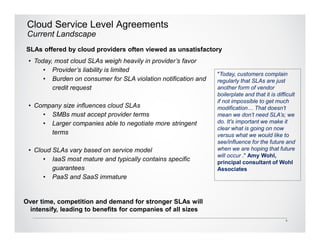
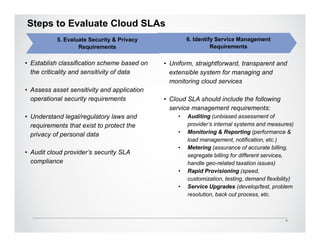
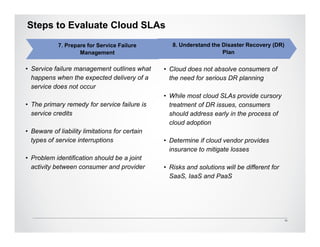
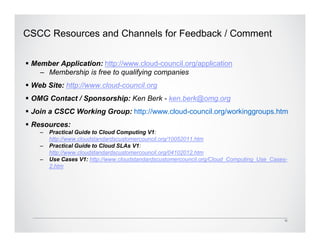
The Cloud Standards Customer Council provides guidance to cloud standards bodies and delivers best practices for cloud computing. Their recent publications include the Practical Guide to Cloud Computing, which outlines a nine-step plan for successful cloud deployments, and the Practical Guide to Cloud Service Level Agreements (SLAs). The SLA guide analyzes the current unsatisfactory state of cloud SLAs and provides 10 steps for customers to evaluate SLAs, including understanding roles and responsibilities, evaluating security and disaster recovery plans, and defining management and exit processes. The Council seeks feedback to further improve customer guidance on cloud standards and agreements.