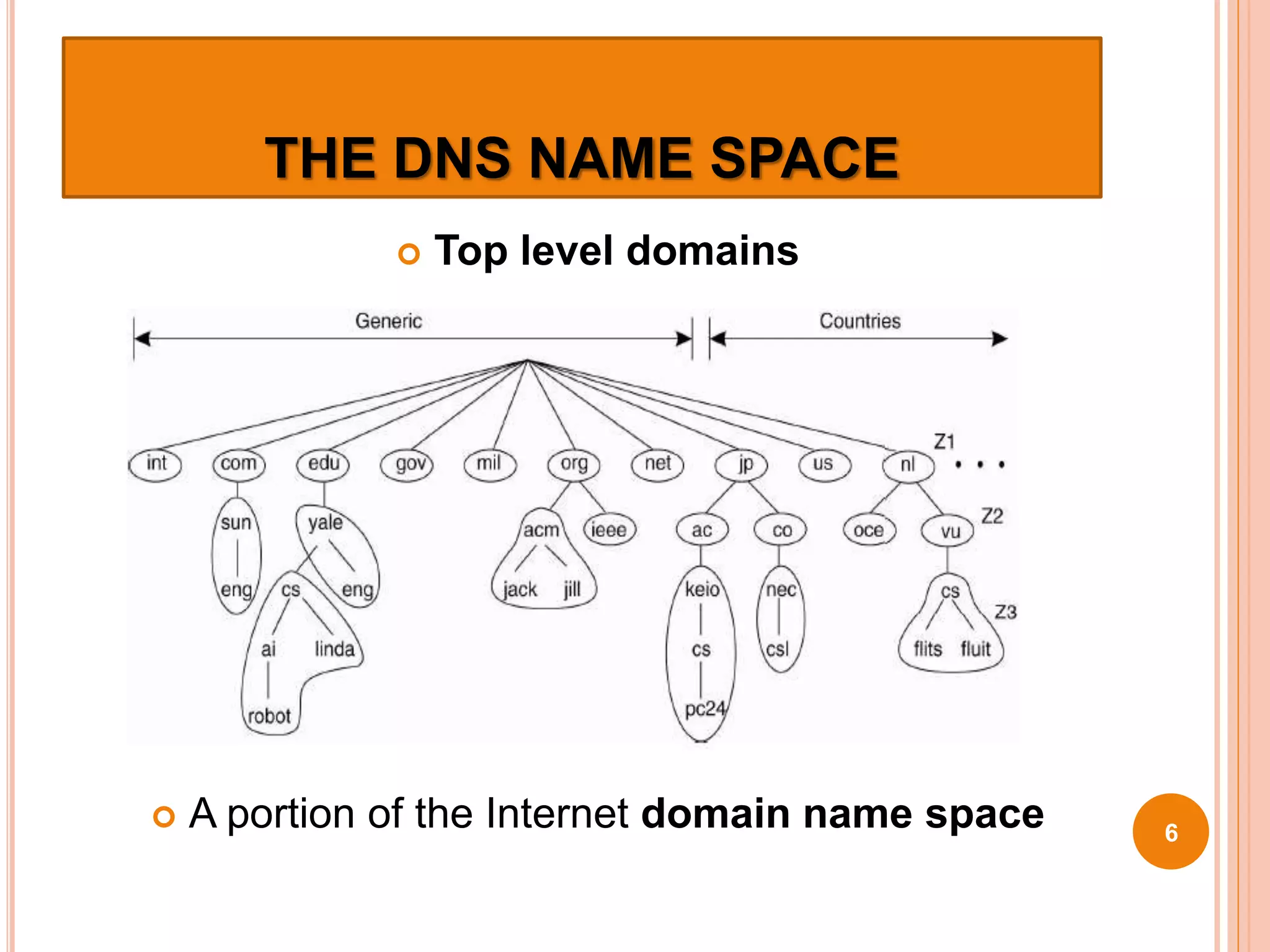
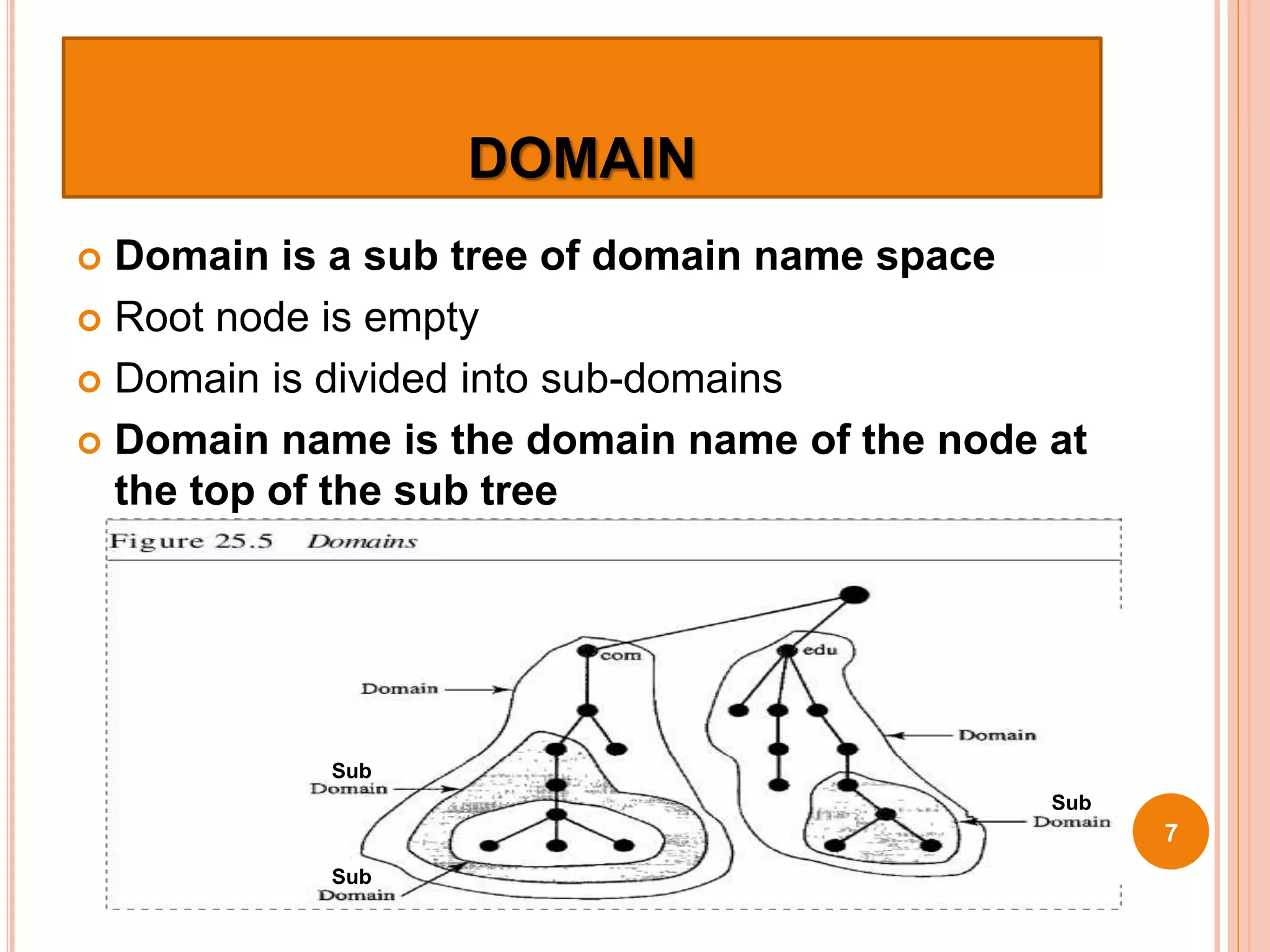
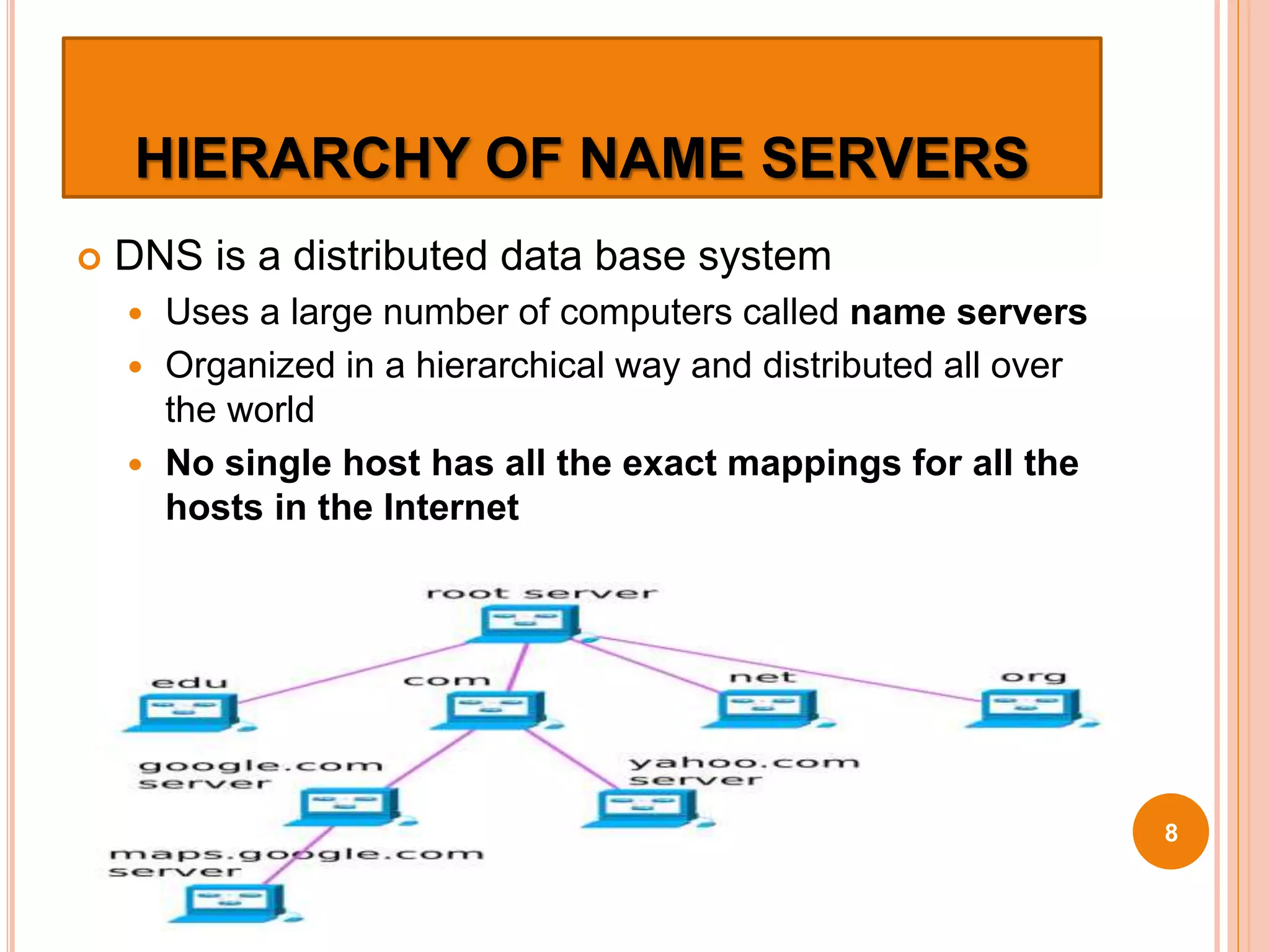
The document discusses the Domain Name System (DNS) and how it works. DNS is an internet directory service that maps hostnames to IP addresses, allowing users to use names instead of numbers. It uses a distributed, hierarchical system of name servers to perform this name resolution in a scalable way. DNS caches mappings for performance, starting queries at the highest level domains and following delegations between servers until the answer is found. DNS has become a major attack vector, so protection of DNS infrastructure and traffic is important.