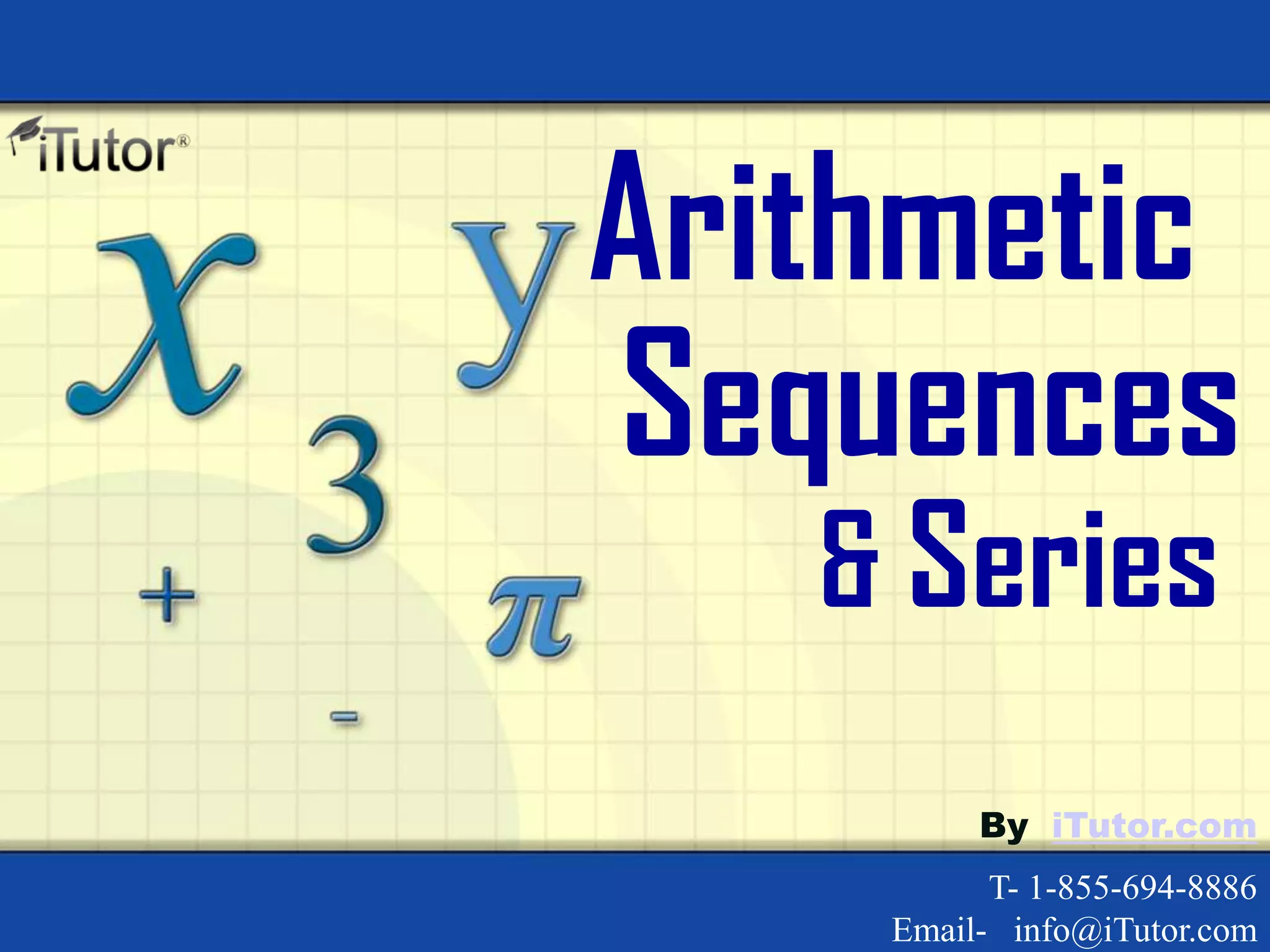
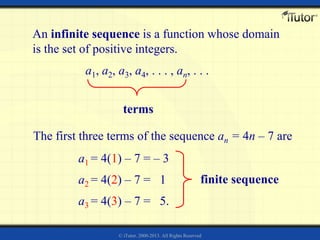
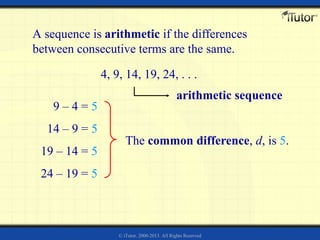
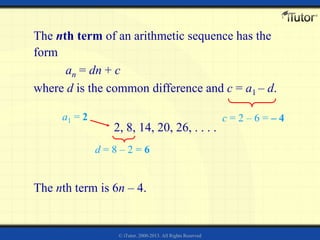
The document discusses arithmetic sequences and series. Some key points:
1) An arithmetic sequence is a sequence where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. This common difference (d) allows determining the nth term as an = dn + c, where c is the first term minus d.
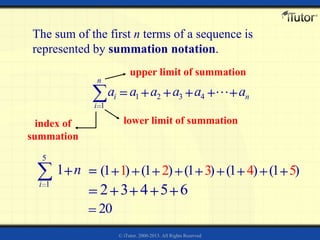
2) The sum of the first n terms of a finite arithmetic sequence is given by S_n = (n/2)(a_1 + a_n), where a_1 is the first term and a_n is the nth term.
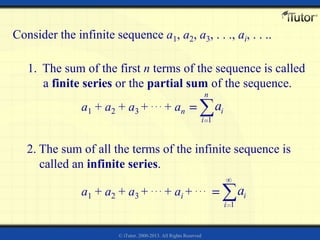
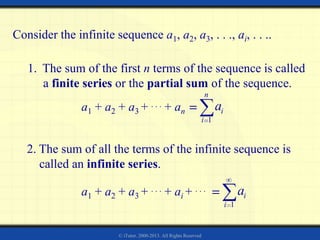
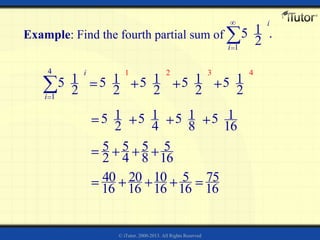
3) The sum of the first n terms of an infinite arithmetic sequence is called the nth partial sum. The partial sums can be represented using summation notation.