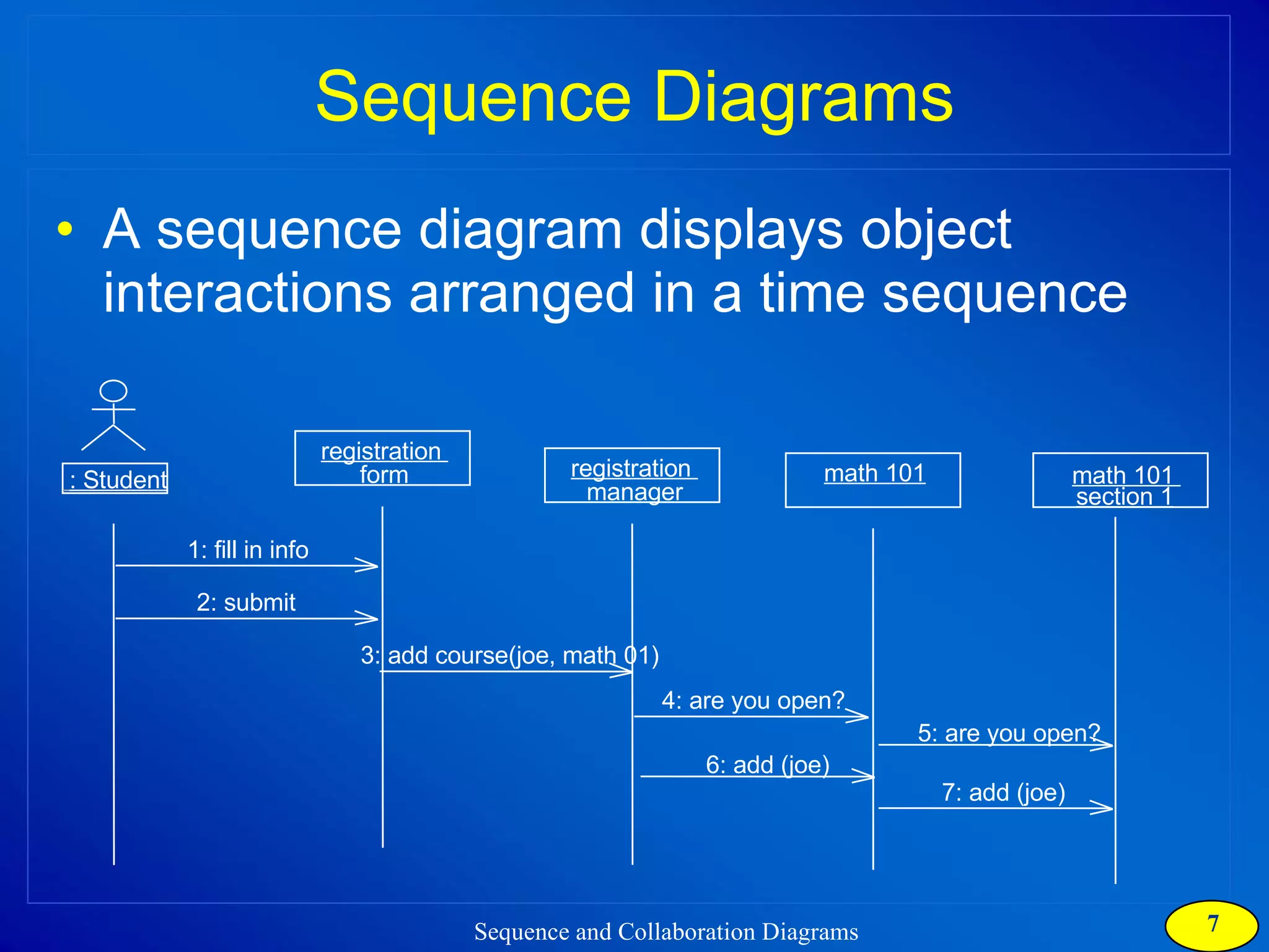
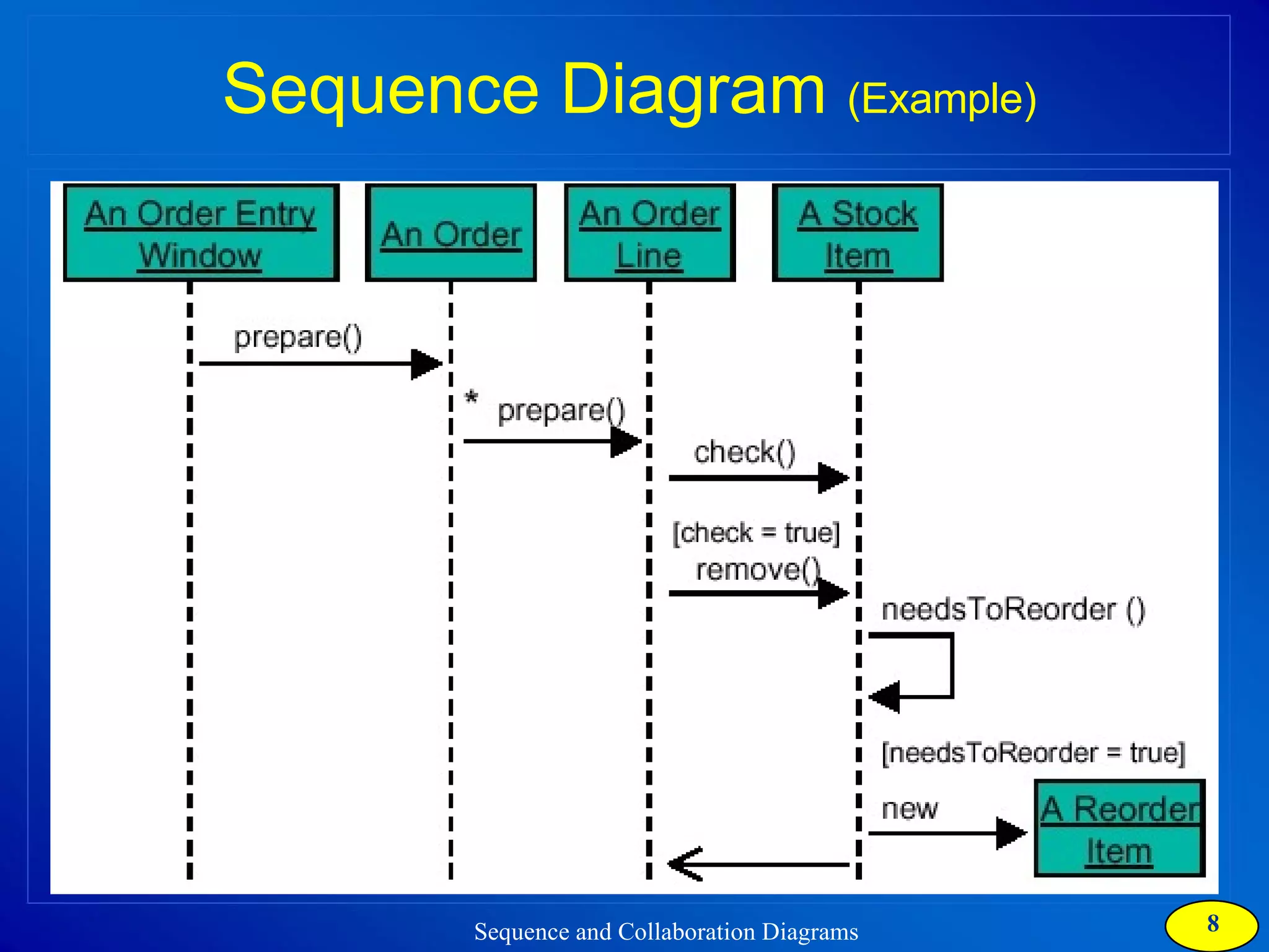
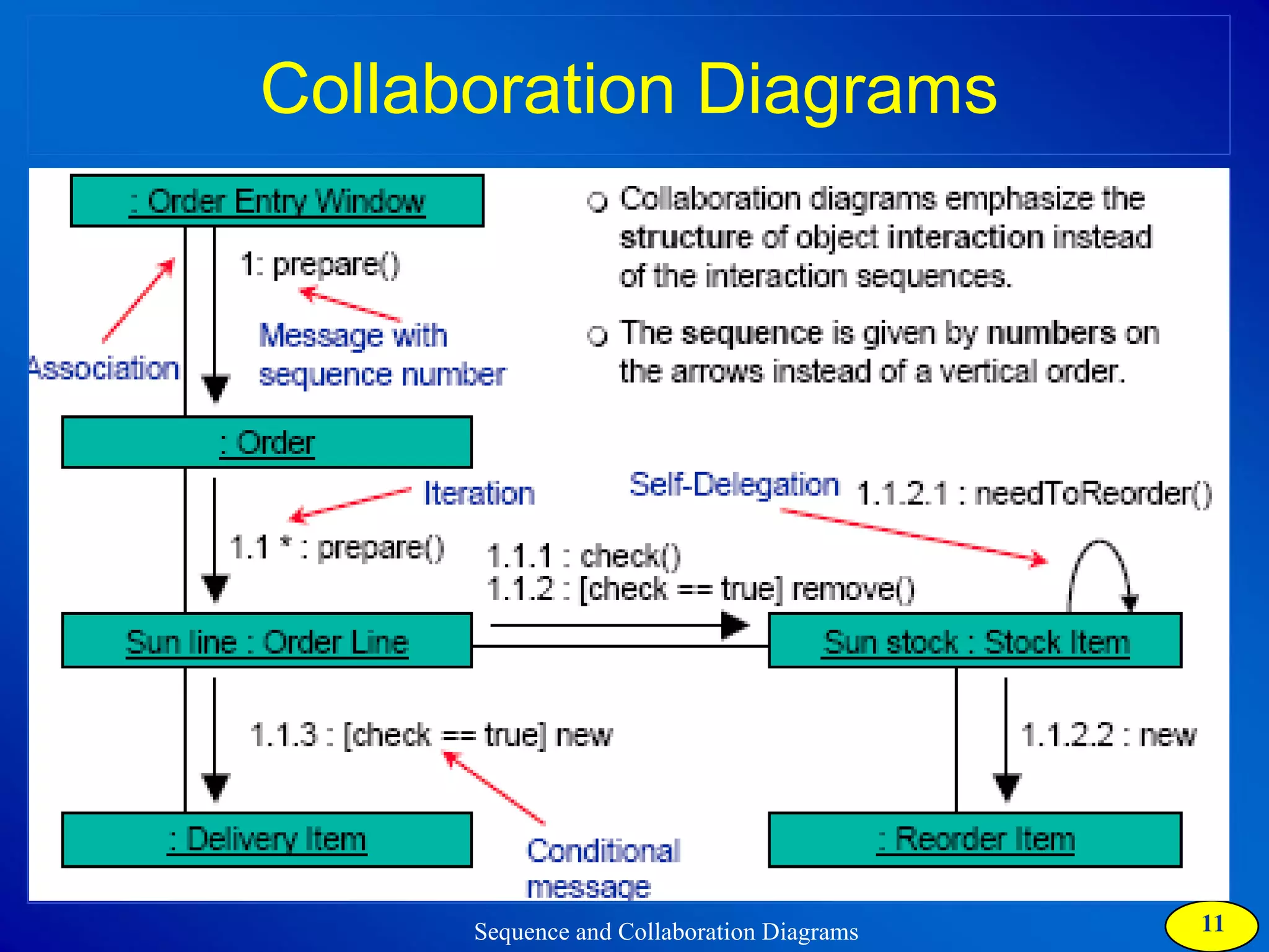
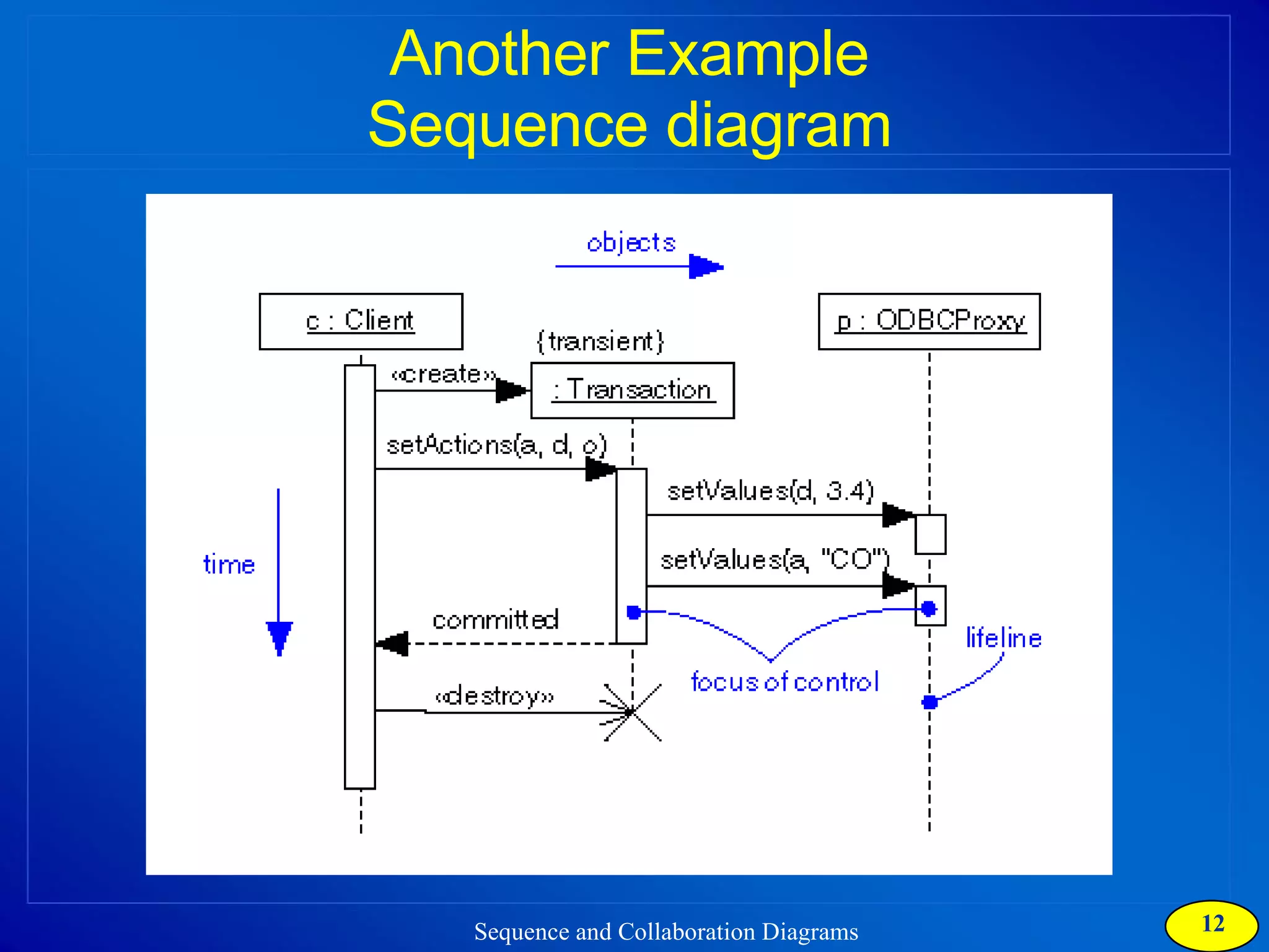
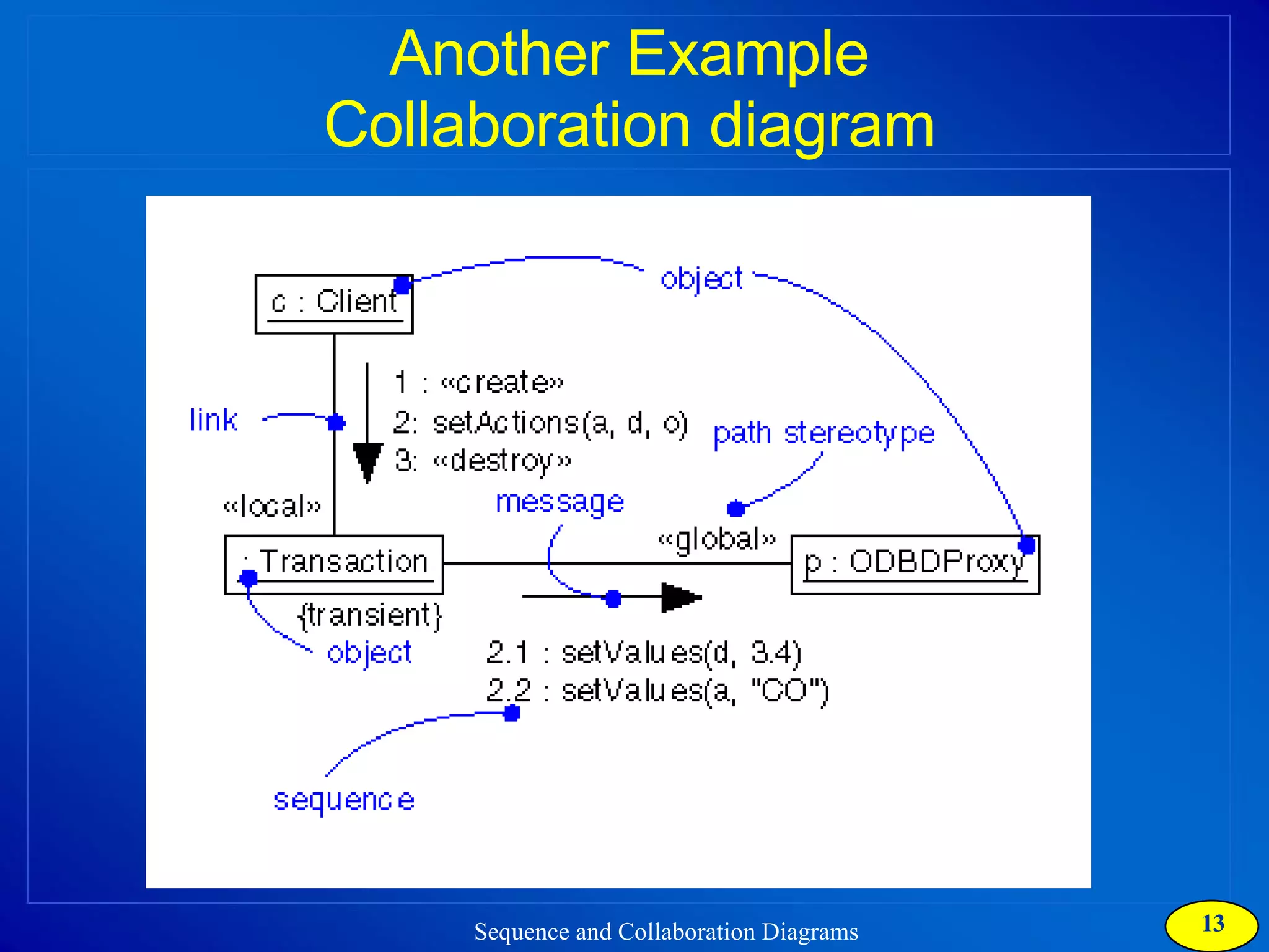
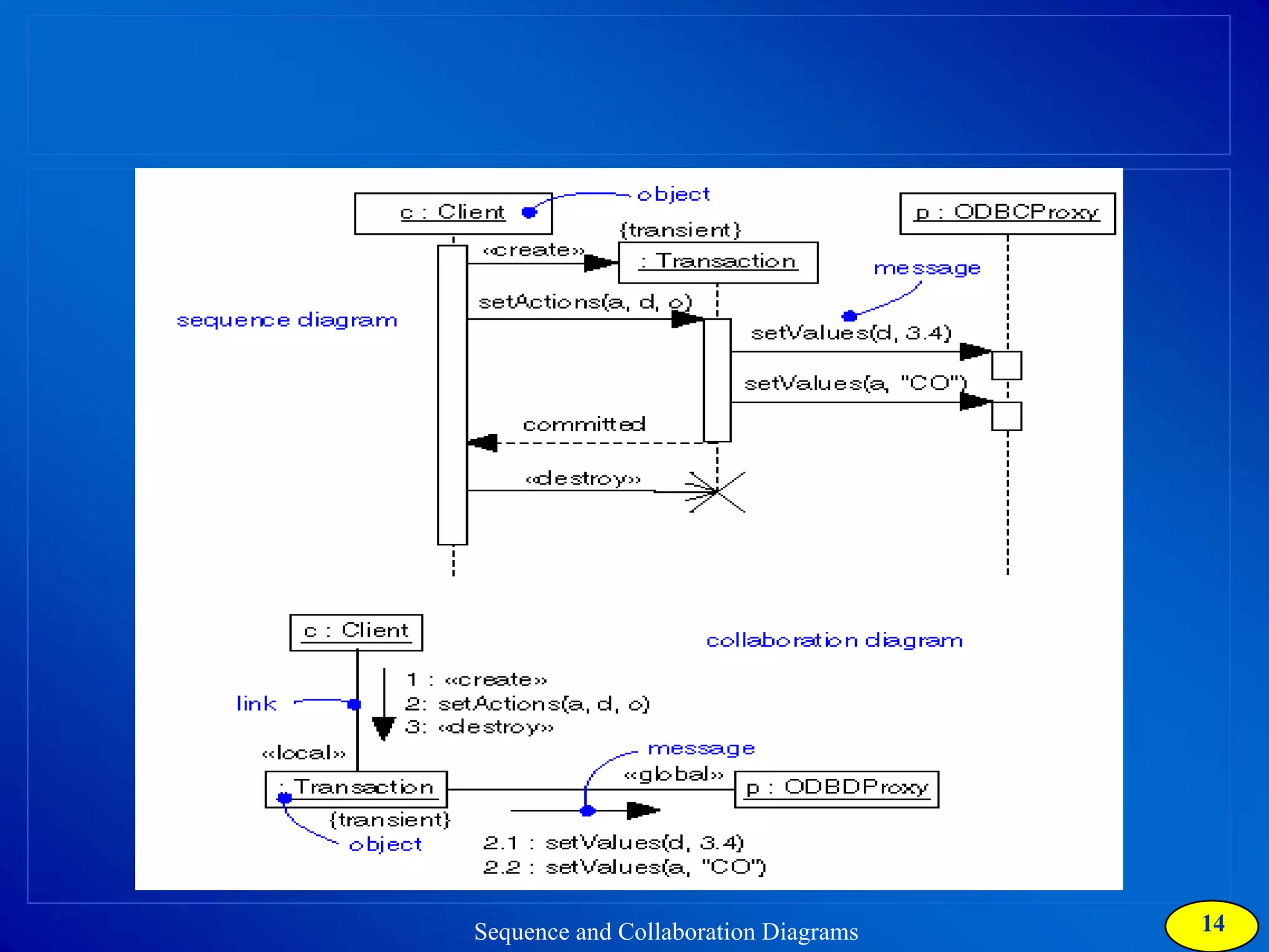
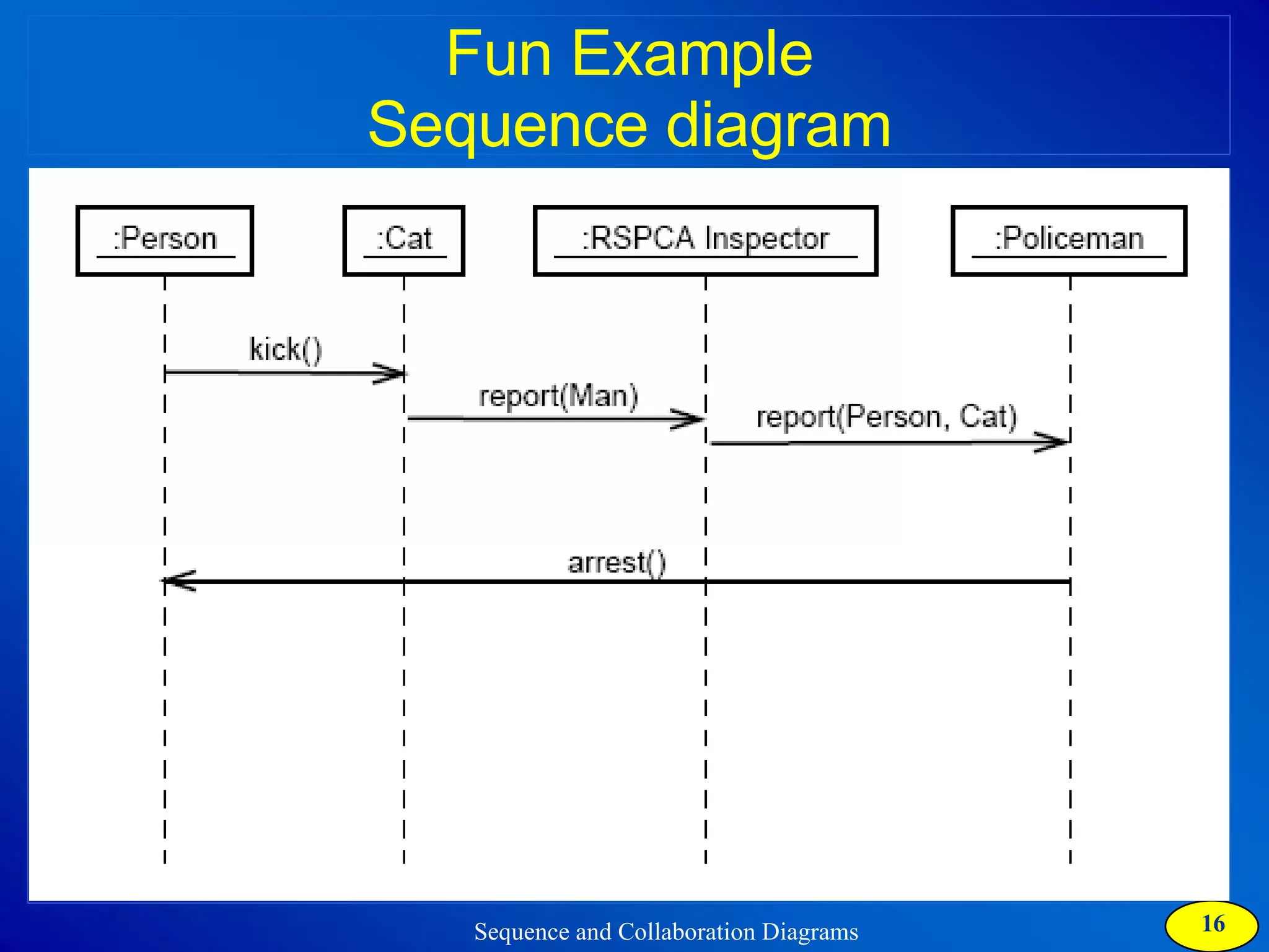
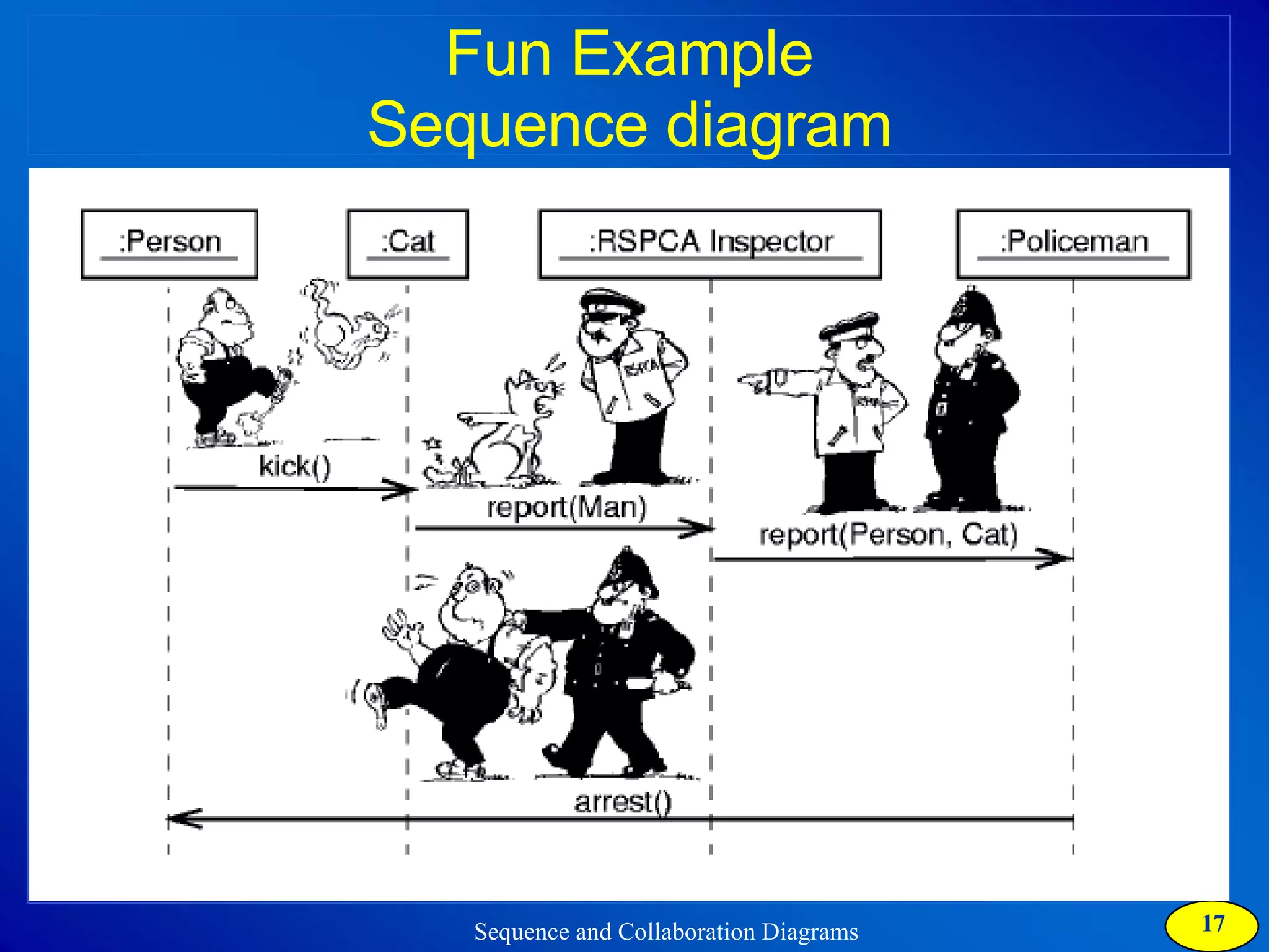
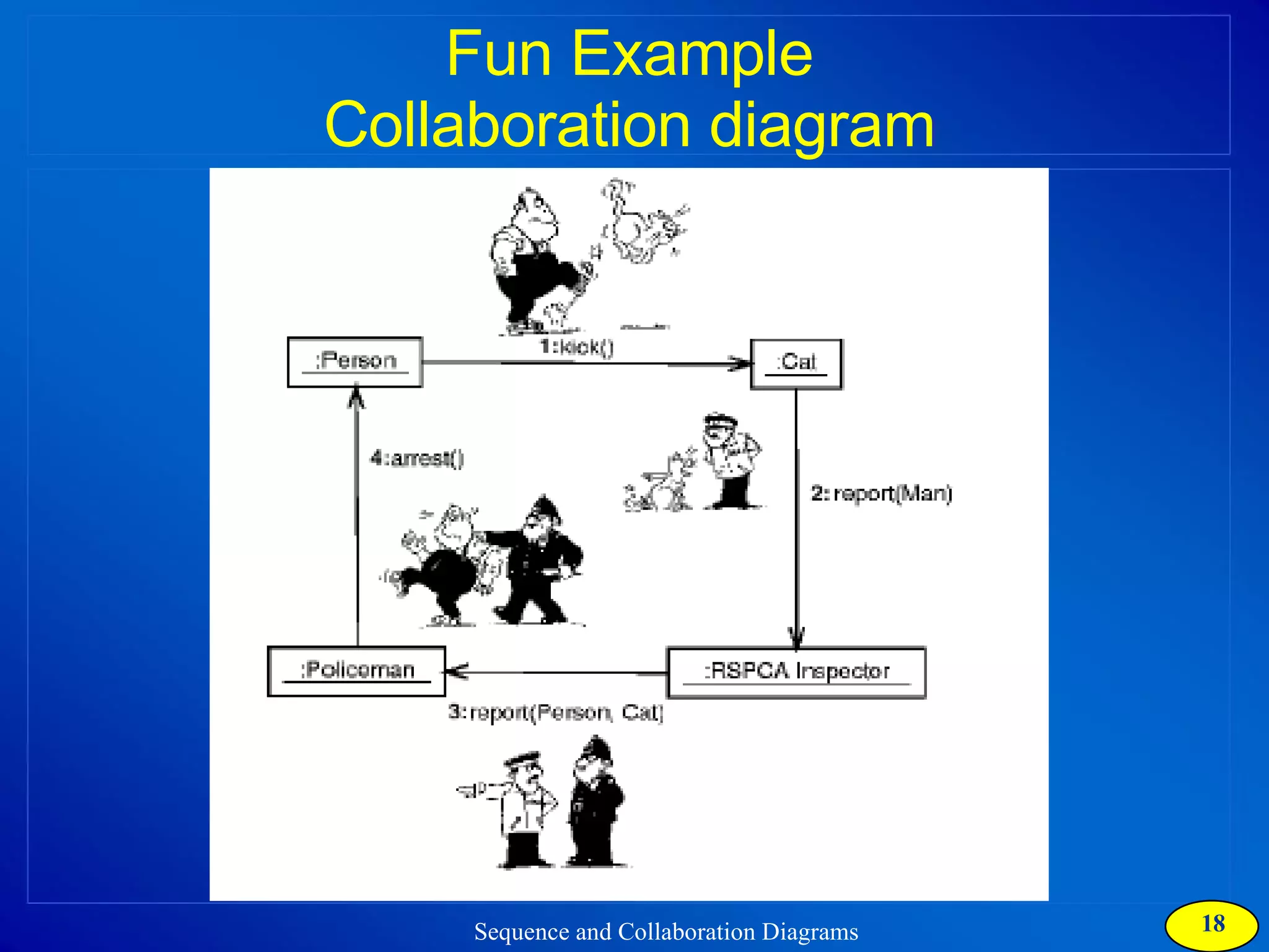
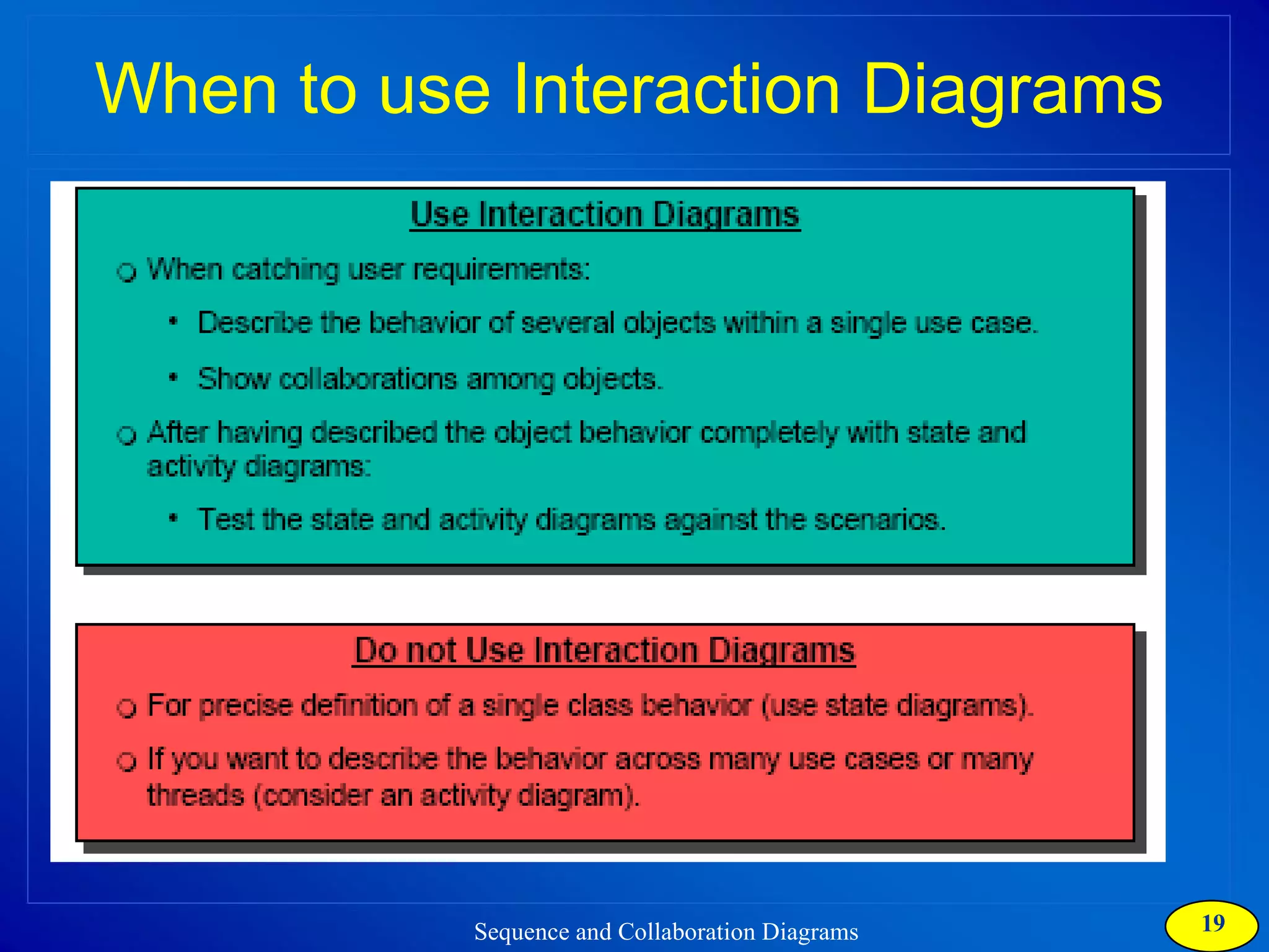
The document discusses two types of interaction diagrams: sequence diagrams, which focus on the order of interactions, and collaboration diagrams, which emphasize the structure of interacting objects. It details how scenarios and use case diagrams help in understanding the functionality and object interactions required for use cases. Additionally, it highlights the transformation between these diagrams and emphasizes their application in discovering classes and capturing dynamic behavior.