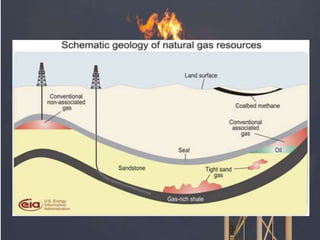
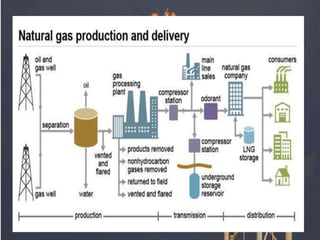
Natural gas is a hydrocarbon composed primarily of methane that is found in conventional and unconventional deposits underground. Conventional deposits are commonly found near oil reservoirs, while unconventional sources include shale gas, tight gas in low-permeability sandstone, coalbed methane, methane hydrates, and biogenic gas. Shale gas is trapped within organic-rich shale formations, tight gas has migrated into reservoirs with small pore spaces, and coalbed methane is contained in coal deposits. Methane hydrates consist of methane molecules trapped within a cage of water molecules in arctic sediments and ocean floors. Natural gas has several environmental and health effects but produces fewer emissions than other fossil fuels when burned, and its transportation and storage requires strict safety regulations