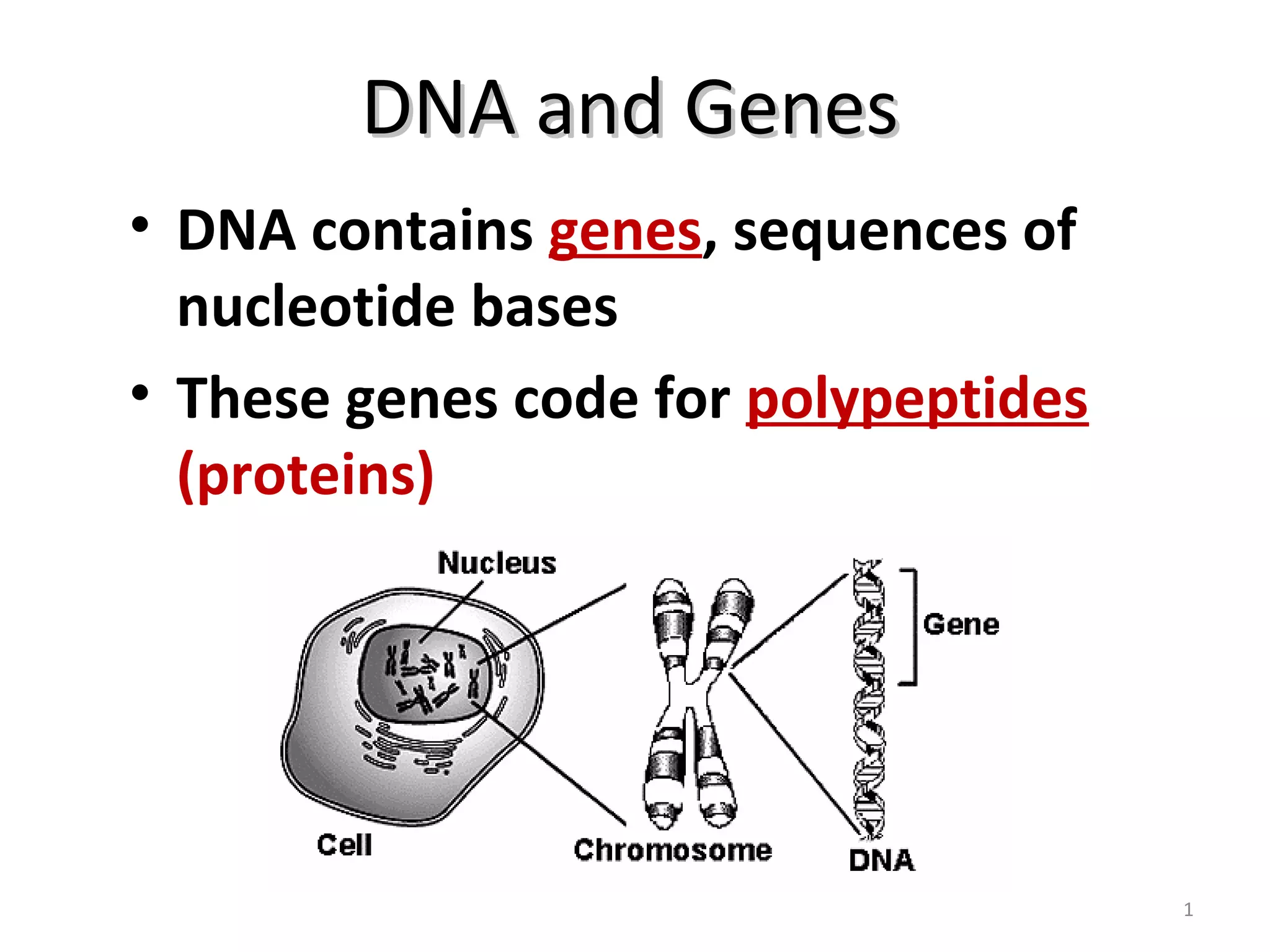
The document discusses DNA, genes, and the process of protein synthesis. It explains that DNA contains genes which code for proteins. There is a two-step process for protein synthesis: transcription copies DNA into mRNA in the nucleus, and translation uses mRNA and tRNA to assemble amino acids into proteins at the ribosome. The ribosome binds mRNA and tRNA to join amino acids together into polypeptide chains based on the genetic code, resulting in the production of proteins.