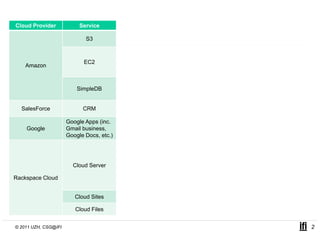
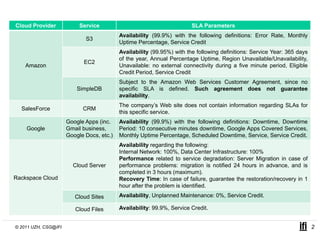
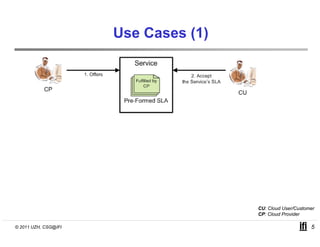
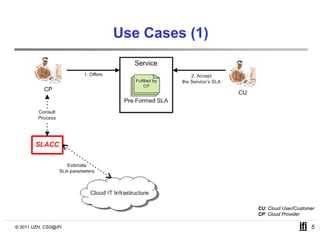
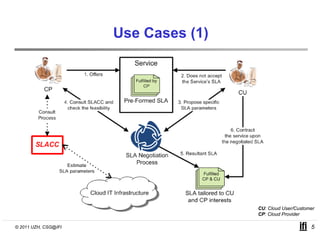
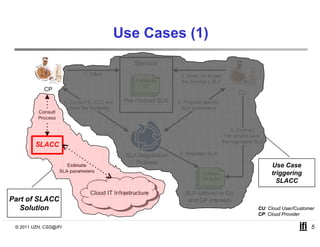
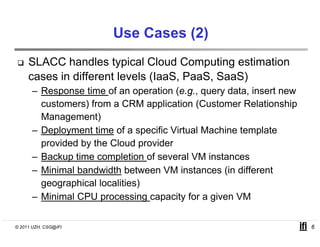
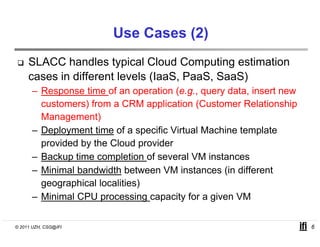
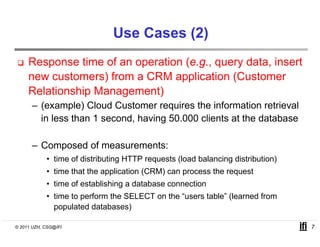
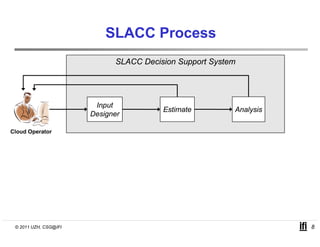
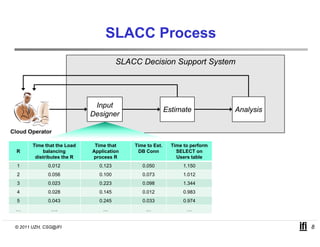
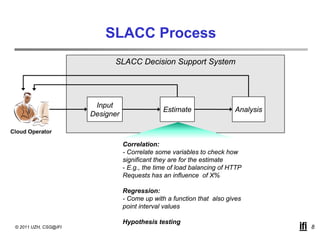
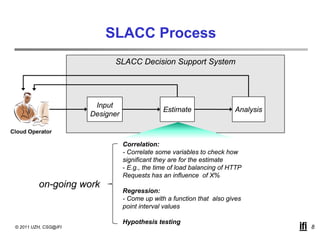
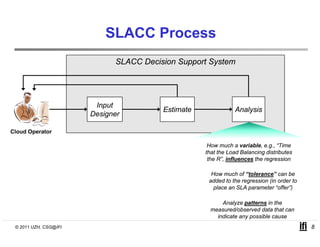
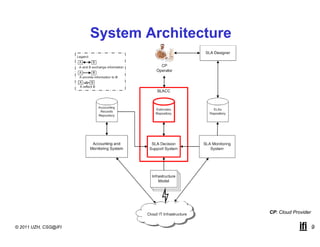
SLACC is a decision support system that aims to help cloud providers and users negotiate service level agreements (SLAs) by estimating key performance indicators (KPIs) and service level objectives (SLOs). It analyzes historical data and information about a provider's IT infrastructure to evaluate what levels of availability, response time, and other parameters a provider can likely offer or accept. The system is intended to enhance SLA specificity and support negotiation processes without directly interfering with existing cloud architectures.

![Motivation
“Companies struggling with Cloud performance” [1]
– Survey from Compuware by Vanson Bourne:
Compuware,
Reference [1]: http://www.computerworlduk.com/news/cloud-computing/
© 2011 UZH, CSG@IFI 3239390/companies-struggling-with-cloud-performance/ 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aims2011-slacc-presentationfinalversion-110621073404-phpapp02/85/Aims2011-slacc-presentation-final-version-2-320.jpg)
![Motivation
“Companies struggling with Cloud performance” [1]
– Survey from Compuware by Vanson Bourne:
Compuware,
57% European businesses were stopping
further i
f h investments on Cloud Computing until
Cl d C i il
they provide more specific guarantees
Reference [1]: http://www.computerworlduk.com/news/cloud-computing/
© 2011 UZH, CSG@IFI 3239390/companies-struggling-with-cloud-performance/ 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aims2011-slacc-presentationfinalversion-110621073404-phpapp02/85/Aims2011-slacc-presentation-final-version-3-320.jpg)
![Motivation
“Companies struggling with Cloud performance” [1]
– Survey from Compuware by Vanson Bourne:
Compuware,
57% European businesses were stopping
further i
f h investments on Cloud Computing until
Cl d C i il
they provide more specific guarantees
72% of businesses: cloud platform was
hampering their ability to maintain set levels of
p g y
service, also affecting company’s revenue
Reference [1]: http://www.computerworlduk.com/news/cloud-computing/
© 2011 UZH, CSG@IFI 3239390/companies-struggling-with-cloud-performance/ 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aims2011-slacc-presentationfinalversion-110621073404-phpapp02/85/Aims2011-slacc-presentation-final-version-4-320.jpg)
![Motivation
“Companies struggling with Cloud performance” [1]
– Survey from Compuware by Vanson Bourne:
Compuware,
57% European businesses were stopping
further i
f h investments on Cloud Computing until
Cl d C i il
they provide more specific guarantees
72% of businesses: cloud platform was
hampering their ability to maintain set levels of
p g y
service, also affecting company’s revenue
For revenue-generating websites: performance would mean revenue
revenue generating
Reference [1]: http://www.computerworlduk.com/news/cloud-computing/
© 2011 UZH, CSG@IFI 3239390/companies-struggling-with-cloud-performance/ 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aims2011-slacc-presentationfinalversion-110621073404-phpapp02/85/Aims2011-slacc-presentation-final-version-5-320.jpg)