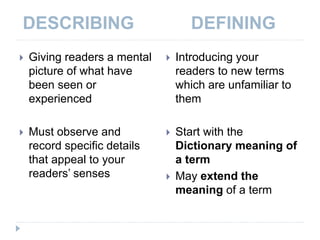
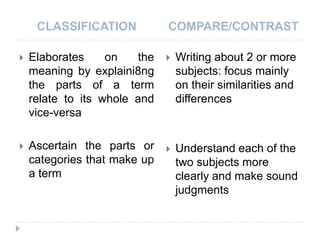
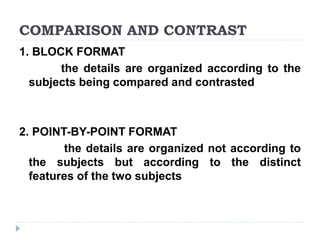
This document provides information on paragraph rhetoric models, including describing, defining, classification, compare/contrast, and cause and effect. It discusses how to write paragraphs using these models, with examples for each. Key details covered include using sensory details in descriptive paragraphs, extending dictionary definitions, organizing compare/contrast paragraphs in block or point-by-point format, and establishing direct and indirect causes and effects. The document also reviews patterns of development in writing like narration, description, definition, exemplification, and persuasion.