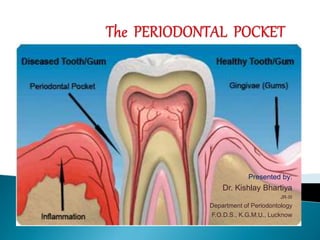
The periodontal pocket is a key feature of periodontal disease that results from the deepening of the gingival sulcus. Pockets can be classified as gingival, suprabony, or intrabony depending on their location relative to the alveolar bone. The document describes the signs, symptoms, clinical features, and histopathological changes that occur as the gingival sulcus transforms into a periodontal pocket through collagen destruction and epithelial downgrowth along the root surface. Bacteria can invade the soft tissue wall and contribute to further inflammatory changes in the pocket.




![Periodontal pockets can also be classified-
[A] According to involved tooth surface
1. Simple
2. Compound
3. Complex or Spiral – originating on one surface and twisting around
the tooth to involve one or more additional surfaces ( most
commonly found in furcation area)
I II III](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodontalpocketkishlay-150105110527-conversion-gate02/85/Periodontal-Pocket-6-320.jpg)
![[B] Depending upon the nature of the soft tissue wall of the
pocket:
(1) Edematous Pocket.
(2) Fibrotic Pocket.
[C] Depending upon disease activity:
(1) Active Pocket.
(2) Inactive Pocket.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodontalpocketkishlay-150105110527-conversion-gate02/85/Periodontal-Pocket-7-320.jpg)








































