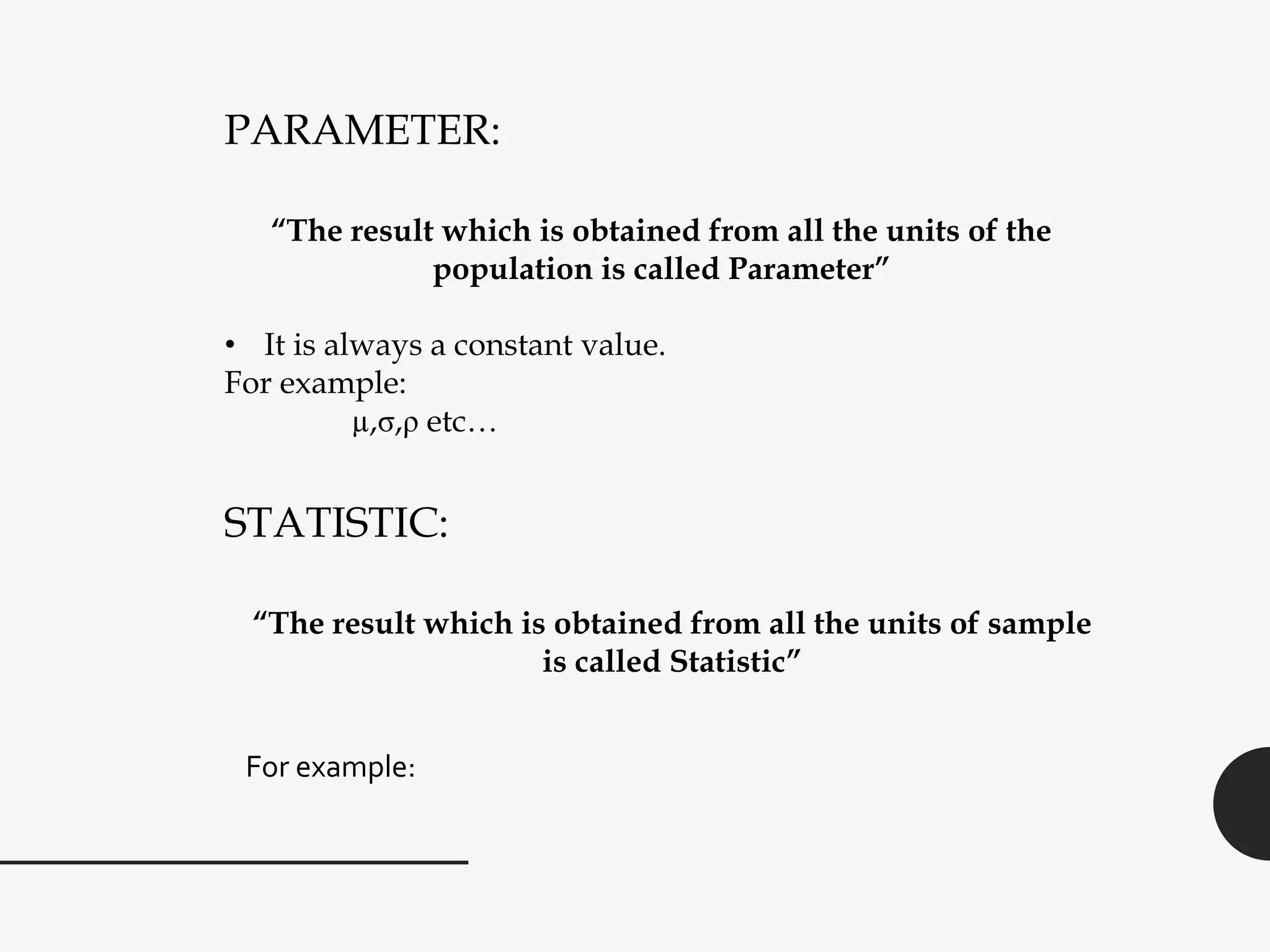
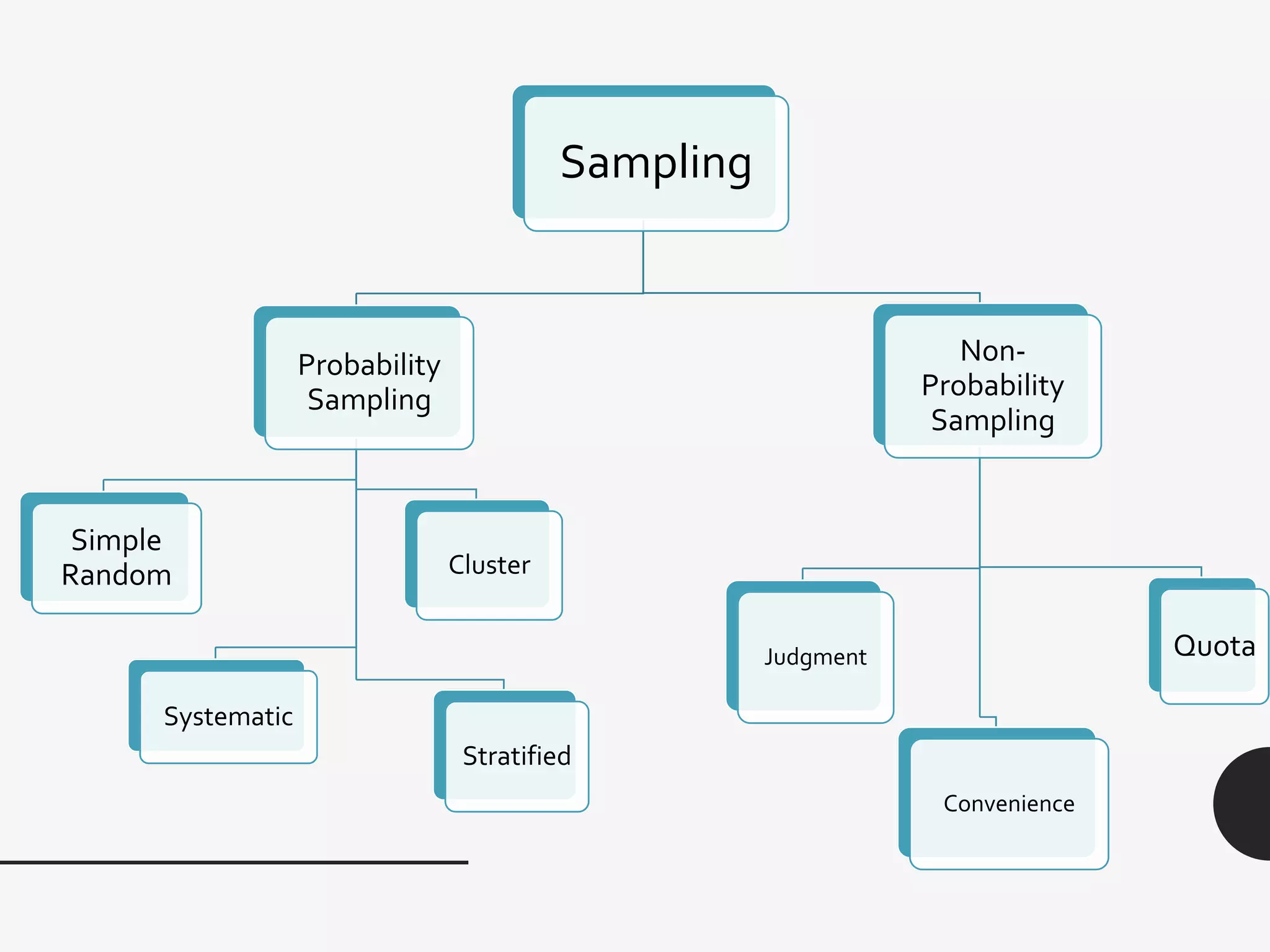
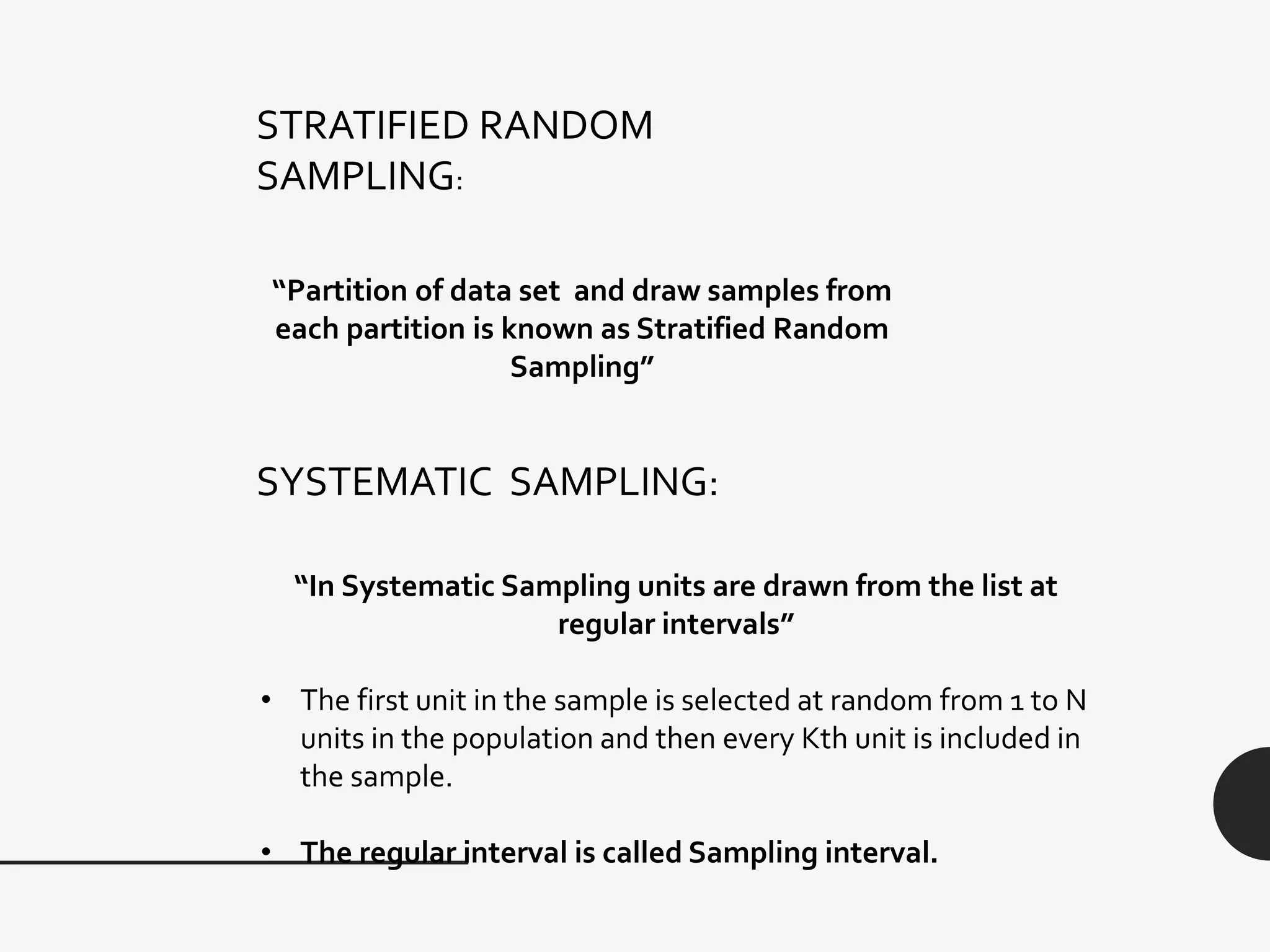
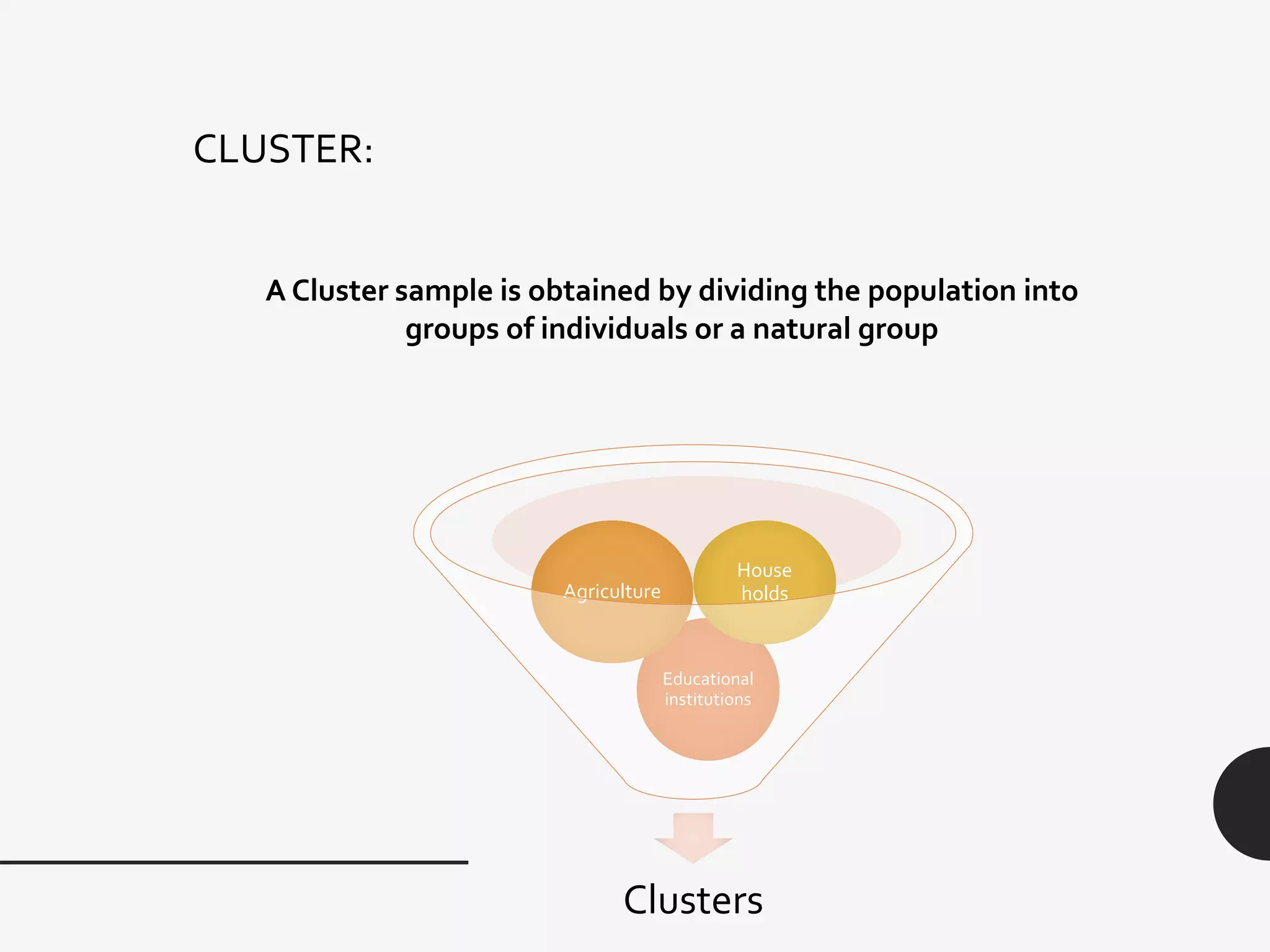
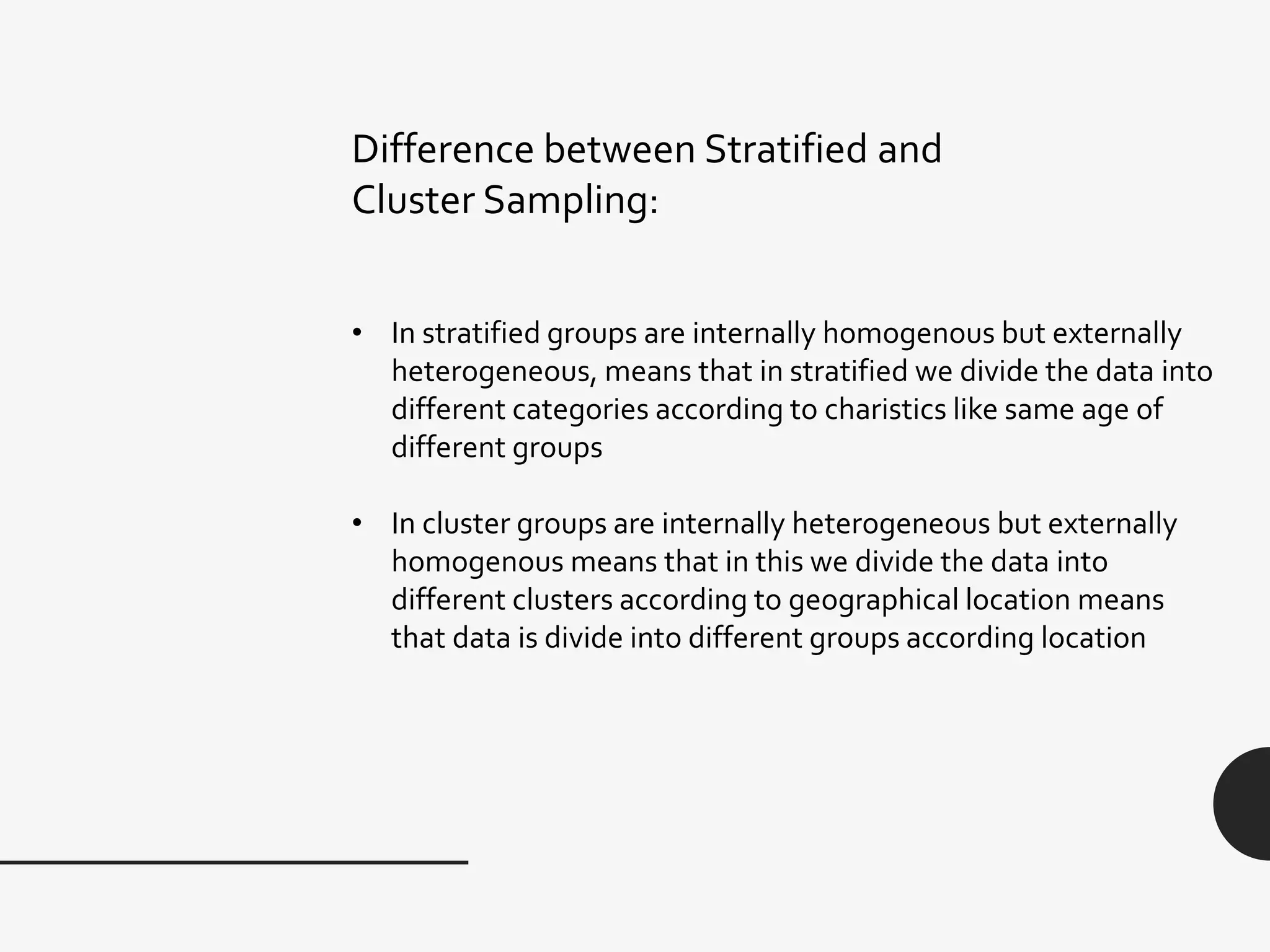
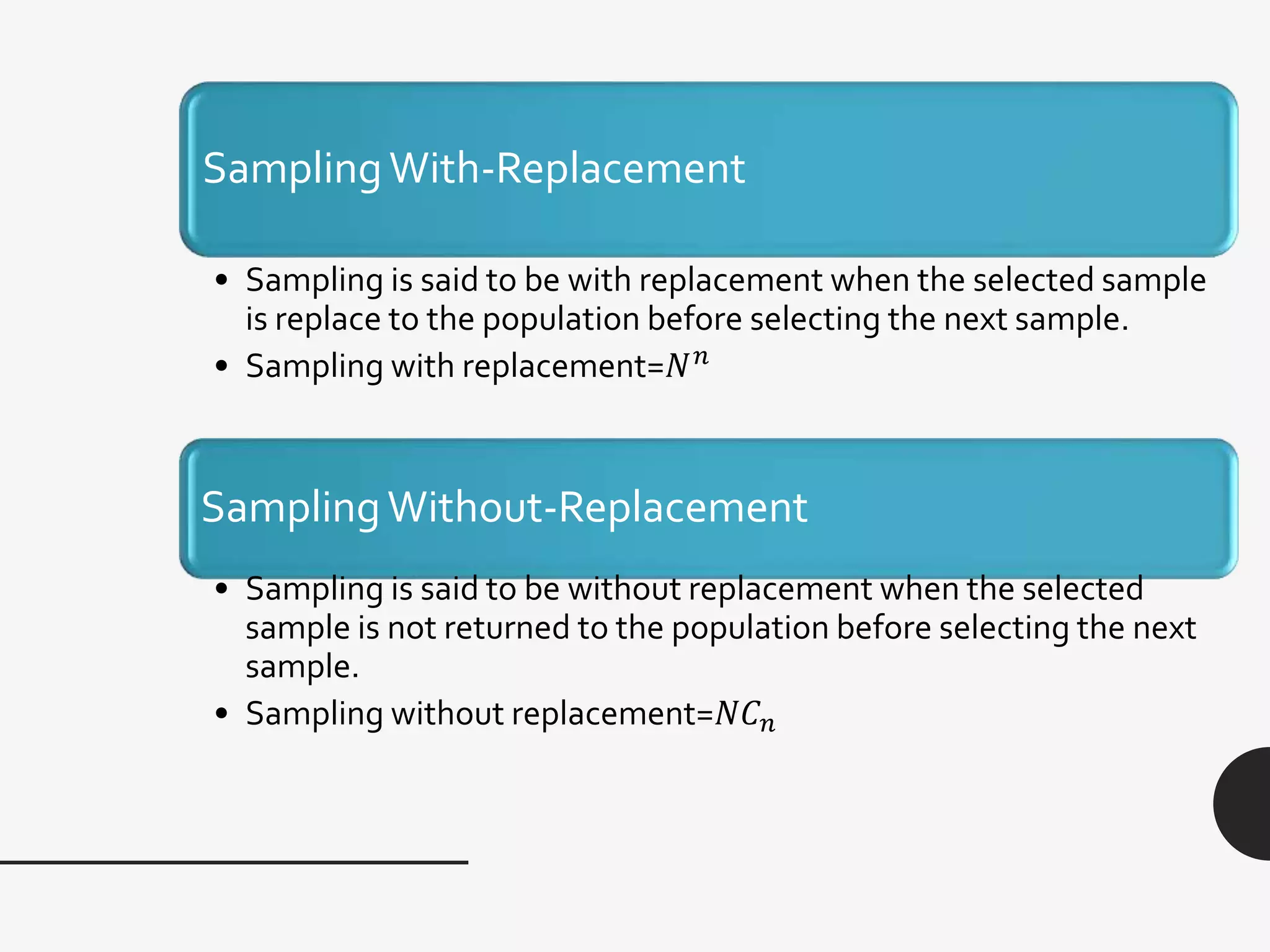
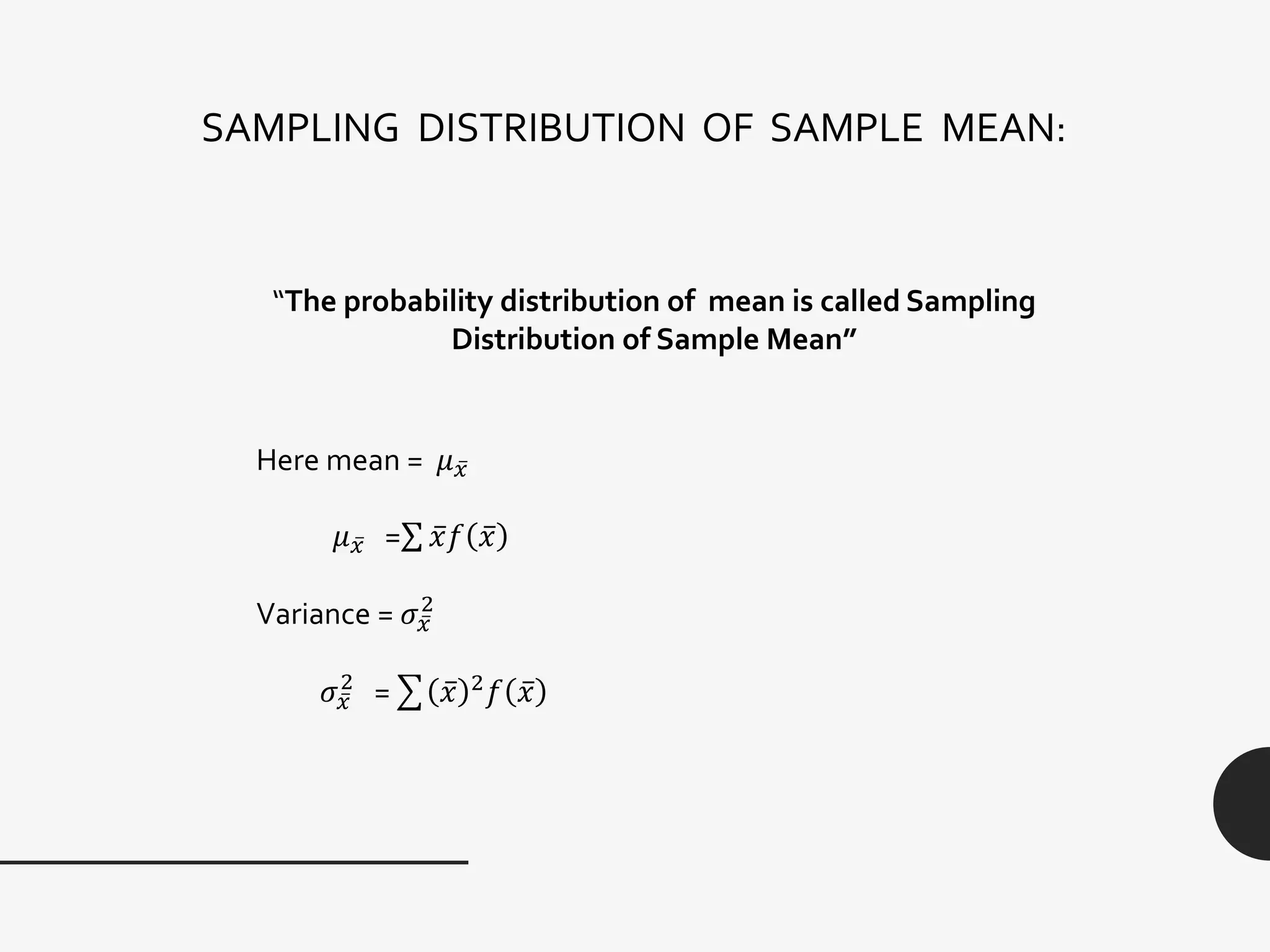
This document discusses sampling distribution about sample mean. It defines key terms like population, sample, sampling units, stratified random sampling, systematic sampling, cluster sampling, probability sampling, non-probability sampling, estimation, estimator, estimate, and sampling distribution. It also discusses the sampling distribution of the sample mean and provides an example to calculate and compare the mean and variance of sample means for sampling with and without replacement.