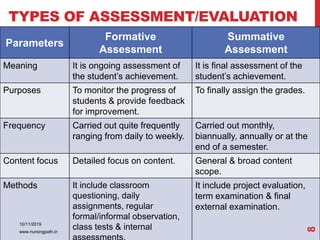
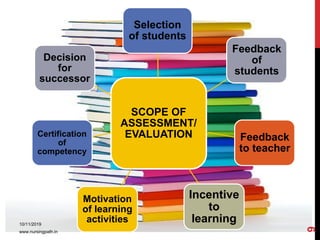
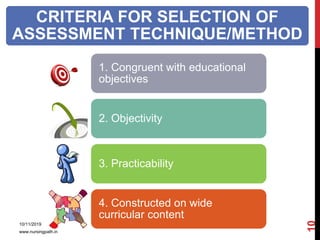
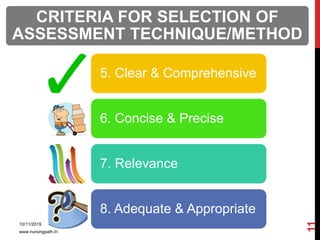
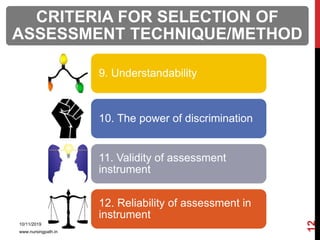
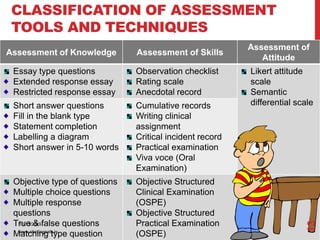
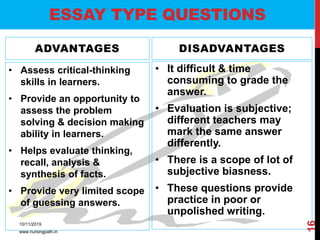
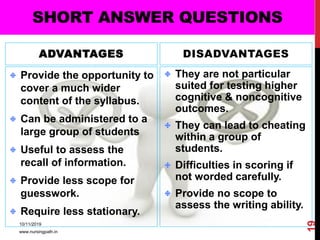
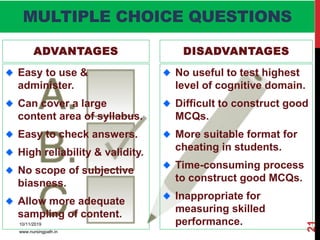
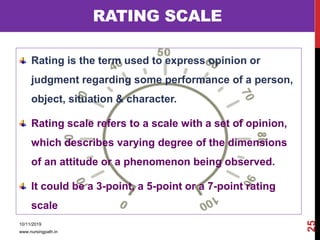
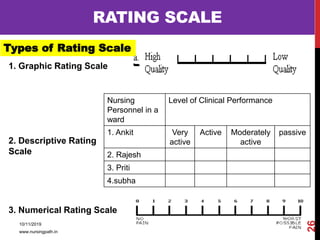
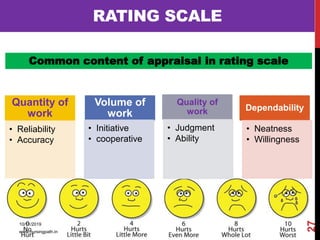
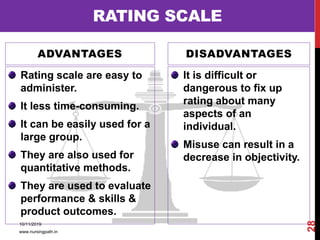
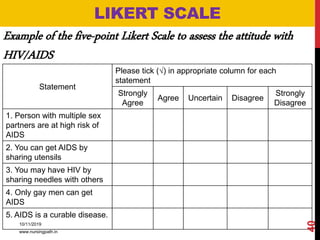
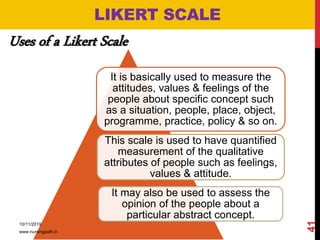
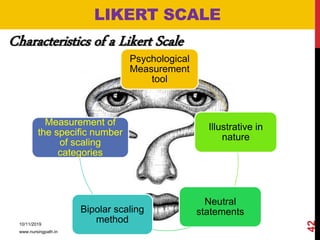
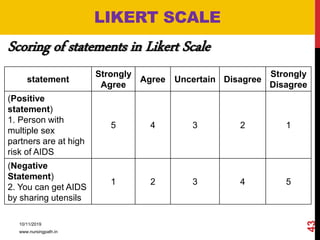
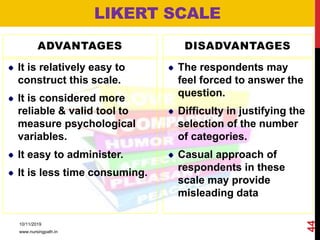
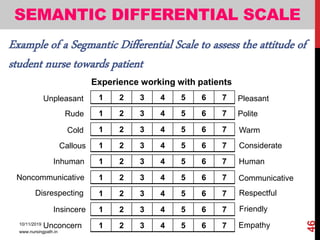
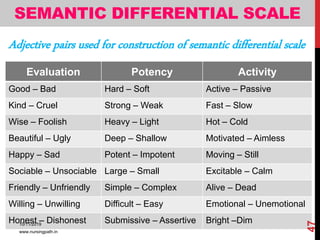
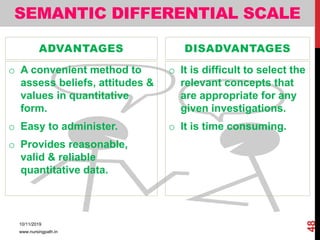
Assessment and evaluation are important parts of the nursing profession. Assessment allows teachers and students to understand how effective teaching was and identify areas for improvement. It also allows students to understand their own learning and strengths. There are various types of assessment, including formative and summative, as well as different tools like essays, short answers, checklists and rating scales. The document discusses the purposes of assessment, types of assessment tools and techniques, and how to select the appropriate assessment method.