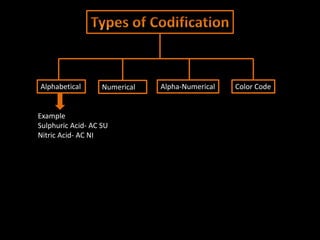
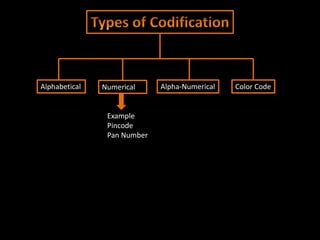
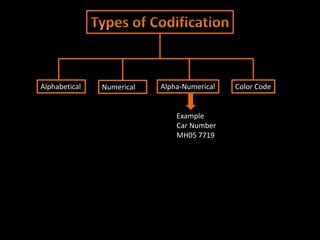
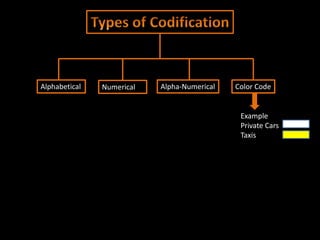
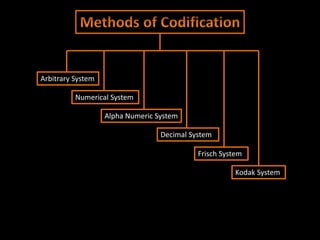
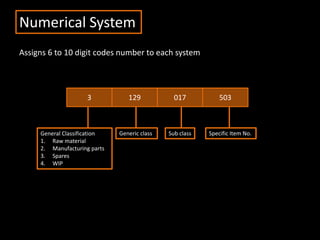
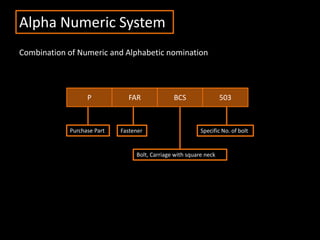
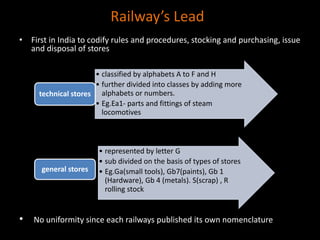
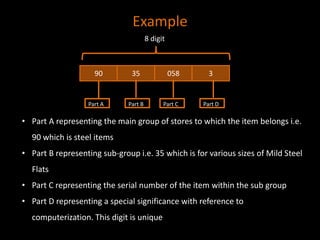
The document discusses coding systems used to systematically organize materials and inventory. It describes various coding criteria like being simple, unique, compact. It then explains different types of coding systems like alphabetical, numerical, alphanumeric and their examples. Specific coding systems like arbitrary, numerical, decimal, Frisch and Kodak are outlined. The case study then details how the Indian Railways standardized its coding practices by adopting an 8-digit coding system following recommendations from the Paranjape Committee. This unified coding system allows for easy exchange of information across the extensive railway network.