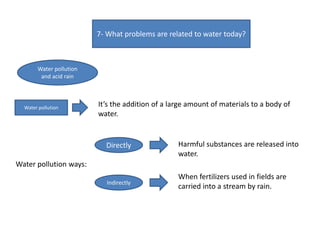
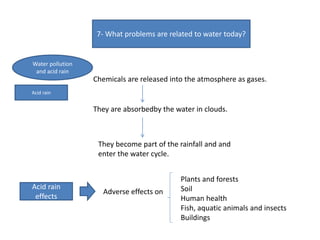
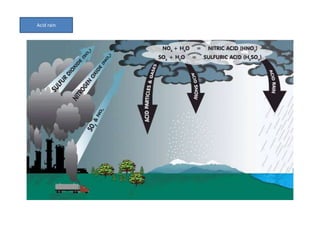
This document discusses various topics related to physical geography of water:
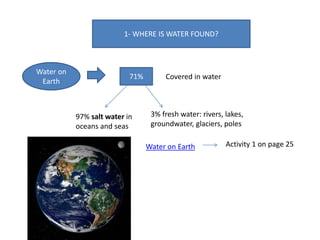
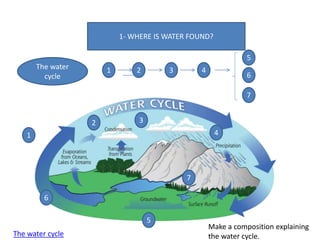
- Water is found on Earth as oceans (97% of water), seas, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and glaciers. It circulates through the water cycle.
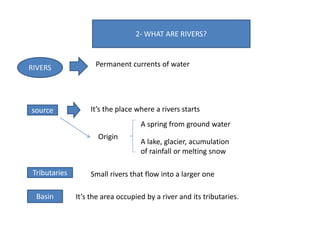
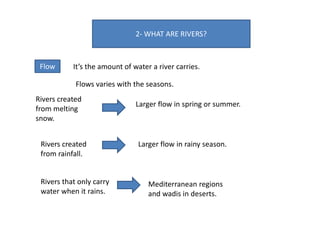
- Rivers start from springs, lakes, glaciers or rainfall and flow into larger rivers and basins, providing water and resources for human uses.
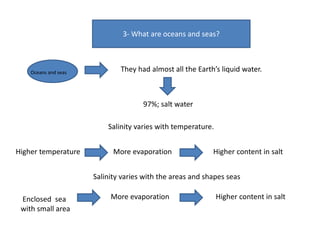
- Oceans and seas contain almost all liquid water and provide food, resources, tourism, and transport but are threatened by pollution and overuse.
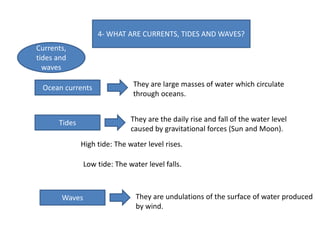
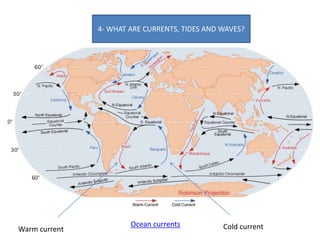
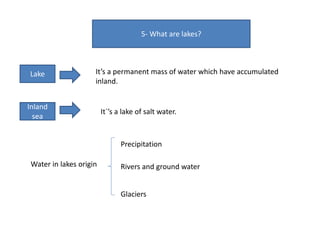
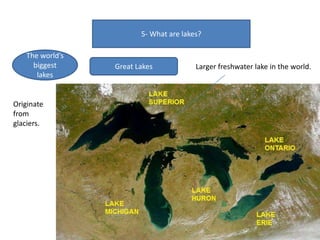
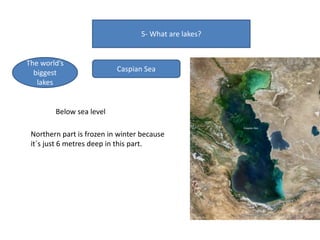
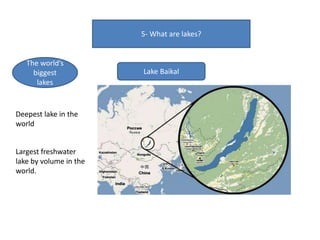
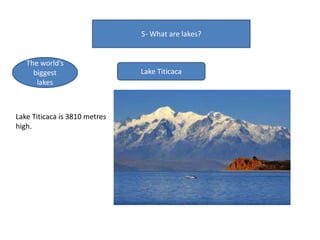
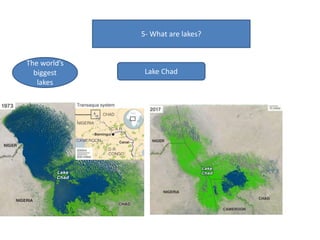
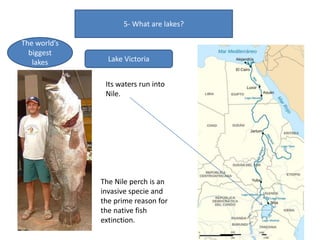
- Currents, tides, and waves influence ocean water and climate while lakes form inland from precipitation or glaciers, with the largest including the Great Lakes and Lake Victoria.