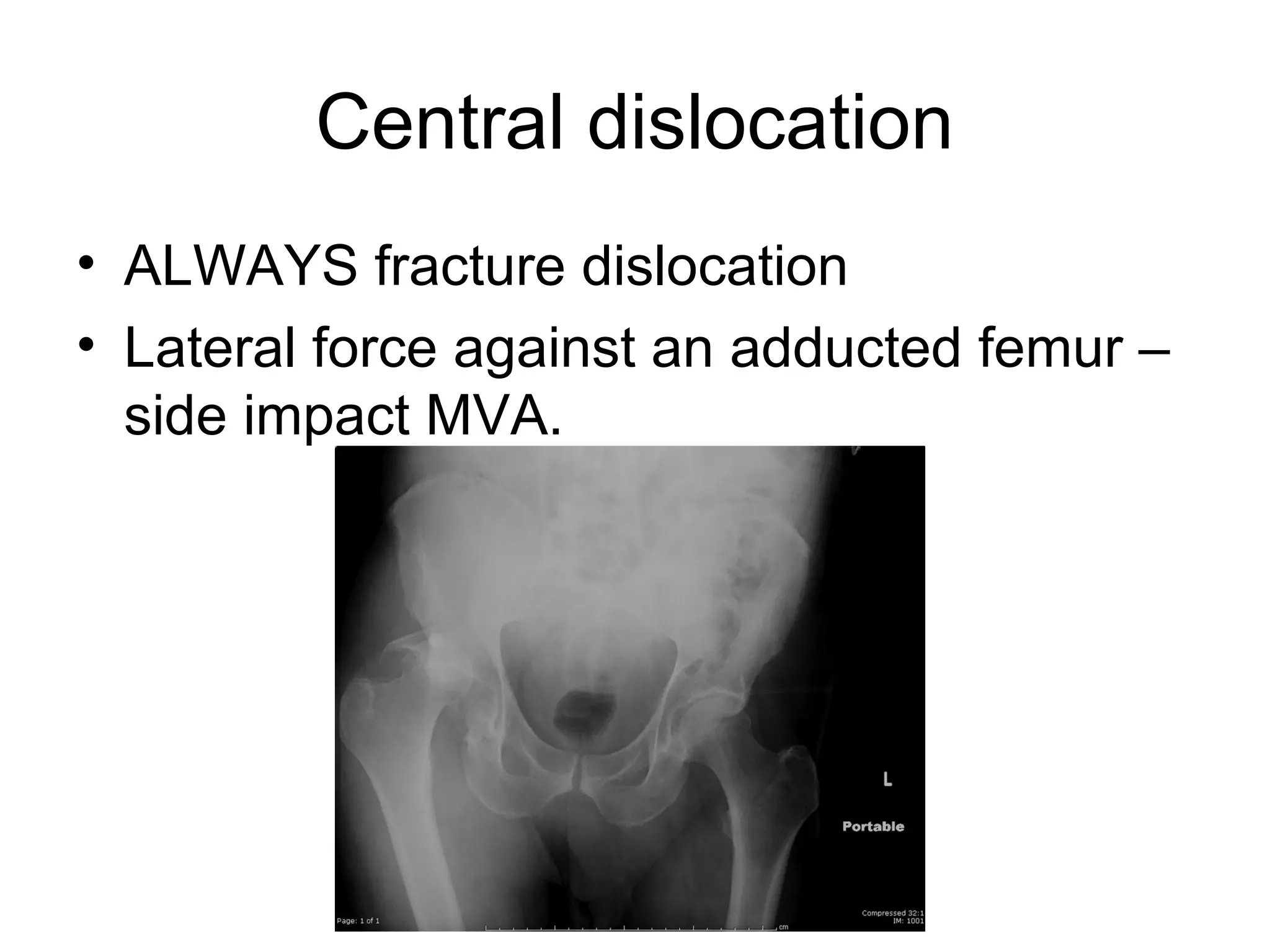
1. Hip dislocations can be posterior, anterior, or central depending on the direction of force and position of the femoral head. Posterior dislocations are most common from force in flexion.
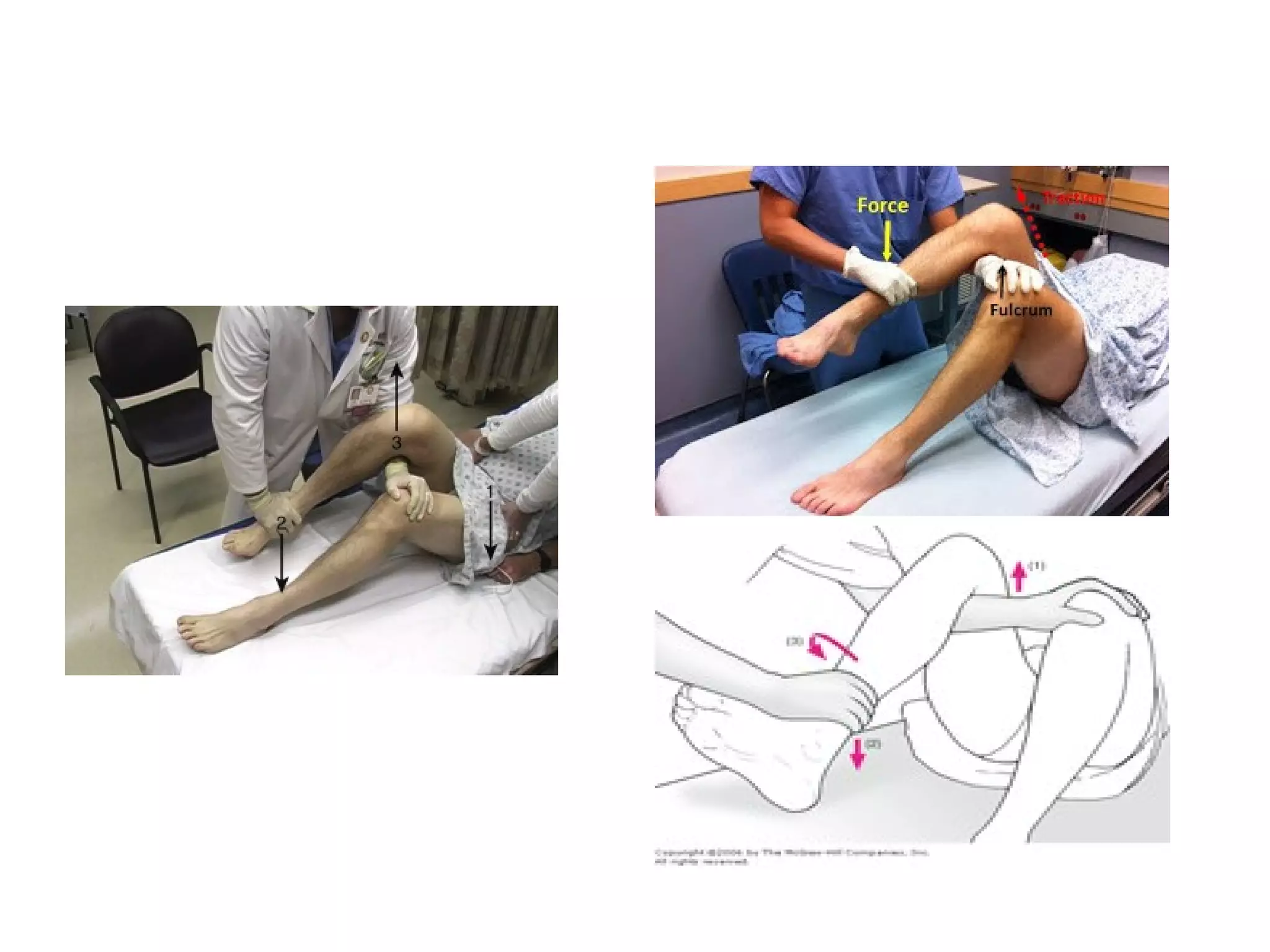
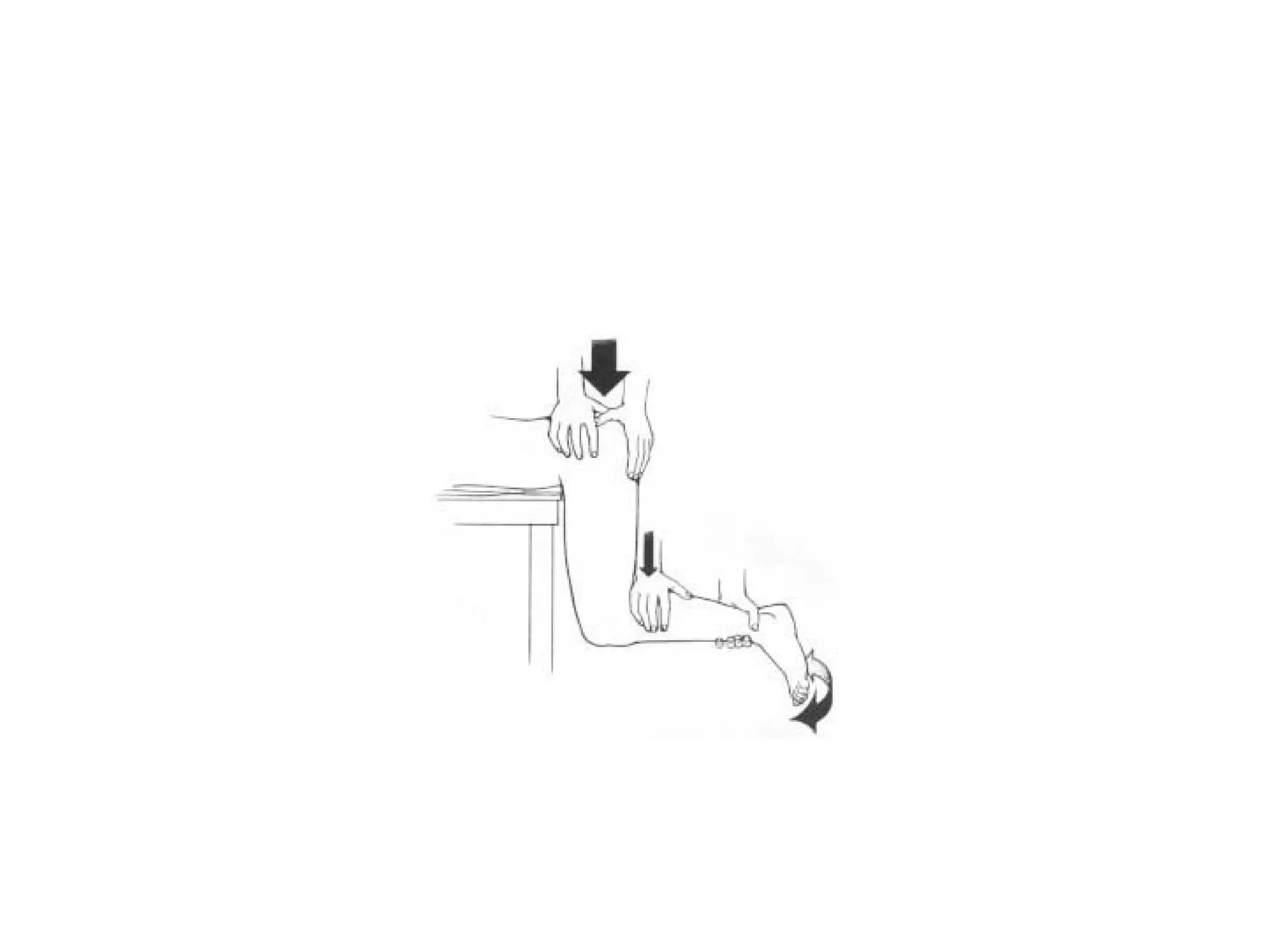
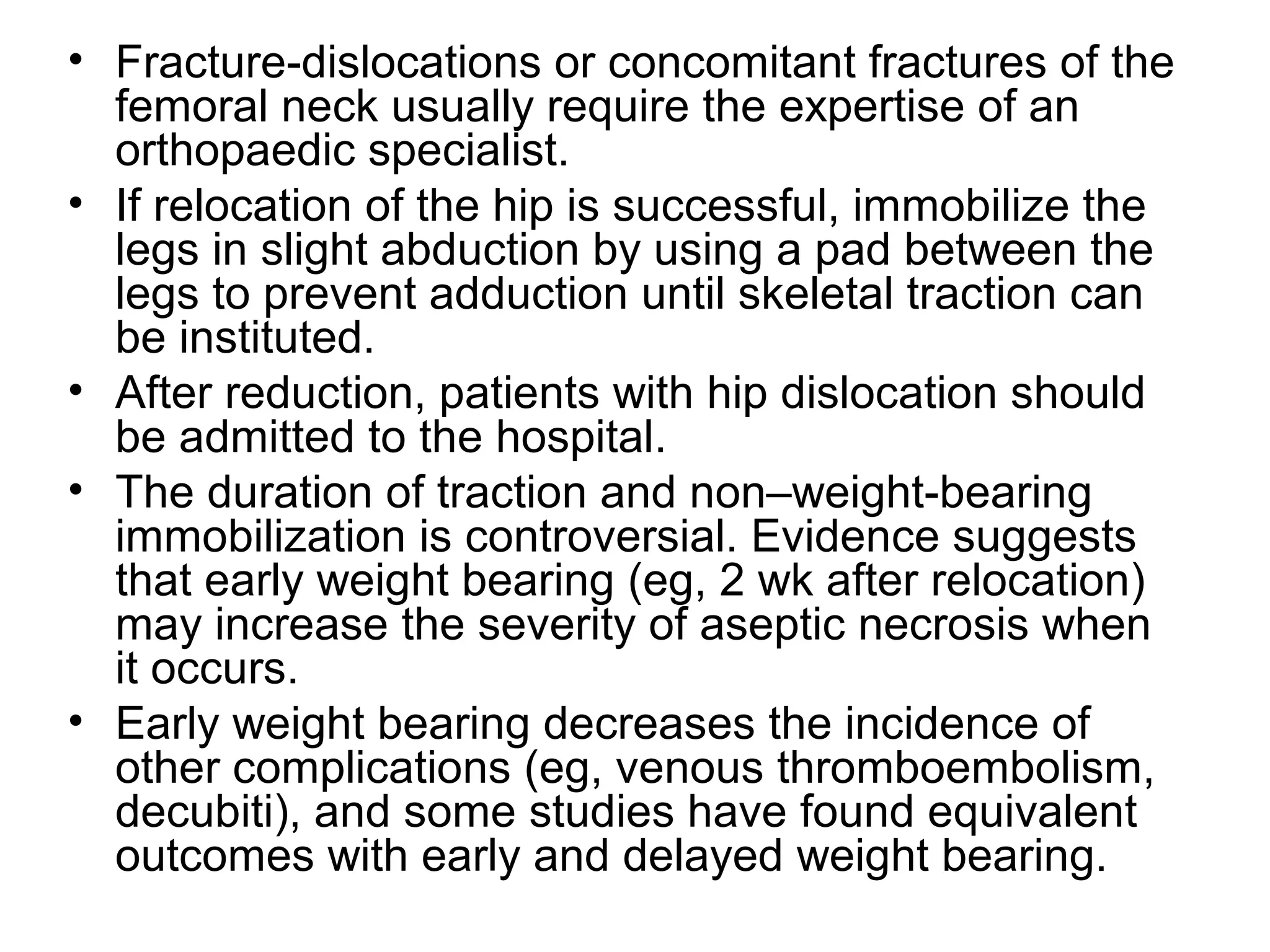
2. Treatment involves closed or open reduction depending on factors like fracture involvement. Closed reduction techniques like Whistler's apply traction and rotational forces to relocate the femoral head.
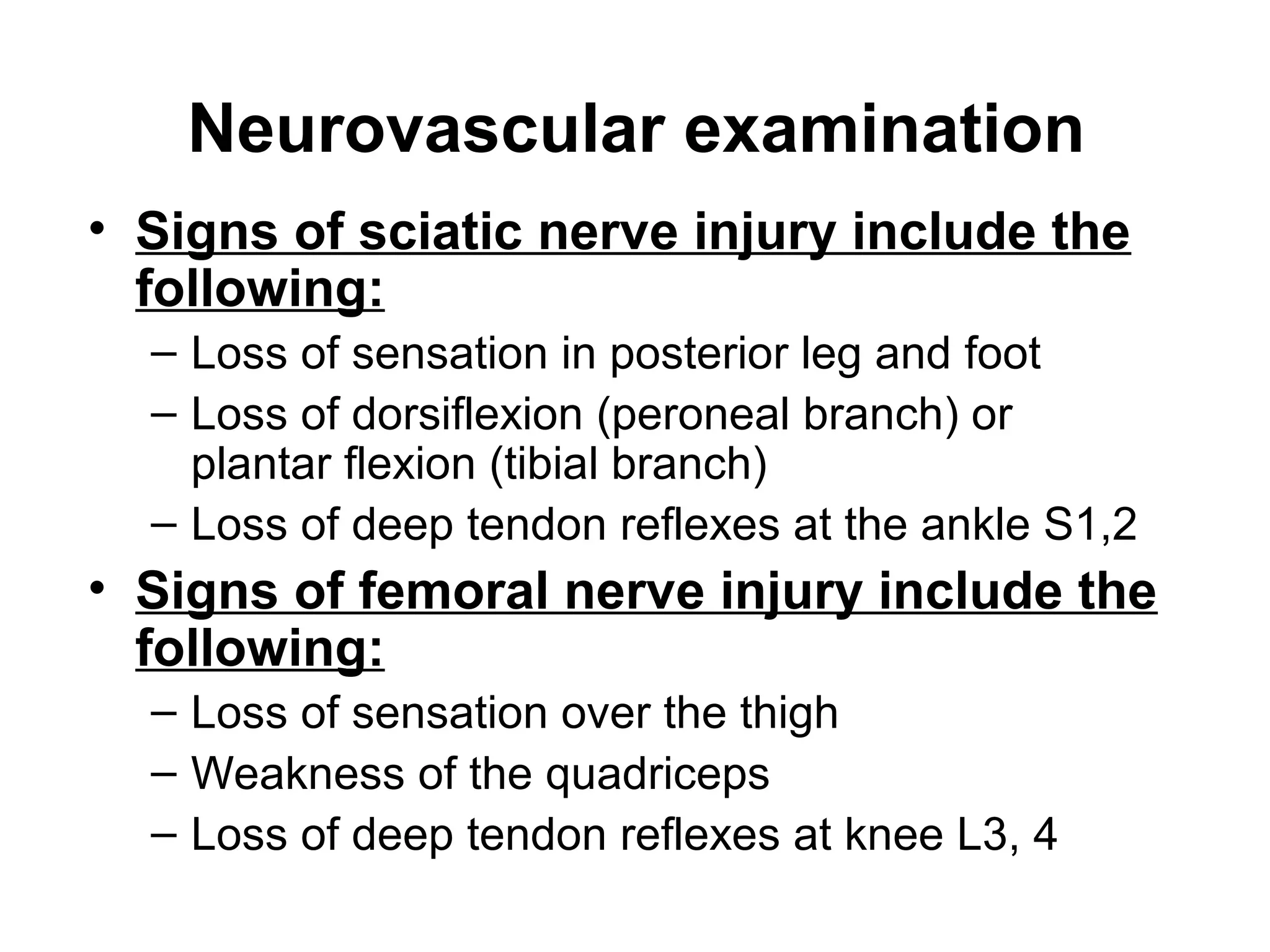
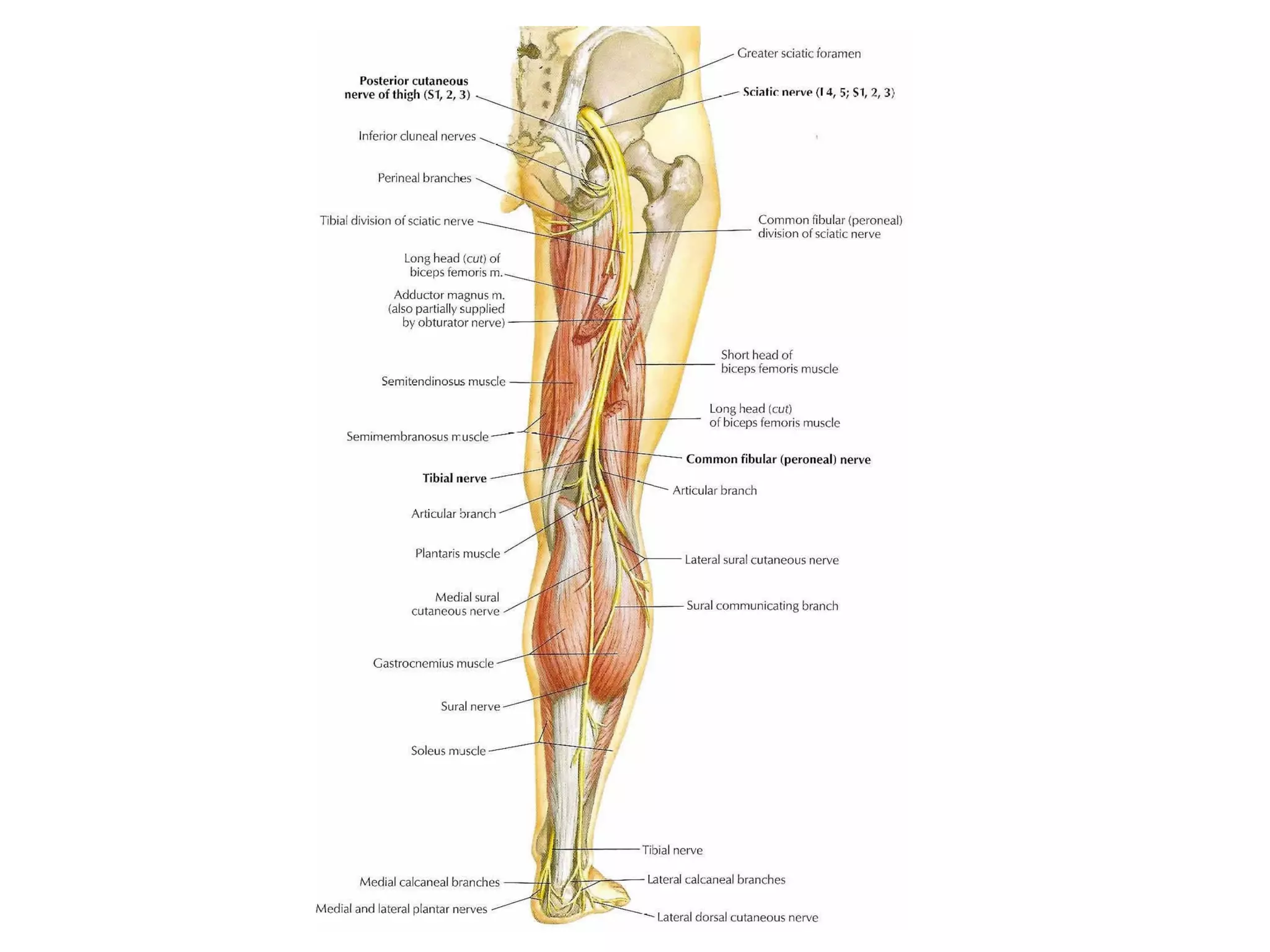
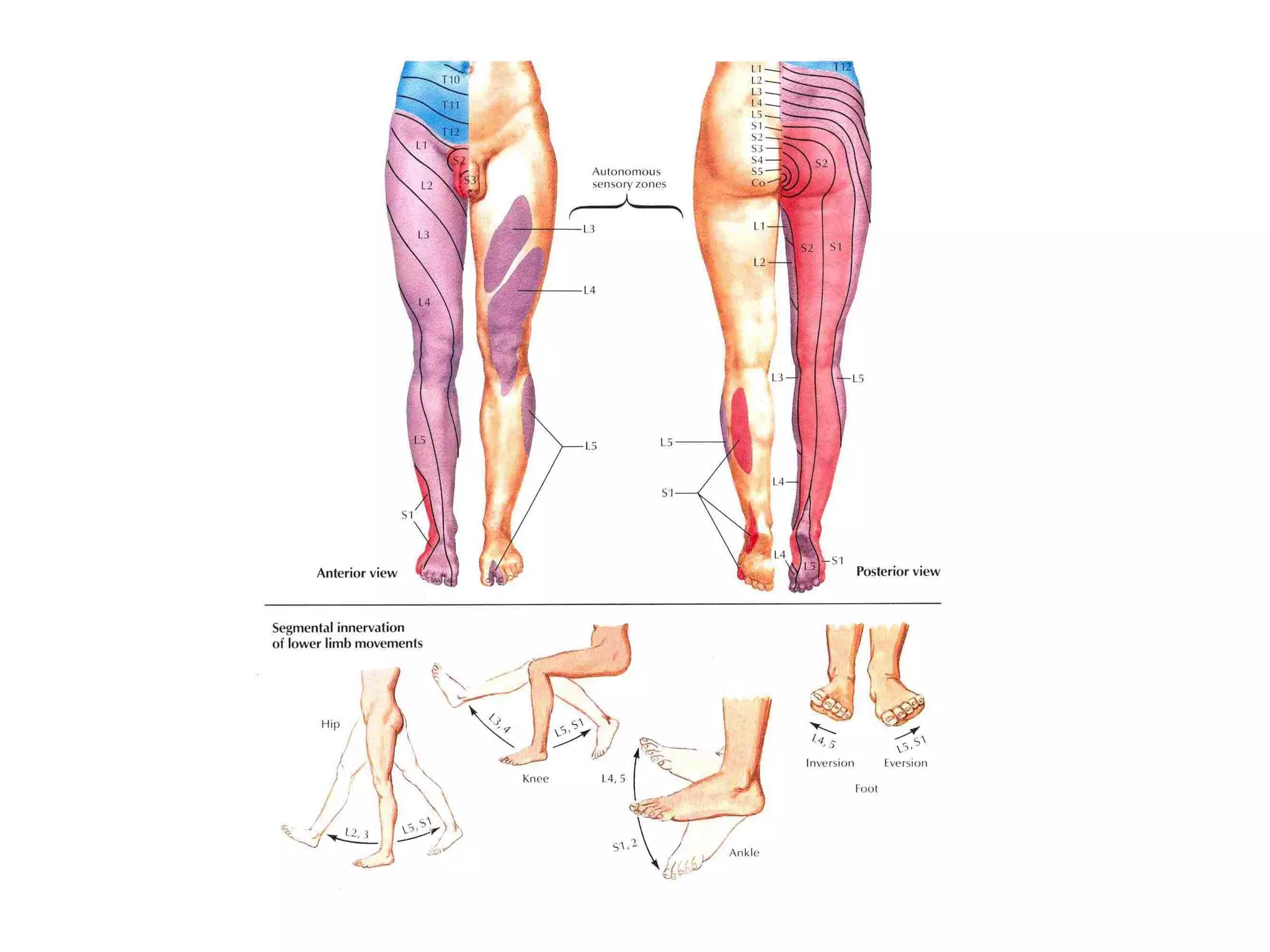
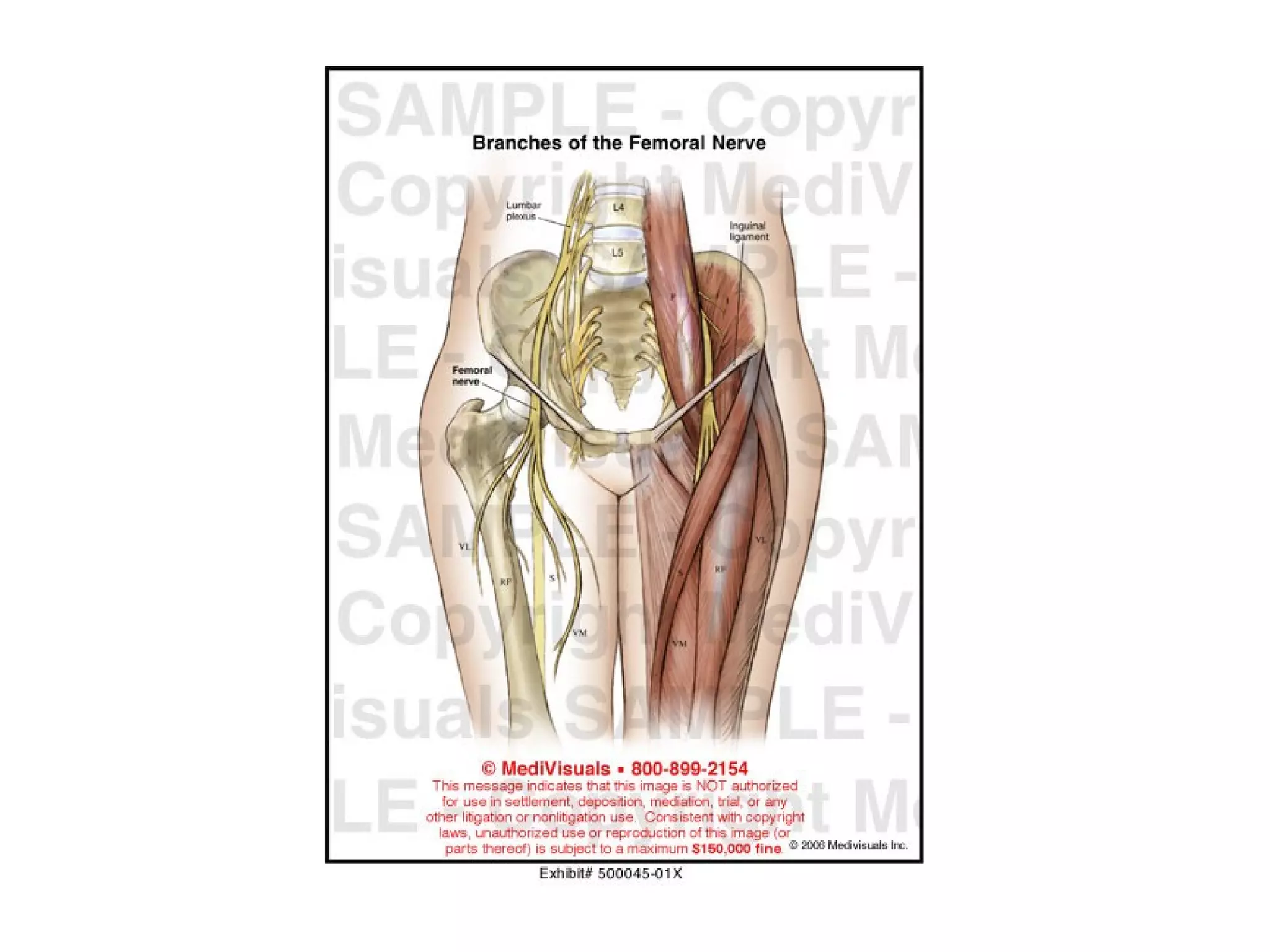
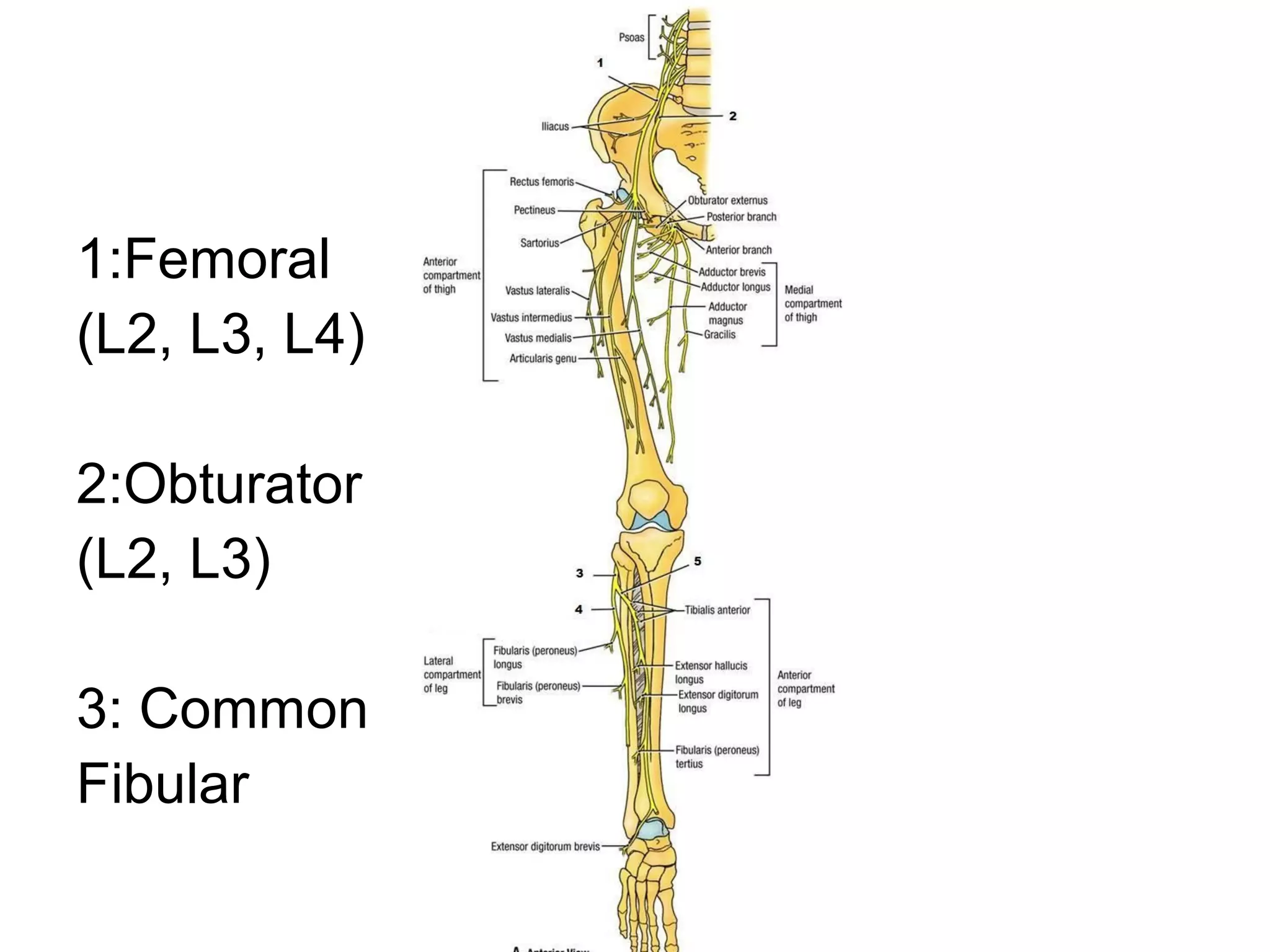
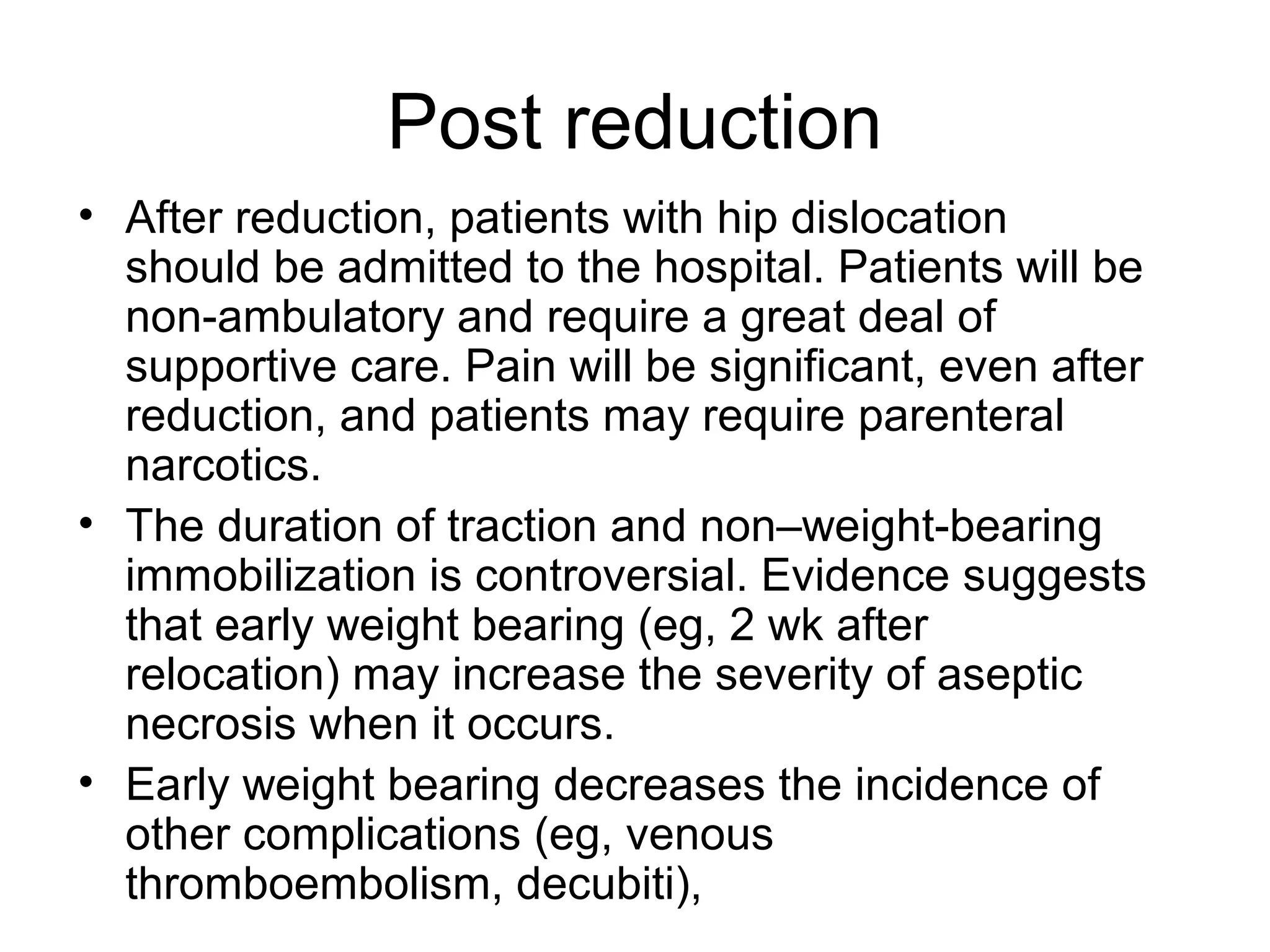
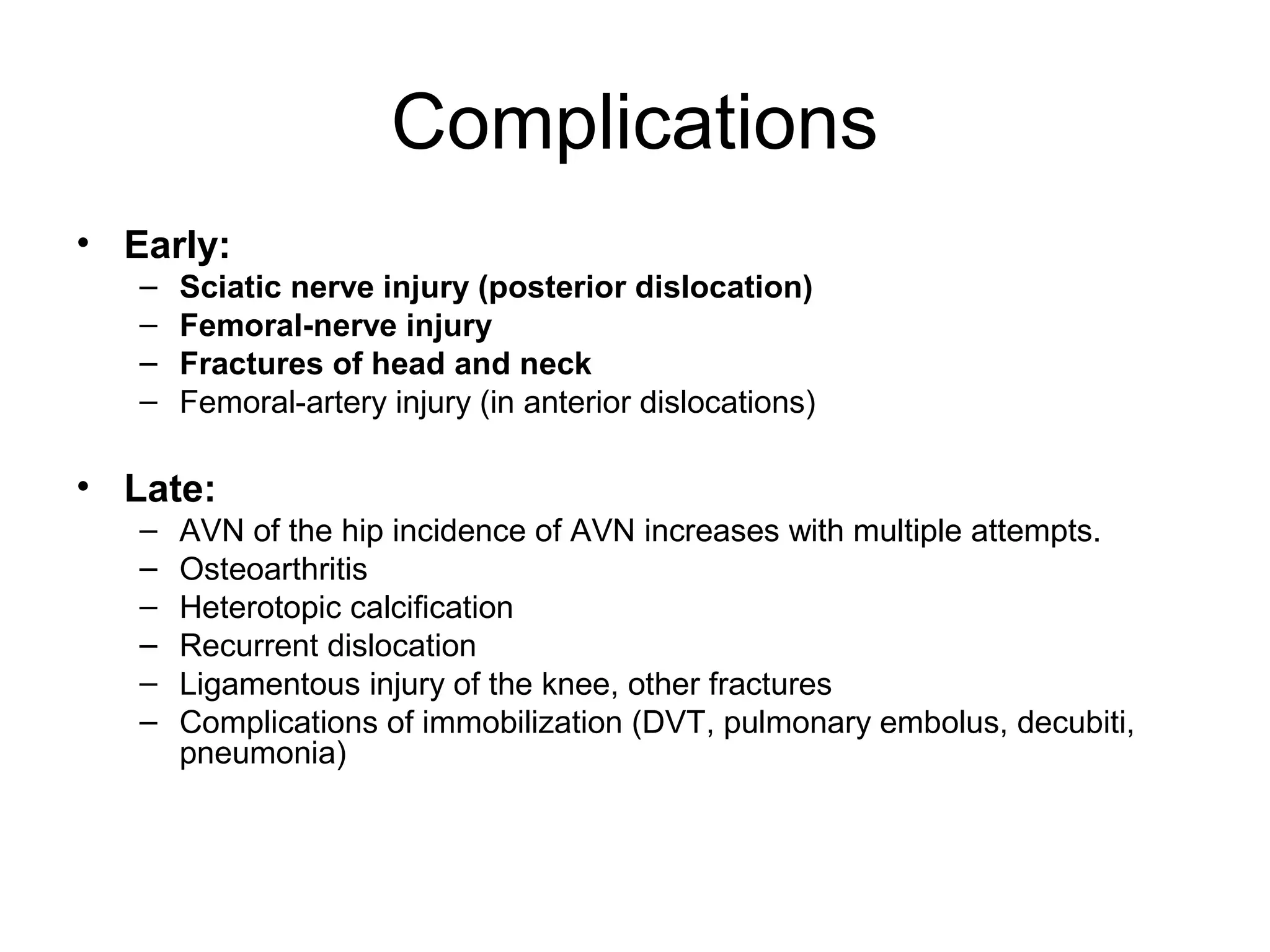
3. After reduction, patients require hospitalization, traction, and delayed weight bearing to prevent complications like avascular necrosis which can lead to osteoarthritis. Early complications include nerve injuries while late complications involve bone and joint problems.