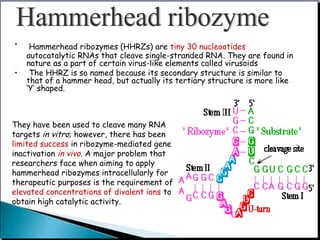
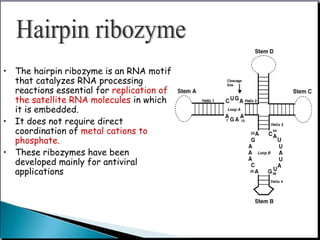
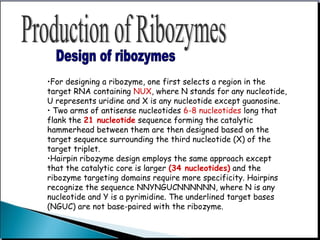
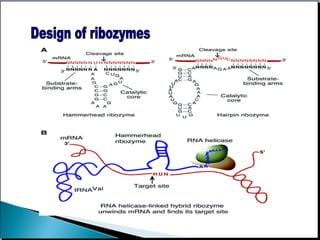
This document provides an overview of ribozymes, including their definition, classes, history of discovery, mechanisms of action, design, delivery methods, and therapeutic applications. Key points include: Ribozymes are RNA molecules with enzymatic catalytic activity; There are two main classes - self-cleaving and self-splicing ribozymes, which include hammerhead, hairpin, hepatitis delta virus, group I and II introns, and RNase P; They were discovered in the 1980s and shown to catalyze critical reactions without protein enzymes; Therapeutic applications aim to target disease-related genes and are showing promise for cancer, infectious diseases, and genetic disorders in clinical trials.



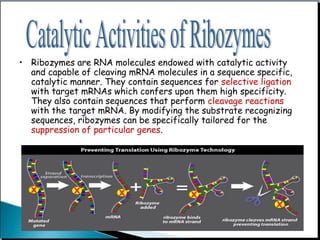




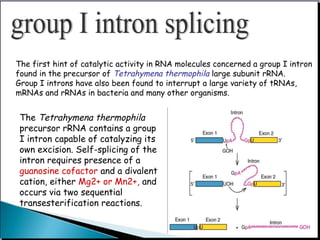

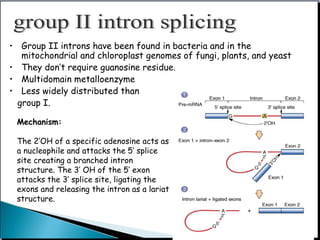
![• Ribonuclease P (RNaseP), a ribonucleoprotein, is an essential tRNA
processing enzyme found in all living organisms. Since its discovery almost
40 years ago, research on RNase P has led to the discovery of the catalytic
properties of RNA.
Mechanism:
• All RNase P enzymes are ribonucleoproteins [bacteria: 1RNA + 1 protein subunit;
eukaryotes: 1 RNA + many protein subunits (11 in human)],
• In Ribonulease – P, protein component facilitates binding between RNase and
t-RNA substrate.
• Requires divalent metal ions (like Mg2+) for its activity.
• Endo-ribonuclease responsible for generating 5’ end of matured tRNA molecules.
• Cleavage via nucleophilic attack on the phosphodiester bond leaving a 5’-phosphate
and 3’-hydroxyl at the cleavage site.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ribozyme-170302133657/85/Ribozyme-12-320.jpg)