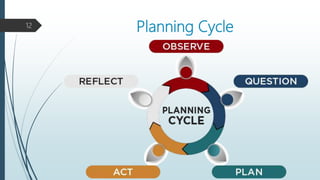
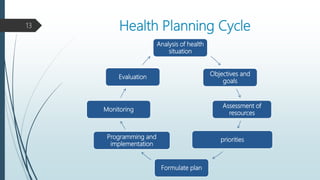
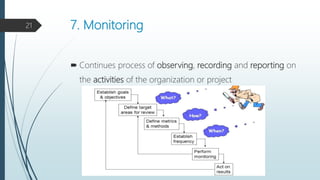
The document outlines the process of health planning, which involves setting goals, developing strategies, and allocating resources to effectively address health issues. It details the key elements of health planning, including objectives, policies, programs, schedules, and budgets, while emphasizing the importance of assessing resources and setting priorities through methods like SWOT analysis. Furthermore, it describes a comprehensive planning cycle that includes analysis, goal setting, plan formulation, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation.