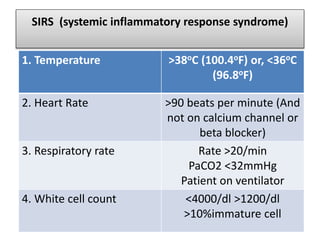
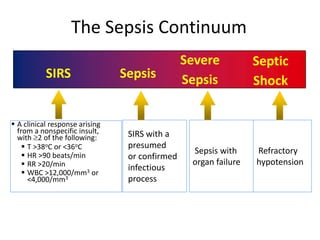
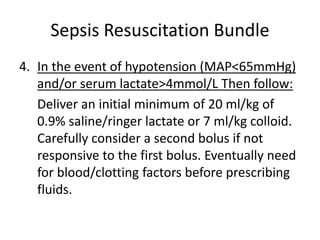
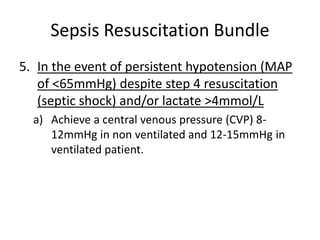
This document provides definitions and screening criteria for sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, and SIRS. It outlines the Sepsis Resuscitation Bundle which includes steps to confirm sepsis, obtain cultures and control infection sources, administer broad-spectrum antibiotics and fluids, use vasopressors for refractory hypotension, and achieve specific hemodynamic and oxygenation goals through additional fluid administration, blood transfusion, or inotropic therapy. The bundle aims to guide early goal-directed treatment and be completed within 3-6 hours.