The document discusses speech acts, which are actions performed through language. A speech act can be divided into a locutionary act (the words used), an illocutionary act (the intended meaning or function), and a perlocutionary act (the effect on the listener). Certain words like "I promise" explicitly indicate the speech act, while others rely on context clues. For a speech act to be valid, certain felicity conditions regarding the situation and participants must be met. Speech acts can be classified based on their functions, such as representatives that convey information or directives that request actions. Indirect speech acts imply a meaning different than the literal words.











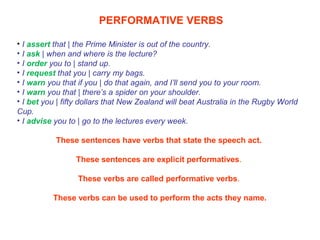






![E. Felicity Conditions for Advising
S advises H to do x:
1. S believes H has not yet done x (or has not yet tried to do x).
2. S believes H might be willing to try x (or be persuaded to try x). [Otherwise
why bother advising someone to do something?]
3. S believes H is able to do x.
4. S believes x will be in the best interest of H (i.e. that x will work).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/speechacts-160321200836/85/Speech-acts-19-320.jpg)








