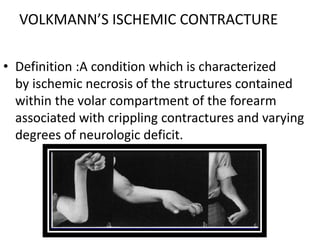
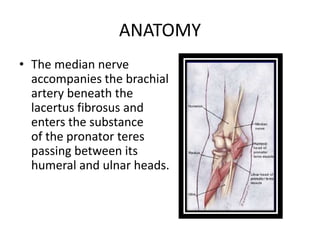
Volkmann's ischemic contracture is caused by compartment syndrome leading to muscle and nerve necrosis in the forearm. It is characterized by contractures and neurological deficits. The condition typically results from untreated injuries that increase forearm compartment pressure, blocking blood flow. Clinical signs include pain, paresthesia, loss of pulses, and contractures. Treatment involves urgent fasciotomy to release pressure if compartment syndrome is present. Established contractures may be treated conservatively or with muscle sliding procedures like Inglis-Cooper or Williams-Haddad to release contracted flexor muscles and tendons.