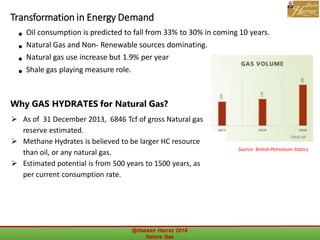
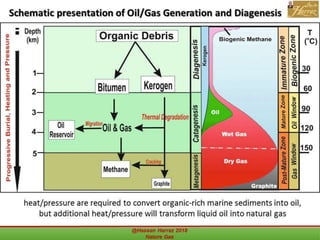
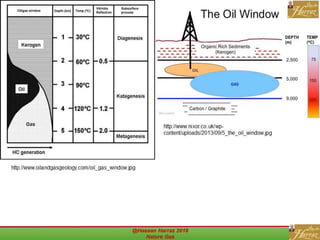
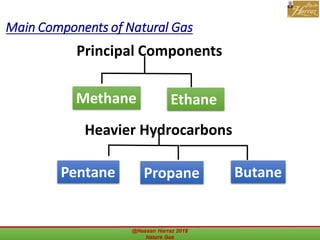
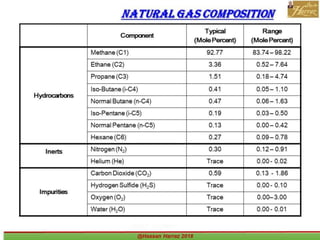
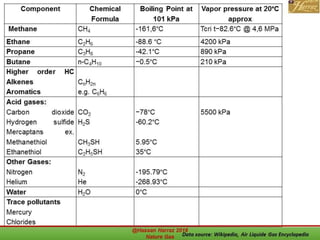
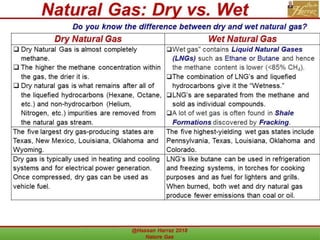
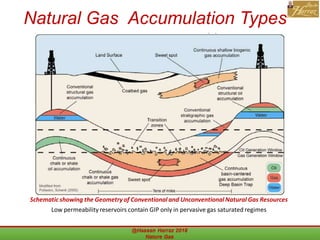
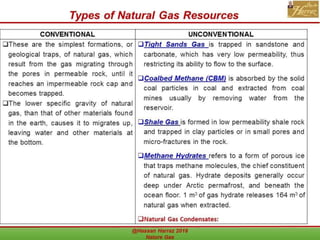
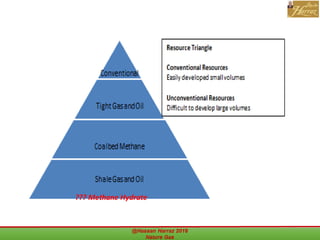
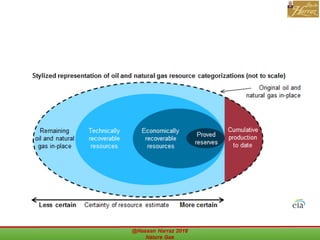
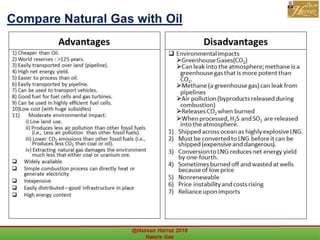
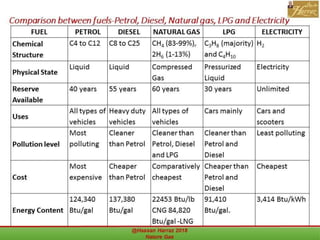
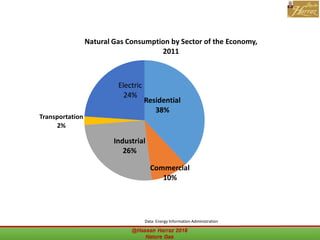
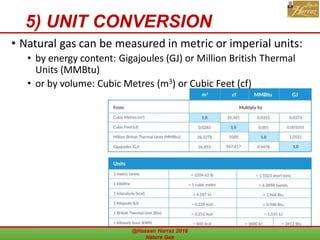
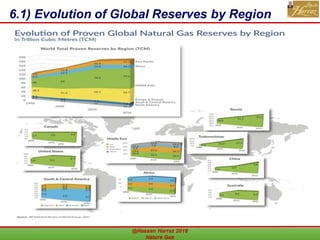
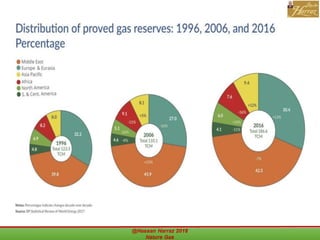
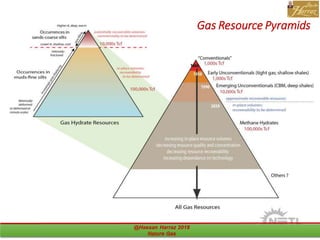
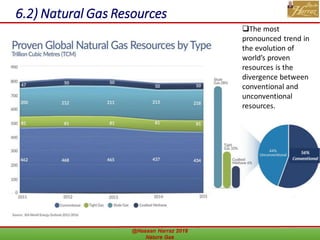
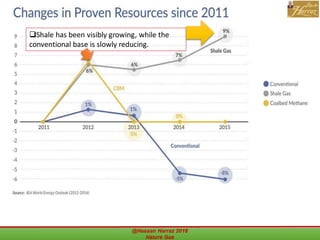
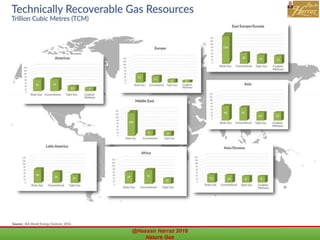
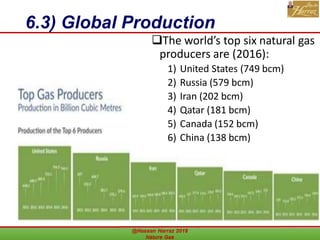
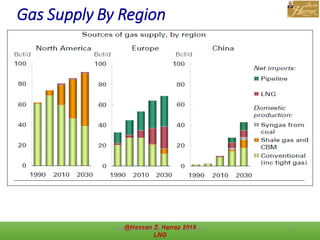
This document outlines a course on natural gas resources, covering topics such as types of natural gas, unconventional gas reservoirs, and processes involved in natural gas extraction and treatment. It aims to familiarize students with natural gas, its environmental impacts, and its geological context, along with providing an overview of the natural gas industry and its value chain. Key points include the historical development, composition, uses, and global production trends of natural gas, emphasizing the growing significance of shale gas and the secure supply of natural gas resources.