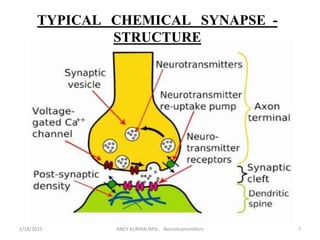
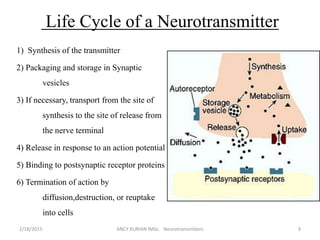
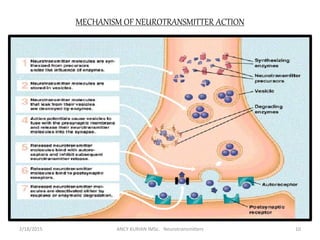
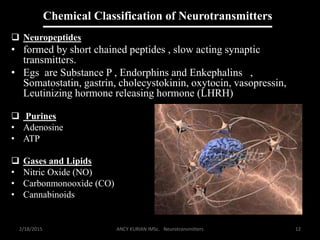
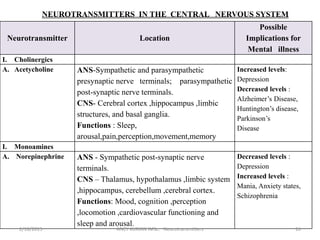
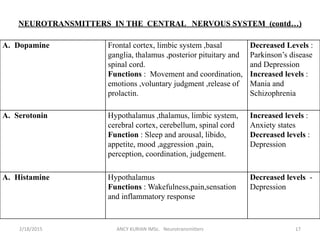
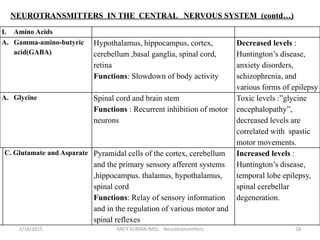
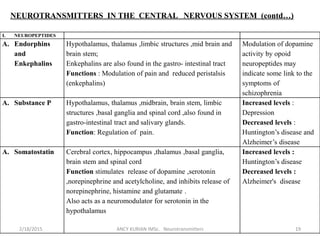
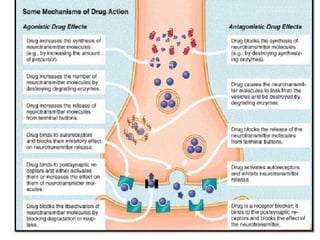
The document discusses neurotransmitters, including their definition, life cycle, mechanisms of action, classification, and role in mental health. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals between neurons. They are classified as cholinergics, monoamines, amino acids, neuropeptides, purines, and gases/lipids. Imbalances can be caused by various factors and influence conditions like depression, Alzheimer's, and schizophrenia. Diagnosis involves identifying symptoms and testing neurotransmitter levels. Drugs can alter neurotransmission by agonizing or antagonizing neurotransmitter receptors. Nurses play a role in assessing patients and supporting neurotransmitter balance through diet, supplements, education, and rehabilitation.