Understanding Speech Acts: Types, Functions, and Real-Life Examples
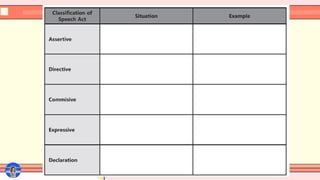
This SlideShare presentation provides a comprehensive introduction to Speech Act Theory based on the works of J.L. Austin and John Searle. Learn how language is used not just to convey information, but to perform actions through speech. This lesson breaks down the three components—locutionary, illocutionary, and perlocutionary acts, and explores Searle’s five speech act classifications: assertives, directives, commissives, expressives, and declaratives.
🎯 What You’ll Learn:
Definitions and examples of speech acts
The three levels of speech acts
Searle’s classification with sample dialogues
Quiz items and classroom activities
Perfect for students, teachers, and English communication learners in high school or college. Aligned with Oral Communication and 21st Century Literature curricula.