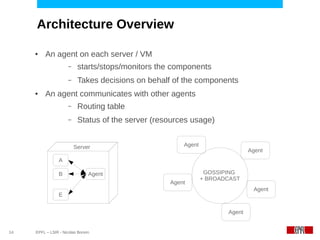
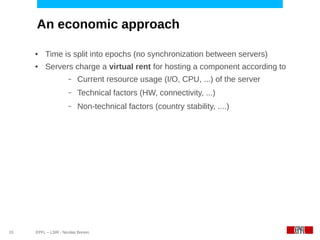
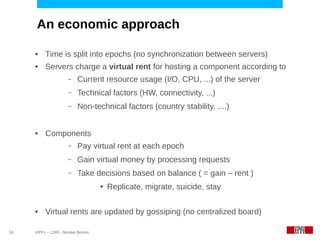
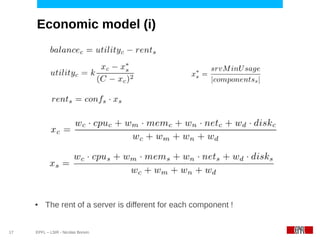
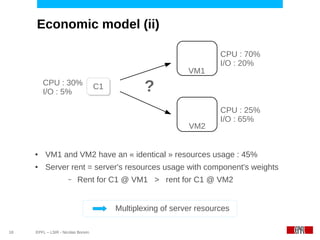
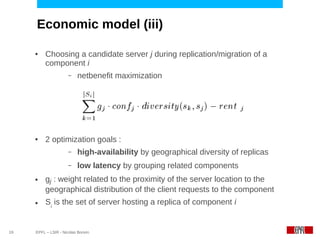
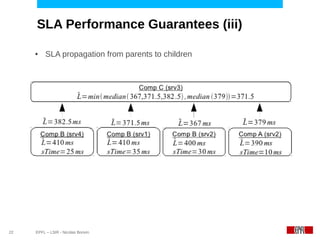
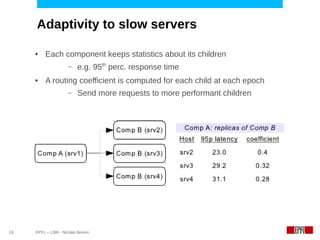
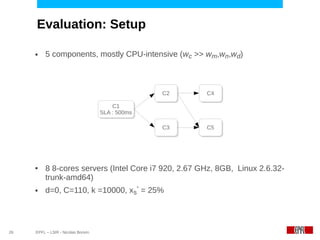
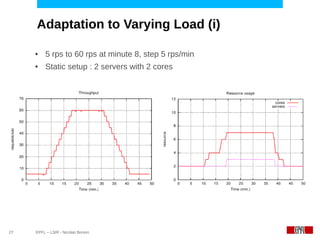
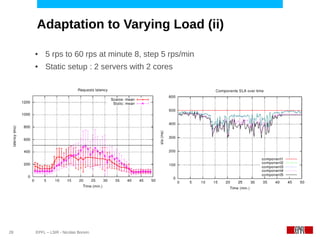
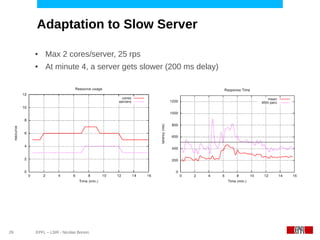
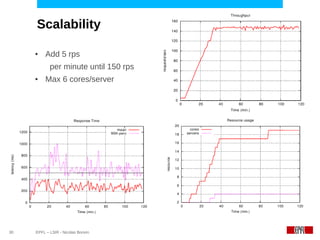
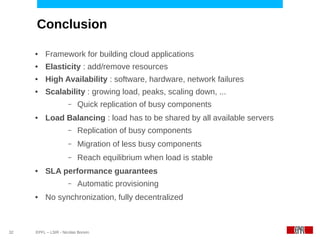
This document discusses challenges in deploying distributed applications on cloud infrastructure and proposes an autonomic framework called Scarce to address them. It notes that applications' components may be unevenly distributed across virtual machines with varying performance. Scarce uses autonomous agents that monitor components and make placement decisions. It employs an economic model where servers charge components rent based on resource usage, and components aim to maximize their balance of earnings and costs through actions like replication and migration. The framework also propagates service level agreements from parent to child components and automatically provisions resources to ensure performance guarantees are met under varying load. Evaluation results demonstrate its ability to adapt to changing loads and failures while maintaining scalability.


![Cloud Apps – Issue #2 : Unstability
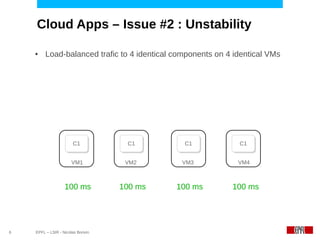
● Load-balanced trafic to 4 identical components on 4 identical VMs
– VM performance can vary up to a ratio 4 ! [Dej2009]
● Physical server, Hypervisor, Storage, ...
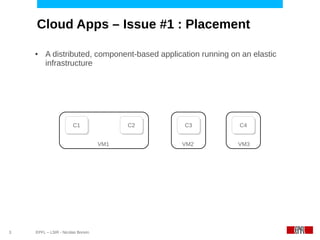
C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1
VM1 VM2 VM3 VM4
100 ms 140 ms 100 ms 100 ms
7 EPFL – LSIR - Nicolas Bonvin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scarce-ccgrid2011-110526135848-phpapp01/85/Autonomic-SLA-driven-Provisioning-for-Cloud-Applications-7-320.jpg)
![Cloud Apps – Issue #2 : Unstability
● Load-balanced trafic to 4 identical components on 4 identical VMs
– VM performance can vary up to a ratio 4 ! [Dej2009]
● Physical server, Hypervisor, Storage, ...
● Component overloaded
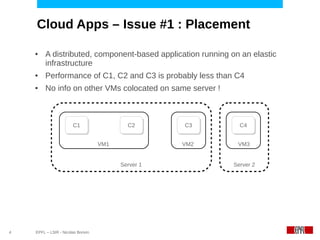
C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1
VM1 VM2 VM3 VM4
130 ms 140 ms 100 ms 100 ms
8 EPFL – LSIR - Nicolas Bonvin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scarce-ccgrid2011-110526135848-phpapp01/85/Autonomic-SLA-driven-Provisioning-for-Cloud-Applications-8-320.jpg)
![Cloud Apps – Issue #2 : Unstability
● Load-balanced trafic to 4 identical components on 4 identical VMs
– VM performance can vary up to a ratio 4 ! [Dej2009]
● Physical server, Hypervisor, Storage, ...
● Component overloaded
● Component bug, crash, deadlock, ...
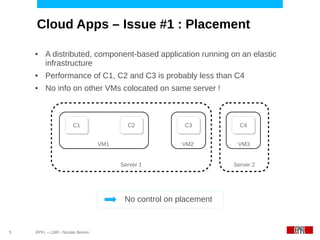
C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1
VM1 VM2 VM3 VM4
130 ms 140 ms 100 ms infinity
9 EPFL – LSIR - Nicolas Bonvin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scarce-ccgrid2011-110526135848-phpapp01/85/Autonomic-SLA-driven-Provisioning-for-Cloud-Applications-9-320.jpg)
![Cloud Apps – Issue #2 : Unstability
● Load-balanced trafic to 4 identical components on 4 identical VMs
– VM performance can vary up to a ratio 4 ! [Dej2009]
● Physical server, Hypervisor, Storage, ...
● Component overloaded
● Component bug, crash, deadlock, ...
● Failure of C1 on VM4 -> load is rebalanced
C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1
VM1 VM2 VM3 VM4
140 ms 150 ms 130 ms infinity
10 EPFL – LSIR - Nicolas Bonvin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scarce-ccgrid2011-110526135848-phpapp01/85/Autonomic-SLA-driven-Provisioning-for-Cloud-Applications-10-320.jpg)
![Cloud Apps – Issue #2 : Unstability
● Load-balanced trafic to 4 identical components on 4 identical VMs
– VM performance can vary up to a ratio 4 ! [Dej2009]
● Physical server, Hypervisor, Storage, ...
● Component overloaded
● Component bug, crash, deadlock, ...
● Failure of C1 on VM4 -> load is rebalanced
C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1 C1
C1
VM1 VM2 VM3 VM4
140 ms 150 ms 130 ms infinity
Application should react early !
11 EPFL – LSIR - Nicolas Bonvin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scarce-ccgrid2011-110526135848-phpapp01/85/Autonomic-SLA-driven-Provisioning-for-Cloud-Applications-11-320.jpg)