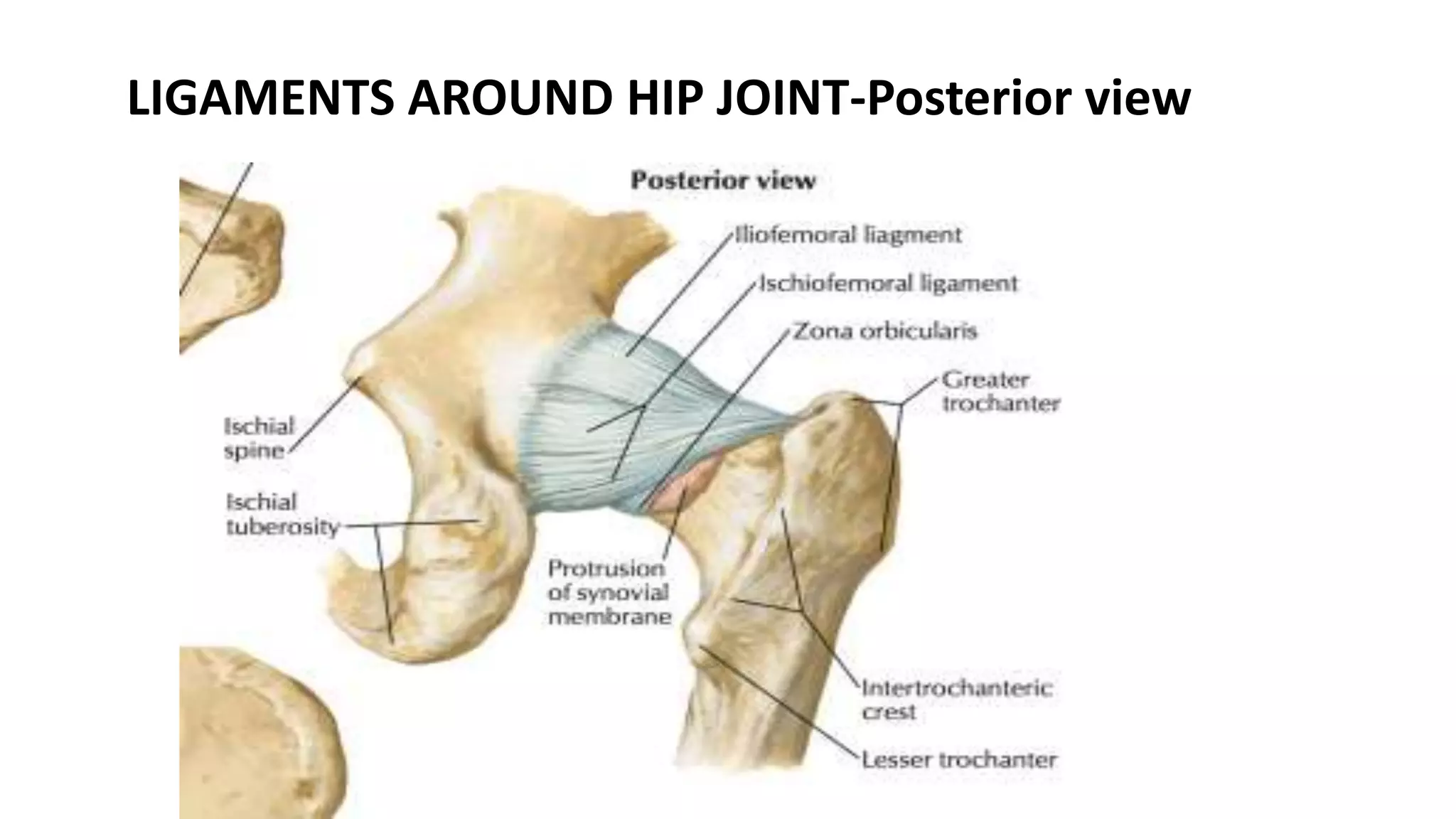
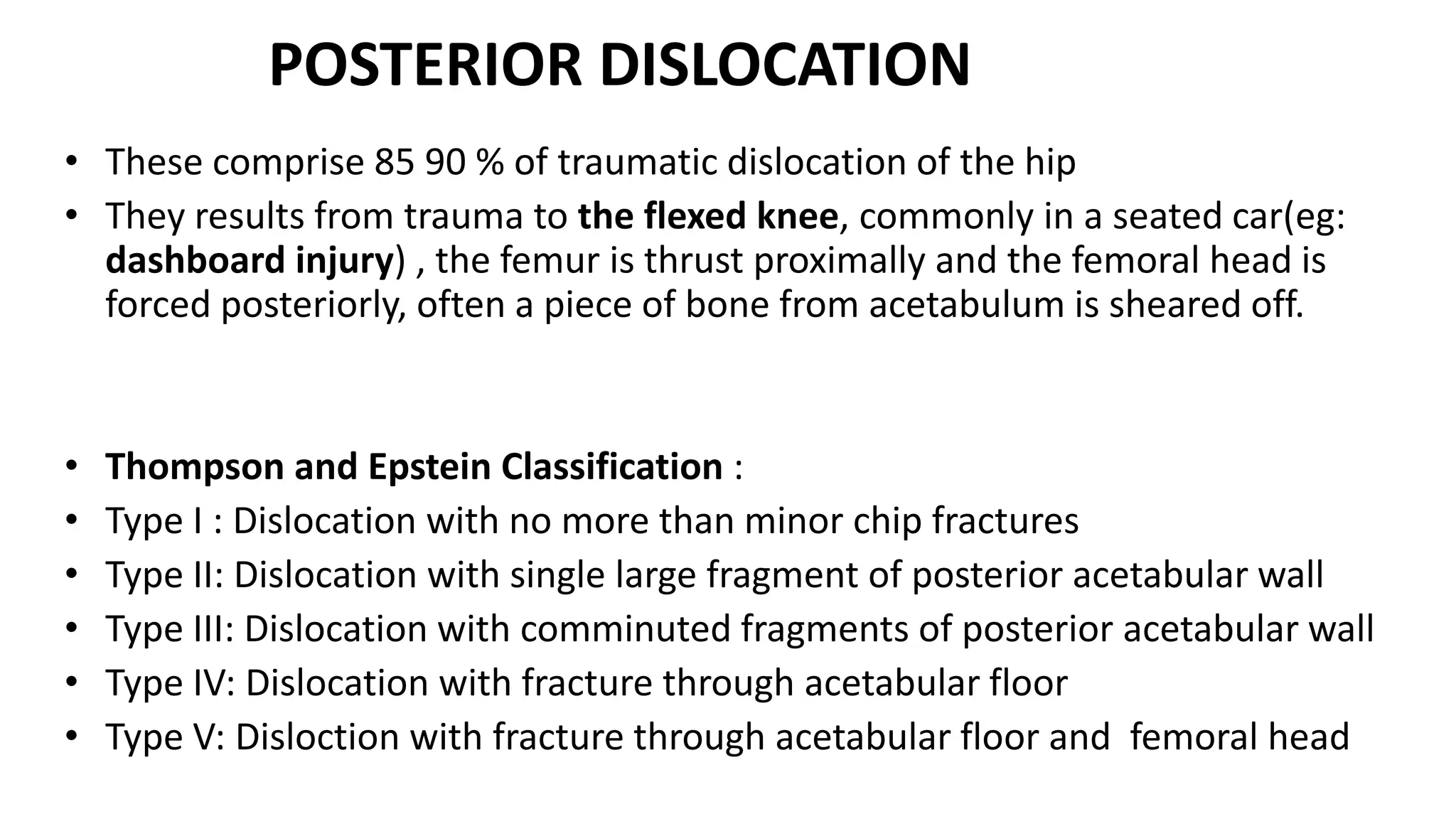
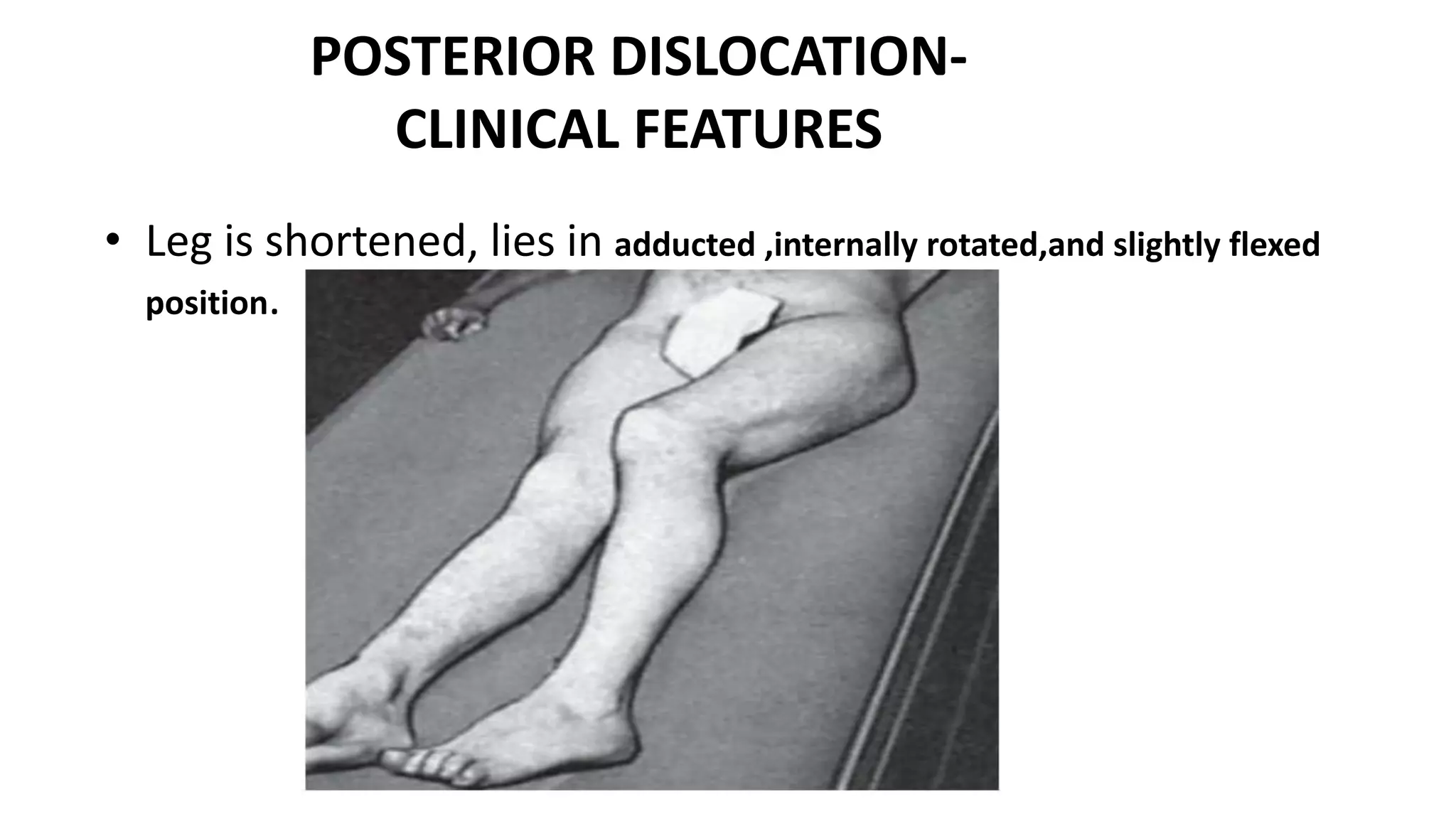
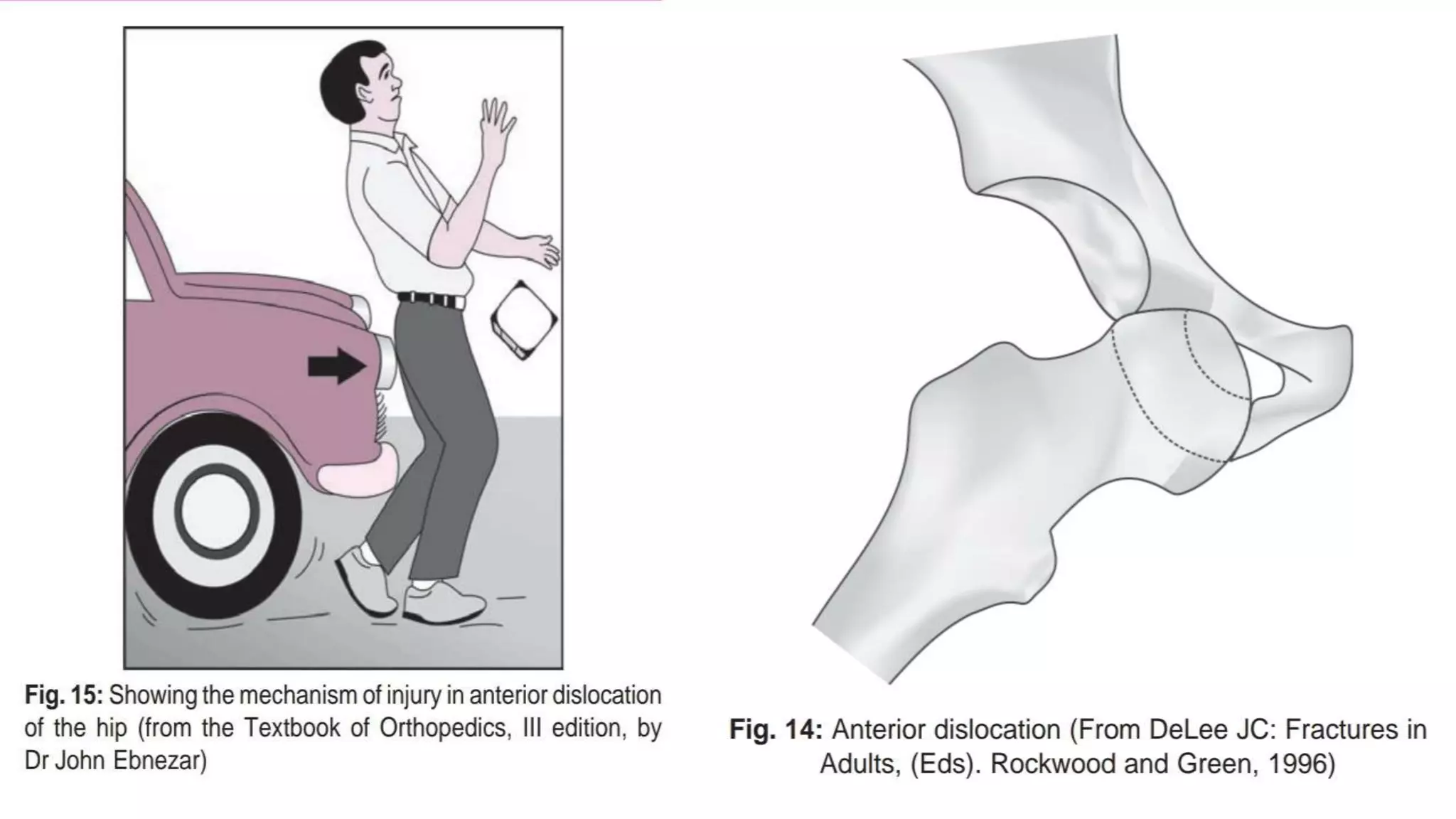
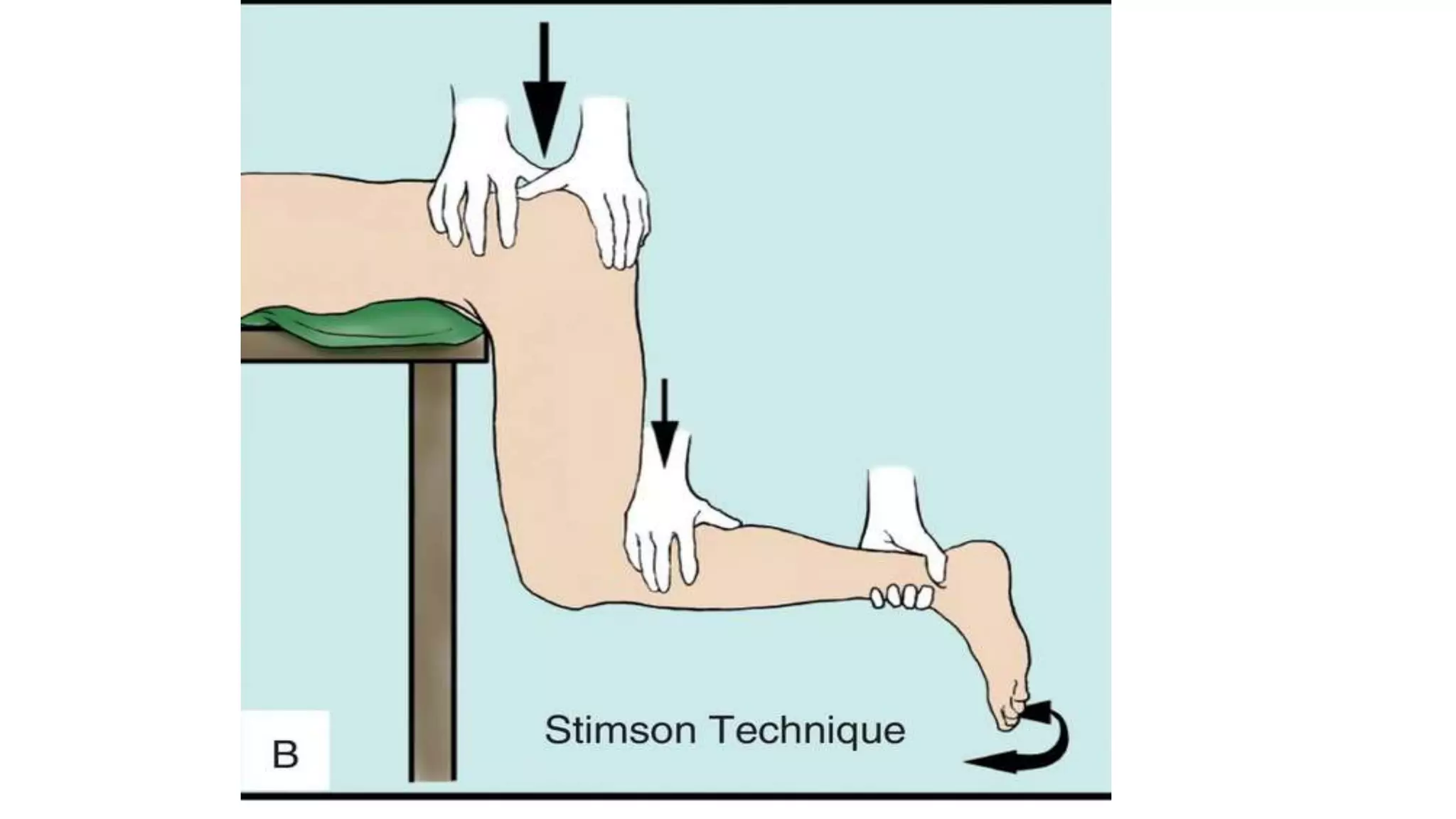
This document discusses hip dislocation, including anatomy, mechanisms of injury, classification, clinical evaluation, treatment, and complications. It notes that hip dislocations are usually caused by high-energy trauma and result in the femoral head being displaced from the acetabulum. Posterior dislocations are more common, occurring when the flexed knee strikes an object. Treatment involves closed or open reduction to place the femoral head back in the acetabulum, sometimes requiring surgical reconstruction for fractures. Complications can include osteonecrosis, osteoarthritis, nerve injuries, and recurrent dislocations.