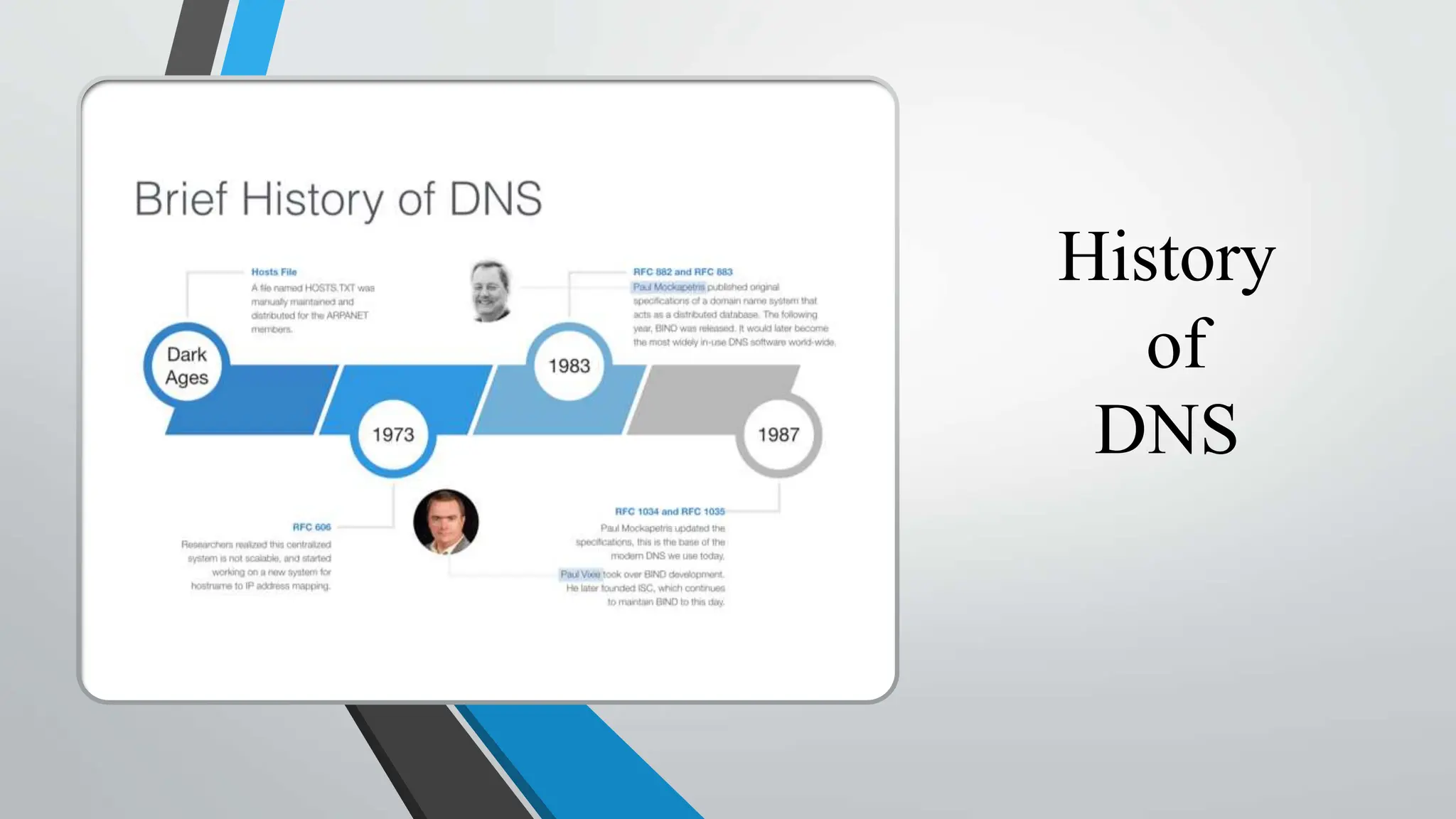
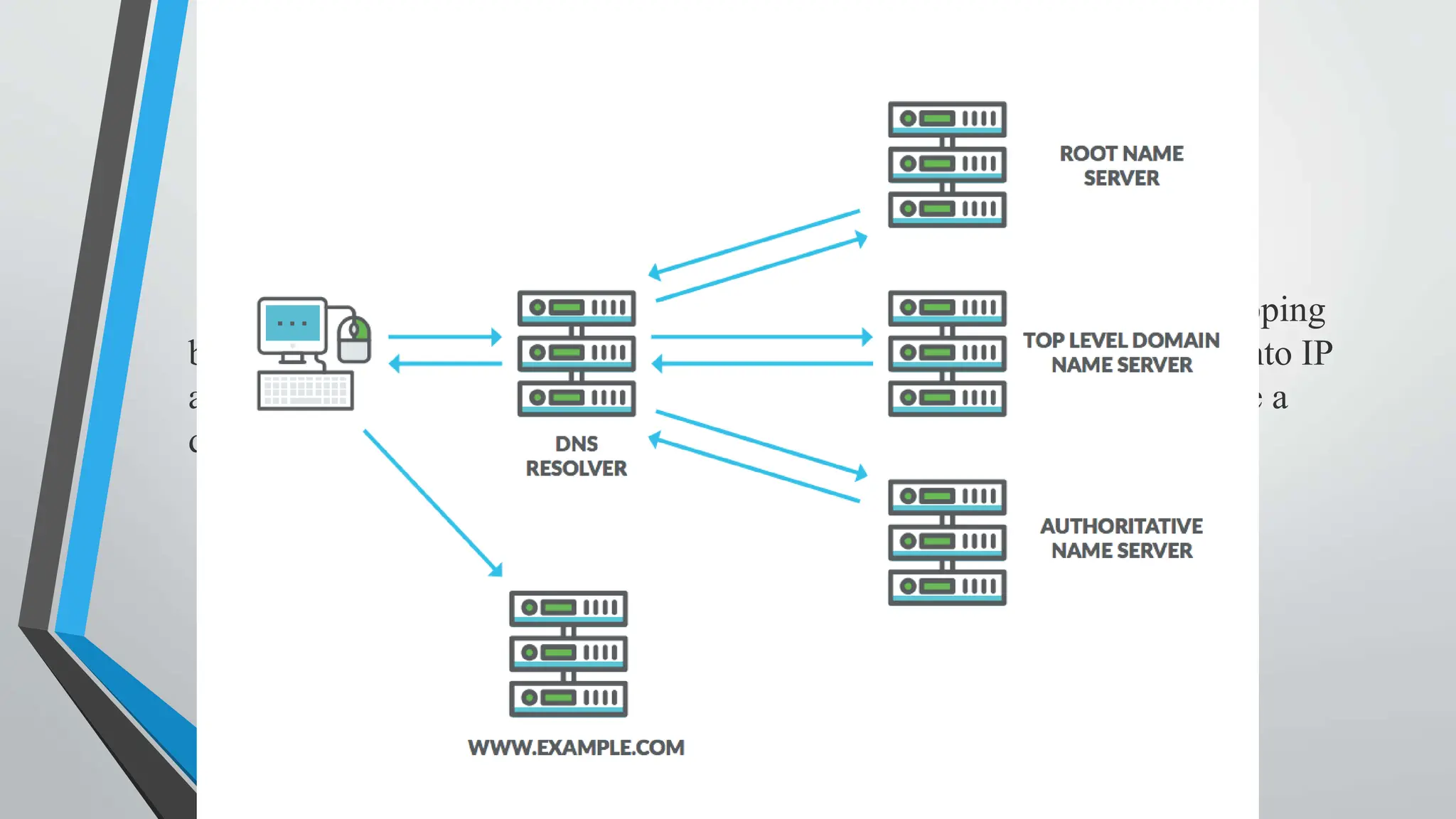
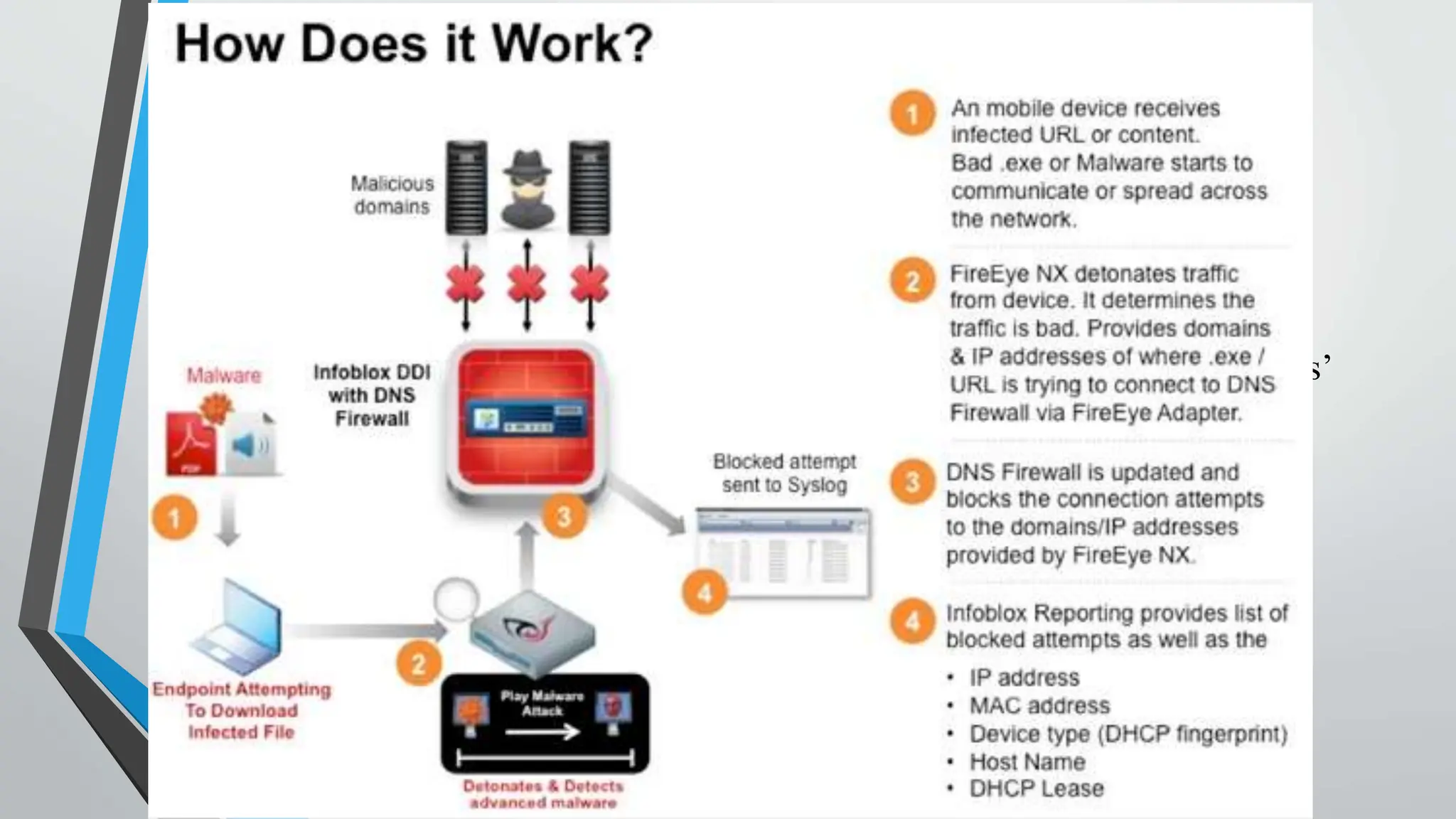
The document discusses DNS (Domain Name System) and how to secure it. It explains that DNS translates domain names to IP addresses, involving recursive queries to root nameservers and authoritative nameservers. Common DNS attacks are spoofing, poisoning, hijacking, amplification and flooding. Recommended security measures include DNS encryption using DNS over HTTPS and TLS, DNSSEC for response authentication, DNSCrypt for encryption and anonymity, redundant infrastructure for DDoS protection, and DNS firewalls.